When you get with web links on our short articles, Future and its submission companions might gain a payment.
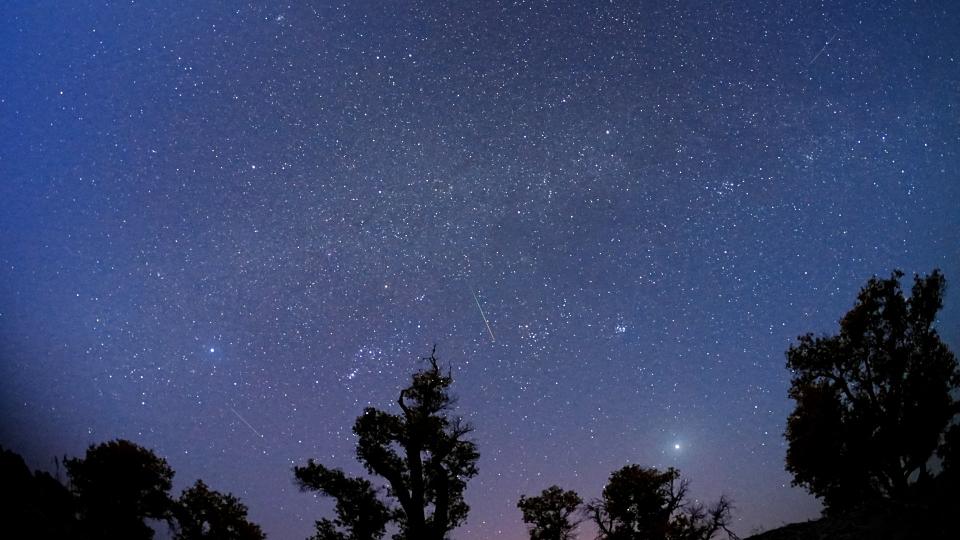


Alongside the Geminids of December and the Perseids of August, one of the most trusted of the yearly screens of “shooting celebrities” are the October Orionids.
The Orionid meteor shower generally lasts from concerning Oct. 16 to 26. A couple of speedy Orionids might look like very early as the beginning of October and a remaining lagger or 2 as late as Nov. 7. The numbers seen by any type of one viewer have a tendency to get to an optimum of around 20 per hour when problems are clear and dark and the shower glowing factor near the Orion-Gemini boundary is well up in the skies.
However, this year, the Orionids are mosting likely to encounter a powerful handicap. When these meteors reach their peak early Monday early morning (Oct. 21), the waning gibbous moon will certainly remain in the skies nearly all evening long. Therefore, its glow will significantly interfere with monitorings in 2024.
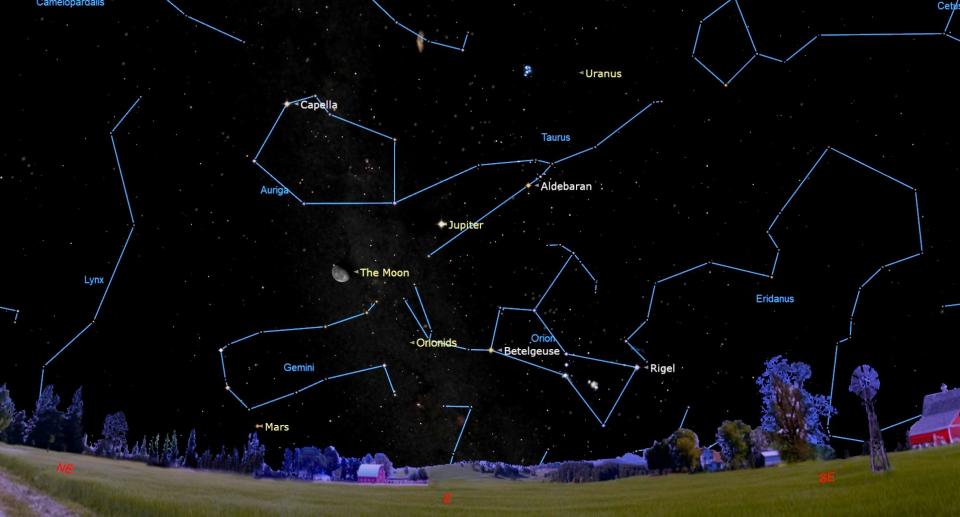
The meteors are called “Orionids” due to the fact that the meteors appear to extend from an area to the north of Orion’s 2nd brightest celebrity, the ruddy hued Betelgeuse.
Presently, Orion shows up in advance of us in our trip around the sunlight, and has actually not totally increased over the eastern perspective up until after 11:30 p.m. neighborhood daytime time. These meteors go to their finest throughout the predawn hours at around 5 a.m.– Orion will certainly after that be highest possible overhead towards the south. Because Orion’s famous three-star belt straddles the holy equator, the Orionids are just one of simply a handful of understood meteor showers that can be observed just as well from both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
Typically Orionid meteors are generally dark and not well seen from metropolitan areas, so it’s recommended that you discover a risk-free country place to see the most effective Orionid task. After coming to a head on Monday early morning, task will certainly start to gradually come down, hanging back to around 5 per hour around Oct. 25.
However the moon “muscle mass in”
Despite the fact that the moon currently transformed complete this previous week and is currently on the wind down, it will certainly still have an unfavorable influence on this year’s Orionids. On the early morning of the Orionid optimum on Monday, it will certainly be fairly near to the celebrity El Nath in the neighboring constellation of Auriga; an 80% lit up gibbous moon, swamping the skies with its intense light.
So although the Orionids will certainly go to their top, a lot of these touches of light will likely be wiped out by the intense moonlight. Still, an incredibly intense Orionid may still stand out. Current researches have actually revealed that concerning fifty percent of all Orionids that are seen leave tracks that lasted longer than various other meteors of equal illumination.

Halley’s Heritage
The Orionids are commonly described as the “heritage of Halley’s Comet.” As a matter of fact, these little streaks of dirt are just the planetary clutter that the comet has actually left precede along its orbit from previous flows around the sun.
Meteoroids that are launched out right into area are the residues of a comet’s center. All comets at some point break down right into meteor flocks and Halley’s is well right into that procedure right now.
These little fragments– mainly varying in dimension from dirt to sand grains– continue to be along the initial comet’s orbit, developing a “river of debris” precede. When it comes to Halley’s comet, which has most likely circled around the sunlight several hundreds, otherwise countless times, its unclean path of particles has actually been dispersed essentially consistently the whole time its whole orbit. When these little bits of comet hit Planet, rubbing with our ambience elevates them to white warm and generates the impact widely described as “shooting celebrities.”
RELEVANT TALES:
— Orionid meteor shower 2024: When, where & how to see it
— Meteor showers 2024: When is the next one?
— Halley’s Comet: Facts about history’s most famous comet
The orbit of Halley’s Comet carefully comes close to the Planet’s orbit at 2 locations. One factor remains in the very early component of Might, generating a meteor screen called the Eta Aquarids. The various other factor can be found in the center to last component of October, generating the Orionids. Tip outside prior to sunup throughout this weekend break and onto much of following week, and if you see a meteor, there has to do with a 75 percent possibility that it most likely stemmed from the center of Halley’s Comet.
So, for people like me, that want to see Halley once again, yet most likely will not (it will not be back up until the year 2061) we’ll need to opt for the Orionids as an alleviation reward.
Joe Rao acts as a teacher and visitor speaker at New york city’s Hayden Planetarium He covers astronomy for Natural History magazine, the Farmers’ Almanac and various other magazines.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
