Reductions in emissions of aerosols from Chinese language factories could also be partly accountable for latest heatwaves within the Pacific, a brand new research has mentioned.
The research, printed within the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, means that repeated marine heatwaves over the previous decade could possibly be linked to discount in air pollution from factories in China.
Over the previous decade, the north Pacific has skilled a number of such heatwaves – often known as “heat blob” occasions – resulting in fish die-offs, poisonous algae blooms and lacking whales.
Such heatwaves have been typically attributed to international warming although it’s unknown precisely why it may trigger such sudden and variable will increase in a selected a part of the planet.
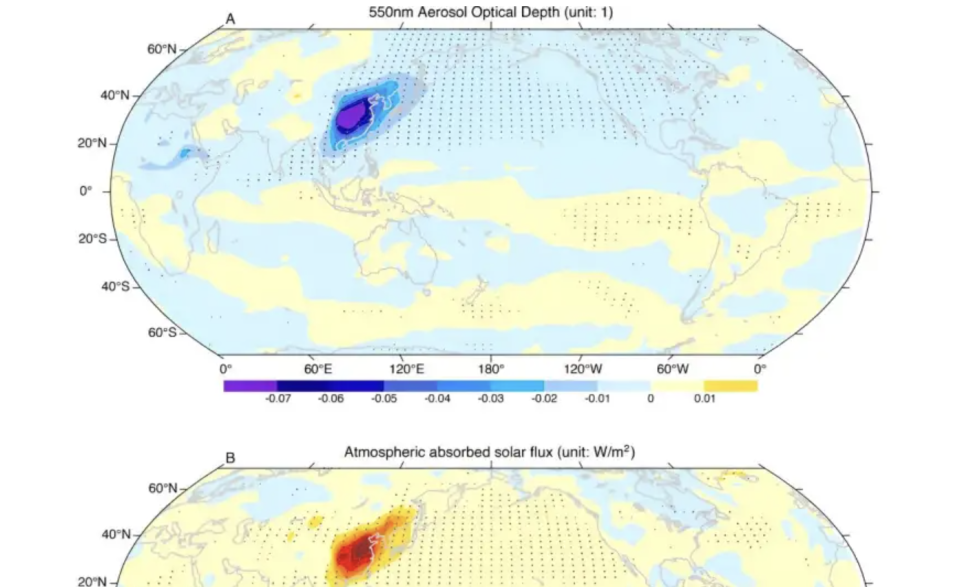
The analysis group of oceanographers and scientists from China, the US and Germany famous that the onset of the heatwaves appeared to comply with profitable efforts by the Chinese language authorities to scale back aerosol emissions from their nation’s factories.
Why would a discount in air pollution heat the planet?
Aerosols are small particles which can be generally emitted from burning coal and oil – they will act like mirrors floating within the air, reflecting warmth from the solar again into house.
Efforts to curb air pollution can generally have a paradoxical impact of warming up areas close by, as a result of the truth that tiny aerosol particles within the air can ‘replicate’ the solar’s warmth again into house.

Within the oceans, for instance, efforts to curb air pollution from ships have been linked to a warming impact as a result of decrease aerosol emissions from transport.
Earlier analysis efforts have prompt that huge reductions of aerosols in a single place may result in warming elsewhere.
Why may it’s linked to China?
Utilizing pc modelling, the researchers discovered that heatwaves within the Pacific appeared to coincide with efforts by the Chinese language authorities to scale back air pollution.
Starting round 2010, factories and energy producing vegetation in China started dramatically lowering emissions of aerosols equivalent to sulphate, leading to a lot cleaner air.
The researchers started amassing information after which enter it into 12 totally different pc local weather fashions.
They ran them beneath two situations – one the place emissions from East Asia remained as they had been over the previous a number of many years and one the place they dropped in the way in which they really had.
They discovered that the fashions with no declines didn’t trigger a lot change elsewhere, whereas these with aerosol drops confirmed heatwaves occurring within the northeast elements of the Pacific Ocean.
As much less warmth was mirrored again into house over China, warming of coastal areas in Asia started, ensuing within the improvement of high-pressure programs.
That, in flip, made low-pressure programs within the center Pacific extra intense, ensuing within the Aleutian Low rising larger and shifting south which weakened the westerly winds that usually cool the ocean floor.
The outcome was hotter situations.
The analysis may supply a warning about efforts in ‘photo voltaic geoengineering’ – plans to intentionally replicate warmth again into house utilizing aerosols.
Such approaches – together with the thought of spraying aerosols into the air from a fleet of planes – have been debated by educational establishments world wide.
Talking to Science.org, Maria Rugenstein, a Colorado State College mentioned that the analysis exhibits the local weather can reply quickly, and with surprising repercussions. She mentioned: “I’d take this as a cautionary story.”
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
