When you get via web links on our short articles, Future and its submission companions might gain a payment.


Lightning strikes throughout Planet might make ultrahot “awesome electrons” rainfall down around our world, according to brand-new study from researchers at the College of Colorado Rock. Because of this outcome, the group recommends that room climate and Planet can unify to play “planetary pinball.”
The exploration was made nearly by coincidence while the group was researching satellite information that revealed high-energy and high-speed “warm” electrons might be removed from the inner radiation belt — an area of billed bits twisted around our world that’s kept in location by Planet’s safety magnetic bubble, referred to as the magnetosphere.
This study might assist researchers safeguard satellites and various other tools in orbit from damages, and help in safeguarding astronauts from possibly lethal radiation on future room objectives. It likewise recommends that room climate and Planet climate are extra linked than formerly thought.
” These bits are the frightening ones or what some individuals call ‘awesome electrons.’ They can pass through steel on satellites, struck circuit card, and can be cancer causing if they struck an individual precede,” group leader and College of Colorado Rock scientist Max Feinland said in a statement.
Connected: SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn astronauts will certainly make a bold trip right into Planet’s Van Allen radiation belt
Awesome electrons bill!
Twisted Around Planet are 2 belts of caught high-energy bits, kept in location by the magnetosphere. These are referred to as the Van Allen radiation belts.
Awesome electrons race via these belts at virtually the speed of light, lugging with them a lot of power. Not just can these bits pass through satellite securing, yet they can likewise trigger tiny lightning strikes that can harm– and even ruin– essential and fragile spacecraft elements.
The internal area of the belts is taken into consideration to start at an elevation of around 600 miles (966 kilometers) over Planet, while the external layer is believed to begin at around 12,000 miles (19,312 kilometres) over our world’s surface area.
The Van Allen belts work as a loosened obstacle in between Planet’s environment and its room setting. They are likewise vibrant, with the ability of relocating and altering. Researchers have actually understood for time that billed bits can drop from the external radiation belt towards Planet. Low-energy, or “chilly,” bits have actually likewise been discovered dropping from the extra secure internal radiation belt.
This is the initial tip that high-energy charged bits can likewise “rainfall” from the internal belt, which had actually been taken into consideration extra secure. It’s likewise the initial tip that this “electron rainfall” can be set off by lightning.
” Room climate is actually driven both from above and below,” staff member Lauren Blum of the Research Laboratory for Climatic and Room Physics (LASP) at CU Rock stated in the declaration. “Normally, the internal belt is believed to be sort of boring. It’s secure. It’s constantly there.”
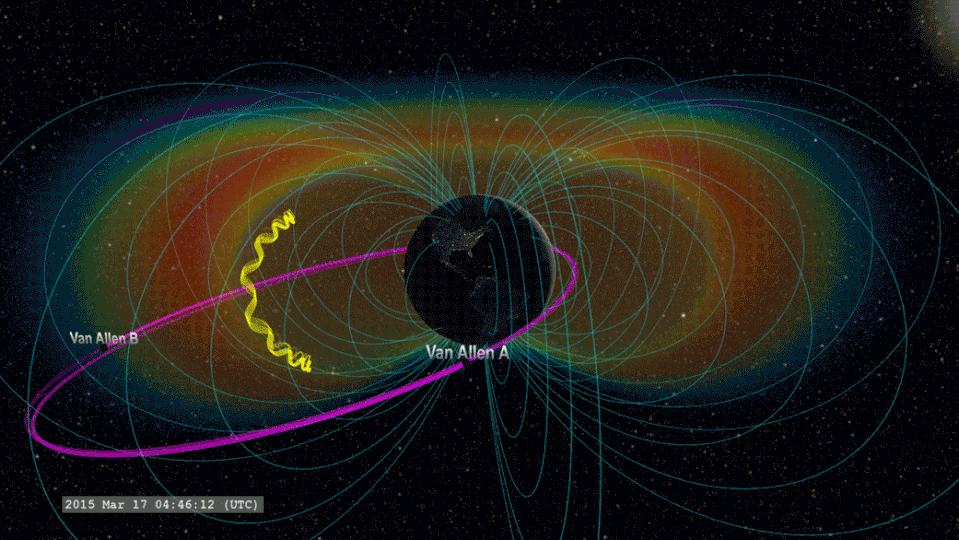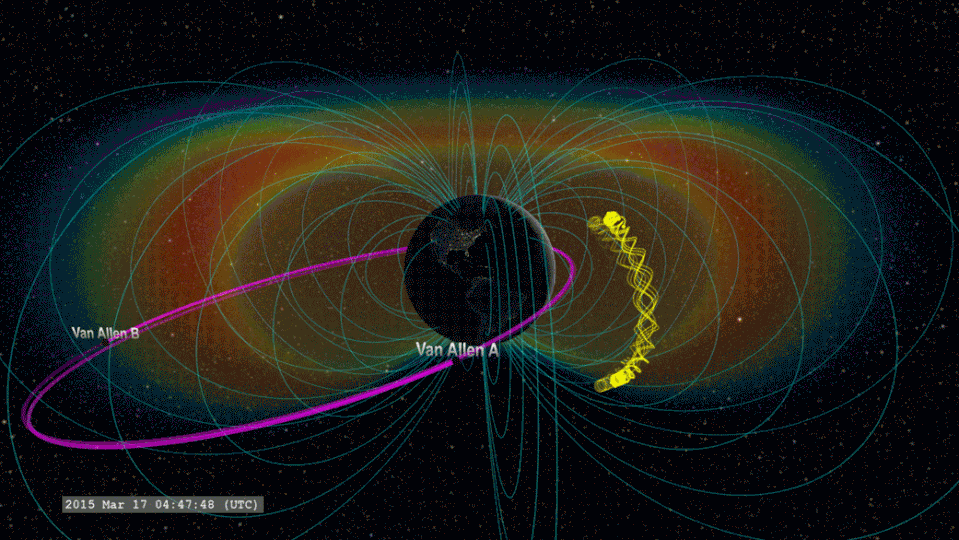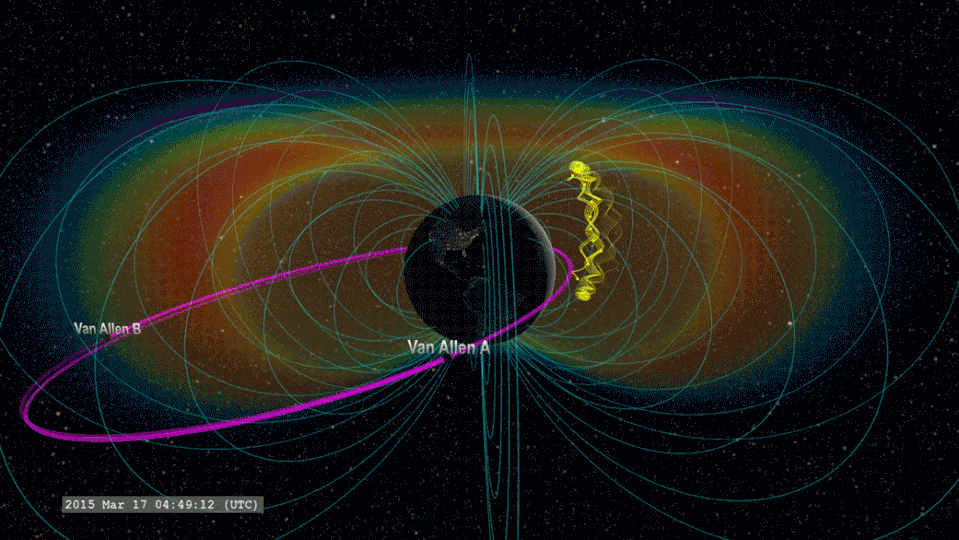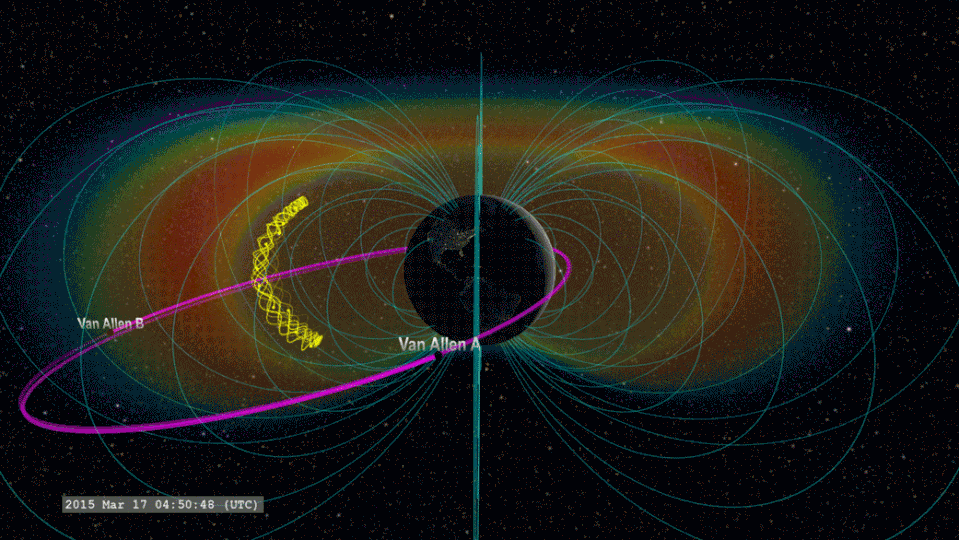

The group thinks that when lightning flashes overhead over Planet, radio waves are introduced towards room. If these radio waves struck electrons in the radiation belts around our world, they can tremble loosened electrons, creating “lightning-induced electron rainfall” or “electron rainfall.”
While assessing information from NASA’s now-decommissioned Solar, Anomalous, and Magnetospheric Particle Explorer (SAMPEX) satellite, Feinland saw “globs” of high-energy electrons relocating via Planet’s internal radiation belt. He took these monitorings to Blum, that informed him: “That’s not where these are intended to be.”
Planetary pinball
Examining this better, the duo determined 45 rises of high-energy electrons in the internal radiation belts happening in the years in between 1996 and 2006. Feinland after that contrasted this information to documents of lightning strikes over The United States and Canada. What arised was a relationship in between lightning strikes and heights in electrons, which took place around a 2nd after lightning struck the ground.
The group believes that when lightning strikes, it starts an agitated video game of pinball that incorporates the whole Planet. Activated radio waves ripple upwards right into room, striking electrons in the internal radiation belt.
This imitates an “include round” function in this metaphorical pinball video game, going down electrons that after that chaotically jump in between the north and southerly hemispheres of Planet. This stage of the procedure lasts simply 0.2 secs. Several of the electrons anxiously shuttling in between our world’s north and southerly hemispheres after that go down right into our environment.
” You have a huge ball of electrons that jumps and after that returns and jumps once again,” Blum stated. “You’ll see this preliminary signal, and it will certainly degeneration away.”
Associated Stories:
— ‘Traffic’ around Uranus might fix the enigma of its weak radiation belts
— Infrared aurora on Uranus verified for the first time
— James Webb Room Telescope finds air stream on Jupiter more powerful than a Group 5 typhoon
Blum, Feinland, and associates do not presently understand exactly how usually these spells of “awesome electron rainfalls” happen. One concept is that they are most typical throughout durations when the sunlight is specifically energetic and blasts extra high-energy electrons at Planet to be gotten hold of by the magnetosphere and restore the Van Allen belts.
The group’s study was released on October 8 in the journal Nature Communications.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
