When you purchase via web links on our write-ups, Future and its submission companions might make a compensation.


We have some exceptionally effective telescopes that have actually offered us magnificent sights of the universes and permitted us to recall to theearly days of the universe These observatories, such as the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), are impressive accomplishments of design that have actually called for billions of bucks and years of job.
However what happens if we could access an also much better telescope that currently exists? This would not be a normal telescope. It would not also include a lens. However it would certainly be without a doubt one of the most effective telescope we had actually ever before constructed.
This telescope would certainly make use of the sun itself.
To provide some point of view on just how effective a sun-based telescope can be, take into consideration JWST. With a mirror that’s 21.3 feet (6.5 meters) in size, JWST can accomplishing a resolution of around one-tenth of an arcsecond, which has to do with 600 times much better than the human eye. At that resolution, the telescope can see the information on a coin positioned 25 miles (40 kilometers) far from it or get the pattern of a policy football round resting 342 miles (550 kilometres) away.
Associated: 12 James Webb Area Telescope searchings for that transformed our understanding of deep space
One more instance is the Event Horizon Telescope, which is truly a network of specific tools spread around the world. By thoroughly collaborating its aspects, the telescope has actually offered us remarkable photos of the disks of gas surroundinggiant black holes To accomplish that, it took care of an outstanding resolution of 20 microarcseconds. At that resolution, the telescope can identify an orange remaining on the surface area of the moon.
However what happens if we intended to go also larger? A bigger telescope would certainly require either big recipes or networks of antennae flying via the solar system, both of which would certainly need substantial jumps in our technical capacities.
Fortunately, there so occurs to be a large telescope currently offered, resting right in the facility of the planetary system: the sunlight.
While the sunlight might not look like a standard lens or mirror, it has a great deal of mass. And in Einstein‘s theory of general relativity, large items bend area-time around them. Any type of light that forages the surface area of the sunlight obtains dispersed and, as opposed to proceeding in a straight line, heads towards a centerpiece, along with all the various other light that forages the sunlight at the exact same time.
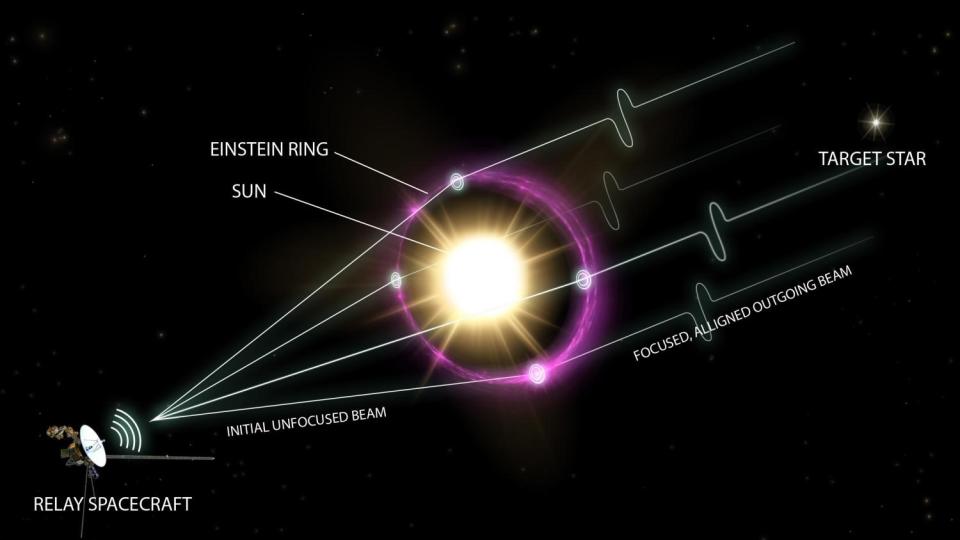

Astronomers currently utilize this impact, called gravitational lensing, to research one of the most remote galaxies inthe universe When light from those galaxies passes near a large collection of galaxies, the mass of that collection magnifies and multiplies the history photo, permitting us to see much further than we typically could.
The “solar gravitational lens” causes a virtually amazingly high resolution. It’s as if we had a telescope mirror the size of the whole sunlight. A tool placed at the appropriate centerpiece would certainly have the ability to harness the gravitational bending of the sunlight’s gravity to enable us to observe the remote cosmos with a jaw-dropping resolution of 10 ^ -10 arcseconds. That’s approximately a million times much more effective than the Occasion Perspective Telescope.
Obviously, there are difficulties with making use of the solar gravitational lens as an all-natural telescope. The centerpiece of all this light flexing rests 542 times above thedistance between Earth and the sun It’s 11 times the distance to Pluto, and 3 times the range attained by mankind’s most distant spacecraft, Voyager 1, which released in 1977.
So not just would we need to send out a spacecraft further than we ever before have previously, yet it would certainly need to have adequate gas to remain there and move. The photos developed by the solar gravitational lens would certainly be expanded over 10s of kilometers of space, so the spacecraft would certainly need to check the whole area to develop a total mosaic photo.
Relevant Stories:
— How can we take pictures of Earth-like exoplanets? Use the sun!
— Sun’s gravitational lens could help find life on exoplanets
— If there’s life on Europa, solar sails can assist us locate it
Strategies to make the most of the solar lens return to the 1970s. Most just recently, astronomers have actually suggested creating a fleet of little, light-weight cubesats that would certainly release solar sails to increase them to 542 AU. As soon as there, they would certainly reduce and collaborate their maneuvers, accumulating a photo and sending out the information back to Earth for handling.
While it might appear over-the-top, the principle isn’t also much from truth. And what would certainly we obtain with this sort of supertelescope? If it were targeted at Proxima b, the local recognized exoplanet, as an example, it would certainly provide a 1-kilometer resolution. Taking into consideration that prepare for followers to JWST want to accomplish imaging capacities of exoplanets where the whole earth beings in a handful of pixels, the solar gravitational lens places those concepts to embarassment; it can supplying a beautiful picture of the comprehensive surface area attributes of any type of exoplanet within 100 light-years, not to mention all the various other huge monitorings it can accomplish.
To state this would certainly be much better than any type of recognized telescope is an exaggeration. It would certainly be much better than any type of telescope we can perhaps integrate in any type of feasible future for the following couple of a century. The telescope currently exists– we simply need to obtain an electronic camera in the ideal placement.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
