When you get via web links on our short articles, Future and its submission companions might make a compensation.
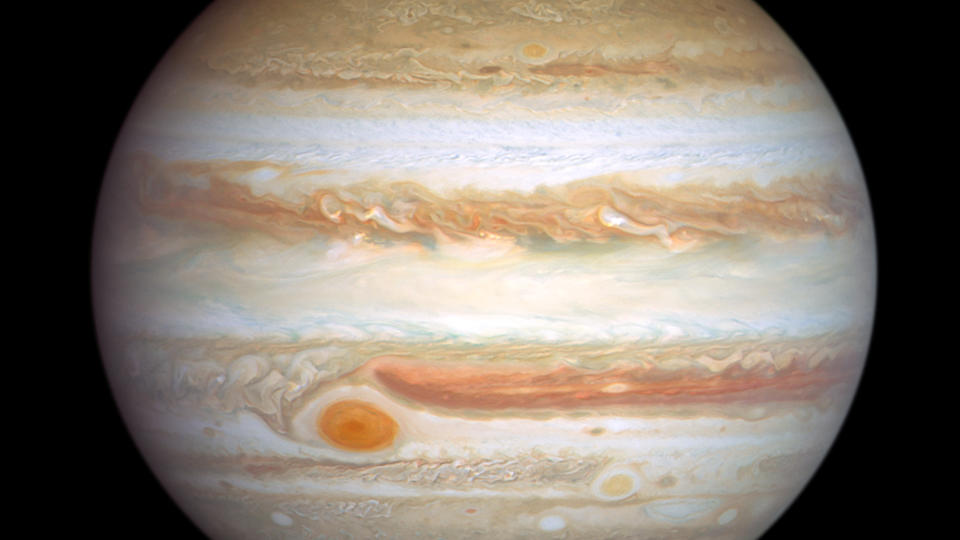


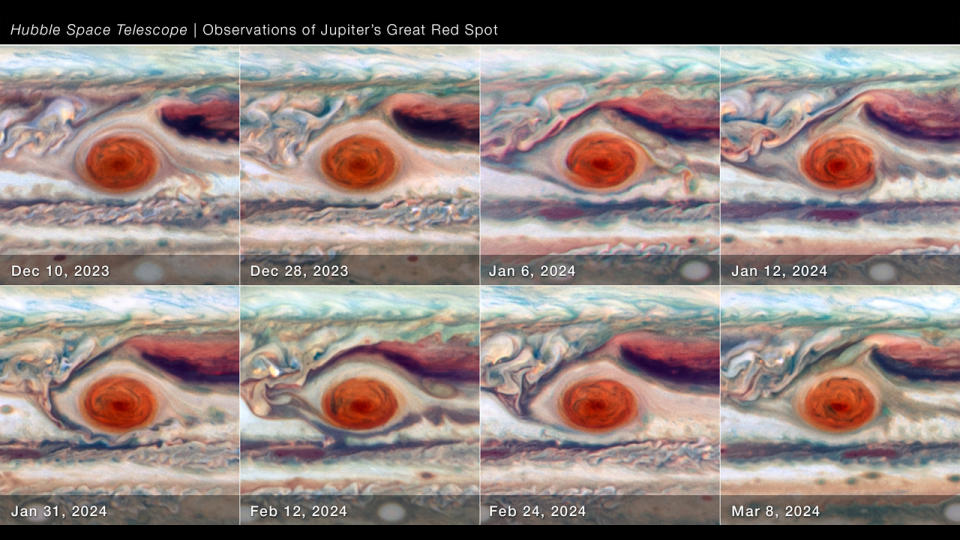
The age-old Hubble Area Telescope has actually enjoyed Jupiter’s Great Red Area (GRS) oscillating, as though it were being pressed in and out about every 90 days.
Why this massive anticyclone, which has actually been shrinking over the years and presently gauges regarding 9,165 miles (14,750 kilometers) throughout (although astrophotographer Damian Peach has actually apparently determined it to be simply 7,770 miles, or 12,500 kilometres, vast), is acting in such style is a secret.
” With Hubble’s high resolution, we can claim that the GRS is certainly pressing in and out at the exact same time as it relocates faster and slower,” stated Amy Simon, of NASA’s Goddard Area Trip Facility in Maryland, in astatement “This was extremely unanticipated, and presently there are no hydrodynamic descriptions.”
Astronomers led by Simon made use of Hubble to observe the Great Red Spot for 88.5 days in between December 2023 and March 2024. A timelapse of photos taken throughout that duration reveals that the GRS regularly increases and diminishes along its semi-major axis (the largest component of an ellipse).
” While we understand its activity differs a little in longitude, we really did not anticipate to see the dimension oscillate too,” stated Simon.
Connected: Jupiter’s Great Red Spot: Everything you need to know
Situated 22 levels southern of Jupiter‘s equator, placed on the side of the Jovian atmosphere‘s South Equatorial Belt, the GRS is buffeted from above and listed below by magnificent air stream that whip around the huge earth at 266 miles per hour 428 kph The air stream quit the massive vortex from roaming right into various other latitudes, although it is attended wander westward relative to the remainder of the environment. This drift isn’t continuous, however it has actually been determined to increase and decrease over an around 90-day oscillation.
” As it speeds up and decreases, the GRS is pressing versus the gusty air stream to the north and south of it,” stated Mike Wong of the College of The Golden State, Berkeley.
Apparently linked to this roughly 90-day oscillation in its westward drift is the pressing of the GRS’ form seen by Hubble.
” It resembles a sandwich where the pieces of bread are compelled to protrude out when there’s excessive dental filling in the center,” stated Wong.
The level of pressing appears to be anti-correlated with the price at which the GRS is wandering. Throughout the durations when the GRS’ drift has actually decreased, the size of the vortex and the dimension of its core go to their biggest. The core likewise radiates brighter in ultraviolet light when it goes to its biggest, a measure of there being much less haze absorption in the environment over it. When the drift speeds up, the size of the GRS and the dimension of its core agreements. This might be the outcome of the GRS engaging with the bordering environment when its drift price quicken.
Thus far, just one oscillatory duration has actually been observed completely by Hubble. Simon leads the Outer World Environments Tradition (OPAL) program, which makes use of Hubble to picture each of the 4 huge worlds in the external planetary system– Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune— a minimum of when each year. Nevertheless, Hubble’s researches of the GRS were a different job along with that.
A team of leading amateur astronomers, such as Damian Peach, likewise regularly picture Jupiter in high resolution, and their information is so great that Simon and the OPAL group frequently deal with them. It’s feasible that this pressing of the area appears in amateur photos, although Simon assumes it may be a little as well refined for amateur information to have actually caught it with any kind of integrity, with the size of the area differing by simply 0.3 levels in longitude over a two-week duration. Nonetheless, since we understand it is happening, beginners might have the ability to operate their picture capture in order to identify it.

ASSOCIATED TALES:
— Is Jupiter’s Great Red Area an impostor? Gigantic tornado might not be the initial one uncovered 350 years back
— The best Hubble Space Telescope images of all time!
— James Webb Area Telescope spies weird forms over Jupiter’s Great Red Area (picture)
Simon likewise wishes to reconsider at the GRS with the James Webb Space Telescope, which formerly imaged the Jovian tornado in near-infrared light previously this year and discovered climatic waves over the GRS. By having the ability to penetrate much deeper right into the GRS at much longer mid-infrared wavelengths, Simon intends to see whether wind speeds within the tornado are likewise transforming in time with the oscillations.
The total diminishing of the GRS, currently combined with the oscillatory pressing, indicate that the tornado is going through some fascinating adjustments. Where will it finish?
” Now, it’s over-filling its latitude band about the wind area,” stated Simon. “As soon as it diminishes inside that band, the winds will actually be holding it in position.” When this takes place, it might support in dimension, but also for since stays conjecture till even more information can be collected.
The exploration was reported on Oct. 9 in a paper released in The Planetary Science Journal.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
