Enroll In CNN’s Marvel Concept scientific research e-newsletter. Explore the universe with news on fascinating discoveries, scientific advancements and more
A substantial area rock, approximated to be the dimension of 4 Mount Everests, banged right into Planet greater than 3 billion years back– and the influence can have been suddenly useful for the earliest types of life on our world, according to brand-new study.
Normally, when a big area rock accidents right into Planet, the effects are connected with disastrous destruction, as when it comes to the death of the dinosaurs 66 million years back, when an about 6.2-mile-wide (10-kilometer) asteroid crashed off the coastline of the Yucatan Peninsula in what’s currently Mexico.
However Planet was young and a really various location when the S2 meteorite, approximated to have 50 to 200 times even more mass than the dinosaur extinction-triggering Chicxulub planet, rammed the world 3.26 billion years back, according to Nadja Drabon, assistant teacher of Planet and global scientific researches at Harvard College. She is additionally lead writer of a brand-new research explaining the S2 influence and what complied with in its consequences that released Monday in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
” No complicated life had actually developed yet, and just single-celled life existed in the kind of germs and archaea,” Drabon created in an e-mail. “The seas most likely included some life, yet not as high as today partly because of an absence of nutrients. Some individuals also explain the Archean seas as ‘organic deserts.’ The Archean Planet was a water globe with couple of islands standing out. It would certainly have been an interested view, as the seas were most likely eco-friendly in shade from iron-rich deep waters.”
When the S2 meteorite hit, worldwide turmoil followed– yet the influence additionally stimulated active ingredients that could have enhanced microbial life, Drabon claimed. The brand-new searchings for can alter the method researchers comprehend exactly how Planet and its fledgling life replied to barrage from area rocks not long after the world developed.


Discovering old effects
Early in Planet’s background, area rocks often strike the young world. It is approximated that “gigantic impactors,” more than 6.2 miles (10 kilometers) throughout, pounded the world at the very least every 15 million years, according to the research writers, indicating that at the very least 16 gigantic meteorites struck Planet throughout the Archean Years, which lasted from 4 billion to 2.5 billion years back.
However the results of those influence occasions isn’t well comprehended. And offered Planet’s ever-changing geology, in which large craters are covered over by volcanic task and the motion of structural plates, the proof of what occurred numerous years back is tough to discover.
Drabon is an early-Earth rock hound captivated by recognizing what the world resembled prior to the very first continents developed and exactly how fierce meteoritic effects impacted the advancement of life.
” These effects need to have considerably impacted the beginning and the advancement of life in the world. However exactly how specifically stays a secret,” Drabon claimed. “In my study, I intended to analyze real ‘tough’ proof– excuse the word play here– of exactly how gigantic effects impacted very early life.”
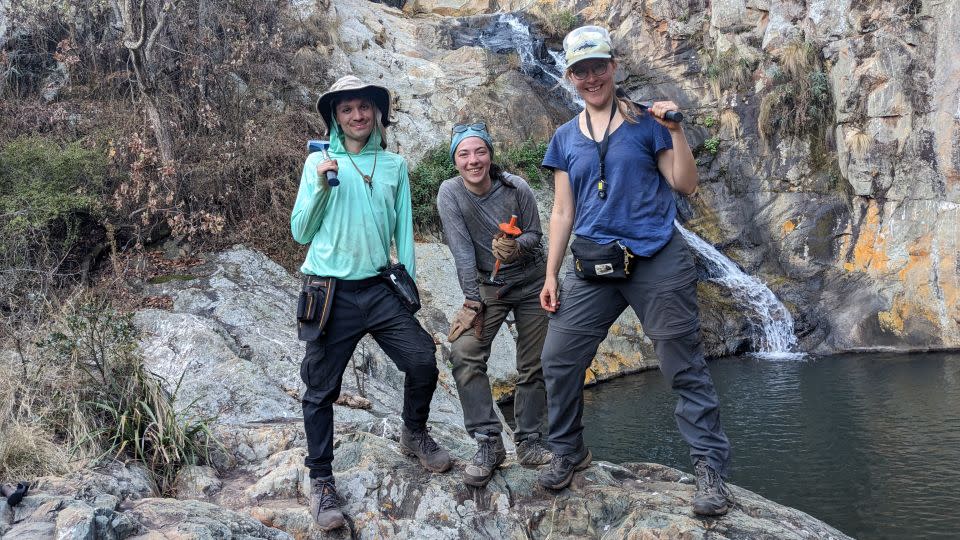
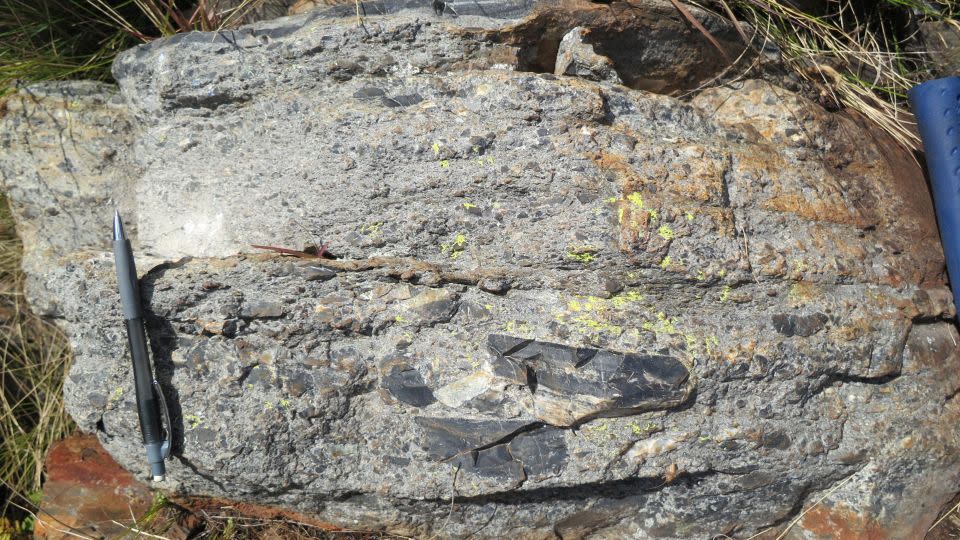
Drabon and her coworkers performed fieldwork to look for ideas in the rocks of the Barberton Makhonjwa Hills of South Africa. There, geological proof of 8 influence occasions, which happened in between 3.6 billion and 3.2 billion years back, can be discovered in the rocks and mapped with little meteorite influence fragments called spherules.
The little, rounded fragments, which can be glazed or crystalline, happen when huge meteorites struck Planet, and they develop sedimentary layers in rocks that are referred to as spherule beds.
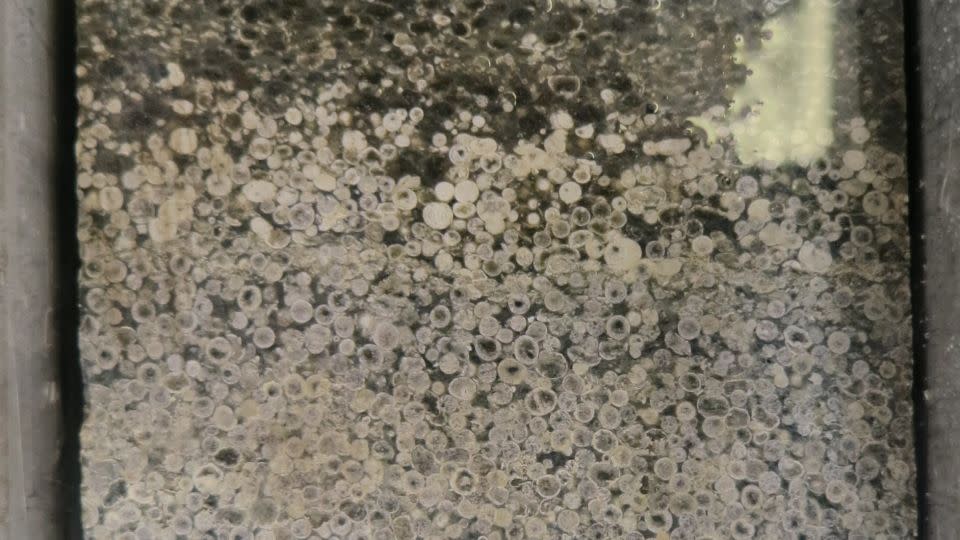


The group gathered a series of examples in South Africa and assessed the rocks’ structures and geochemistry.
” Our days commonly start with a lengthy walk right into the hills to reach our tasting areas,” Drabon claimed. “Often we’re lucky to have dust roadways that bring us closer. At the website, we research the frameworks in the rocks throughout the influence occasion layer in fantastic information and usage sledgehammers to remove examples for later evaluation in the laboratory.”
The snugly sandwiched layers of rock maintained a mineral timeline that enabled the scientists to rebuild what occurred when the S2 meteorite hit.
Waves of devastation
The S2 meteorite was in between 23 and 36 miles (37 and 58 kilometers) in size as it struck the world. The impacts were quick and vicious, Drabon claimed.
” Photo on your own stalling the coastline of Cape Cod, in a rack of superficial water,” Drabon claimed. “It’s a low-energy atmosphere, without solid currents. After that suddenly, you have a gigantic tidal wave, sweeping by and destroying the seafloor.”
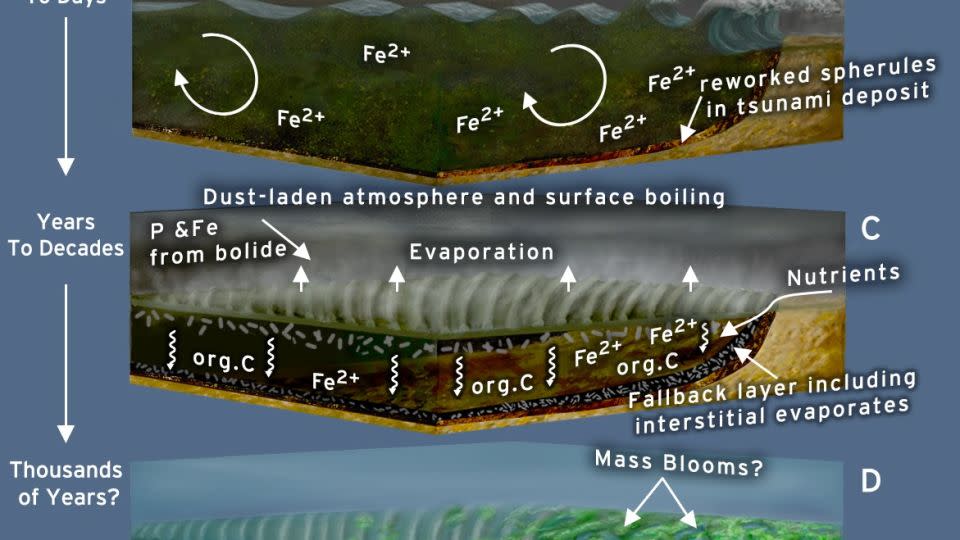

The tidal wave brushed up around the world, and warm from the influence was so extreme that it steamed off the leading layer of the sea. When seas steam and vaporize, they develop salts such as those observed in the rocks straight after the influence, Drabon claimed.
Dirt infused right into the environment from the influence dimmed the skies within hours, also on the contrary side of the world. The environment warmed up, and the thick dirt cloud protected against microorganisms from transforming sunshine right into power. Any type of life ashore or in superficial waters would certainly have really felt the negative impacts quickly, and those impacts would certainly have lingered from a couple of years to years.
At some point, rainfall would certainly have restored the leading layers of the sea, and the dirt worked out.
However the deep sea atmosphere was an additional tale. The tidal wave spun up components such as iron and brought them to the surface area. On the other hand, disintegration aided clean seaside particles right into the sea and launched phosphorus from the meteorite. The laboratory evaluation revealed a spike in the existence of single-celled microorganisms that feed off iron and phosphorus quickly after the influence.
Life quickly recouped, and afterwards it flourished, Drabon claimed.
” Prior to the influence, there was some, yet very little, life in the seas because of the absence of nutrients and electron contributors such as iron in the superficial water,” she claimed. “The influence launched vital nutrients, such as phosphorus, on a worldwide range. A trainee appropriately called this influence a ‘plant food bomb.’ On the whole, this is great information for the advancement of very early life in the world, as effects would certainly have been a lot more constant throughout the beginning of life’s advancement than they are today.”
Exactly how Planet reacts to guide hits
The S2 and Chicxulub planet effects had various effects because of the area rocks’ corresponding dimensions and the phase the world remained in when every one struck, Drabon claimed.
The Chicxulub impactor struck a carbonate system in the world, which launched sulfur right into the environment. The discharges developed aerosols that created a sharp, severe decrease in surface area temperature levels.


And while both effects created substantial die-offs, durable, sunlight-dependent microbes in superficial waters would certainly have quickly recouped after the S2 influence once the seas loaded back in and the dirt worked out, Drabon claimed.
” Life while of the S2 influence was much less complex,” she claimed. “Think about cleaning your teeth in the early morning: You could get rid of 99.9% of germs, yet by night, they have actually returned.”
Ben Weiss, the Robert R. Shrock Teacher of Planet and Planetary Sciences at the Massachusetts Institute of Innovation, was captivated by the geological monitorings of the spherule beds in the paper, which he thinks are permitting scientists to discover Planet’s old influence document the method astronomers can research the surface areas of earths like Mars. Weiss was not associated with the research.
” There are no influence craters maintained on the Planet today that come anywhere near in dimension to what has actually been presumed to have actually generated the rocks examined right here,” Weiss claimed. “Naturally, what is unique regarding our document is that, nonetheless fragmental and insufficient, it is the only document we can presently research carefully that can inform us regarding the impacts of influence on the very early advancement of life. It’s additionally excellent that in spite of the really neighborhood nature of these monitorings (outcrops in a tiny area in South Africa), we can begin to comprehend something regarding the worldwide nature of these gigantic influence occasions.”
The rocks in the Barberton Makhonjwa Hills are opening up an entire brand-new line of study right into Planet’s background of effects for Drabon and her coworkers.
” We intend to establish exactly how typical these ecological modifications and organic reactions sought various other influence occasions in very early Planet’s background,” she claimed. “Because the result of each influence relies on numerous elements, we intend to examine exactly how often such favorable and adverse impacts on life happened.”
For even more CNN information and e-newsletters produce an account at CNN.com
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
