When you acquire via web links on our write-ups, Future and its submission companions might make a compensation.
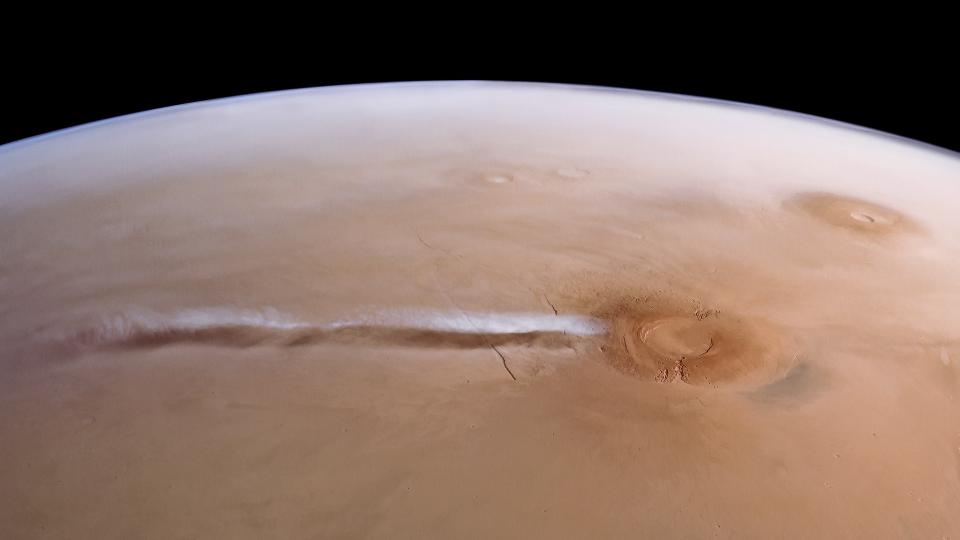


Researchers have actually introduced one of the most considerable map of clouds on Mars ever before produced.
For the previous twenty years, the European Room Company’s (ESA) Mars Express spacecraft has actually photographed Martian clouds and tornados, recording exactly how they form right into striking patterns regardless of the world’svery thin atmosphere This summer season, researchers at the German Aerospace Facility assembled hundreds of pictures taken by an electronic camera aboard the spacecraft right into a “Cloud Atlas” that takes you on an immersive digital excursion of Mars’ clouds.
Comprehending exactly how and where on Mars these clouds develop is vital to understanding their effect on the world’s environment. The brand-new magazine records a selection of cloud patterns, consisting of some unlike anything seen on Earth.
” Clouds on Mars are equally as varied and remarkable as those we see in our skies in the world,” Daniela Tirsch, a worldly rock hound at the German Aerospace Facility, stated in astatement She provided the brand-new atlas Sept. 10 at the Europlanet Scientific Research Congress in Berlin. “We likewise see remarkable dirt clouds that can spread out numerous kilometers,” Tirsch stated– a sensation we do not experience in the world.”
Associated: Mars’ clouds are strangely Earth-like, despite wildly different atmospheres
Cloud “roads” spread out throughout north bogs


Unlike Planet’s liquid-water clouds, Martian clouds are mostly co2 due to the fact that wetness in the world’s air is so reduced, all of it would certainly amount to a layerthinner than a strand of hair In some cases, dirt and water vapor likewise assimilate, assisting craft straight rows of clouds like those seen floating over a substantial swath of bogs near Mars’ north post called Vastitas Borealis.
The Mars Express spacecraft imaged likewise considerable cloud roads in other places on Mars, consisting of around Olympus Mons, Arsia Mons and numerous various other volcanoes in the Tharsis area near the equator. “While they look like cumulus clouds in the world, they are created under various weather,” Tirsch stated in the declaration.
An incredibly lengthy darken Arsia Mons
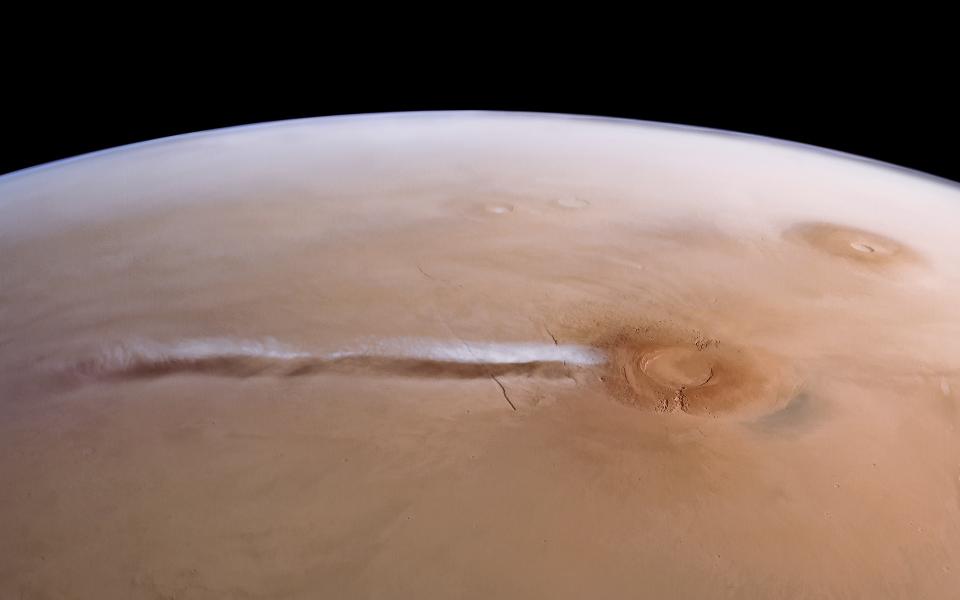


A peculiarly long water-ice cloud has actually shown up numerous times over Arsia Mons, the southernmost of 3 volcanoes near the Martian equator, that in 2020, researchers named it the Arsia Mons Elongated Cloud (AMEC).
The extended bit of water ice has actually created every springtime on southerly Mars, and it ends up being noticeable in the morning and lasts up until twelve noon each day for a minimum of 80 days. Within hours, the cloud spreads out at an overwhelming rate of 370 miles per hour (600 km/h). At its biggest, it extends greater than 1,100 miles (1,800 kilometers) long and 90 miles (150 kilometres) throughout, extending from Arsia Mons right to the extra well-known Olympus Mons, the biggest volcano in the planetary system.
Although the AMEC continuously creates over a volcano, researchers have lengthy dismissed that it’s any kind of kind of volcanic occasion, due to the fact that spacecraft never ever spotted spikes in methane, sulfur dioxide and various other gases recognized to gush from volcanic eruptions. Rather, the cloud arises from the methodlocal winds interact with the surface features It creates when water-ferrying winds are pushed up the flanks of Arsia Mons to greater, much cooler elevations, where a few of the wetness in them condenses.
” Comprehending this cloud offers us the amazing possibility to attempt to duplicate the cloud’s development with versions– versions that will certainly boost our understanding of weather systems on both Mars and Planet,” Agustin Sánchez-Lavega, a teacher at the College of Basque Nation in Spain that co-authored a 2020 study clarifying the cloud’s characteristics, stated in a previous ESA statement.
Wind-lifted dirt clouds left awaiting the air
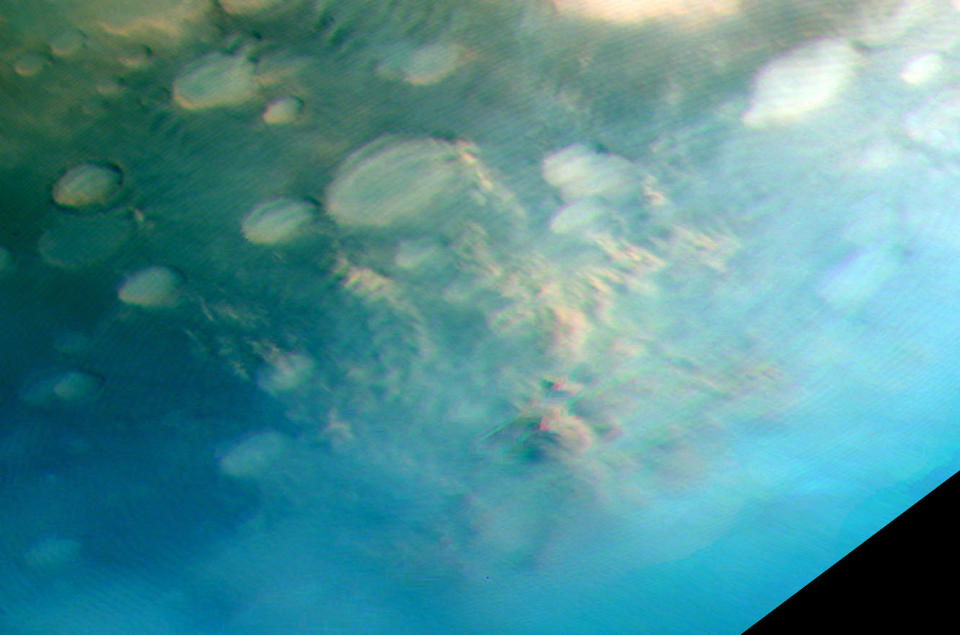


ASSOCIATED TALES:
—NASA’s Curiosity rover spots strange, colorful clouds on Mars
— Person researchers find patterns in darken Mars
— Right here’s what astronauts in orbit around Mars would certainly see from their spacecraft
The photo over programs a striking cloud pattern shaped by gravity waves, which prevail surges in both Mars’ and Planet’s environments triggered by air attempting to recover itself to balance. On Mars, they are generally detected at midlatitudes in the winter season; NASA’s Curiosity rover videotaped the first ground-based views of such clouds back in 2017.
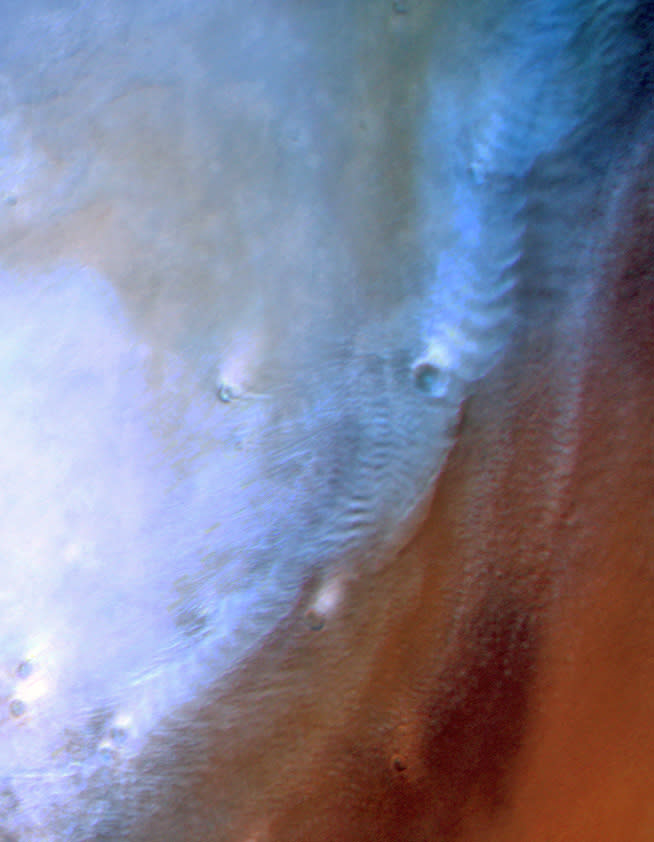

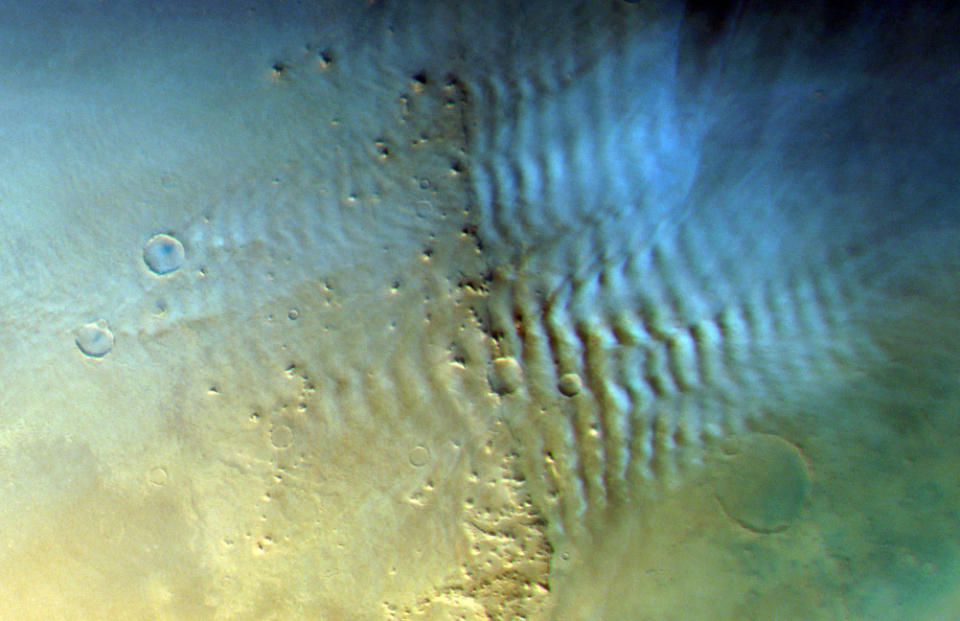

An unique kind of gravity cloud is a lee wave, a persistent ridge-like cloud pattern that improves the downwind side of hills throughout Mars. Relying on the form of its challenge, this kind of cloud handles somewhat various geometries, researchers state.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
