There isn’t much eco-friendly in the Sahara Desert, however after an uncommon increase of rainfall, the shade can be seen from room sneaking right into components of among the driest locations on the planet.
Satellites just recently caught plant growing partially of the usually dry southerly Sahara after tornados relocated there when they should not. It has actually likewise triggered disastrous flooding. And scientists say a globe heating as a result of nonrenewable fuel source air pollution is making both most likely.
Rain north of the equator in Africa usually enhances from July via September as the West African Downpour kicks right into equipment.
The sensation is noted by a rise in thundercloud that emerges when damp, exotic air from near the equator satisfies warm, completely dry air from the north part of the continent. The emphasis for this thundercloud– called the Intertropical Merging Area– changes north of the equator in the North Hemisphere’s summer season. Much of it droops southern of the equator throughout the Southern Hemisphere’s cozy months.
However given that at the very least mid-July, this area has actually changed further north than it usually should, sending out tornados right into the southerly Sahara, consisting of sections of Niger, Chad, Sudan and also as much north as Libya, according to information from NOAA’s Environment Forecast Facility.
Consequently, these sections of the Sahara Desert are anywhere from two times as damp to greater than 6 times wetter than they ought to be.
There are 2 possible reasons for this odd change north, according to Karsten Haustein, an environment scientist at Leipzig College in Germany.
The shift from El Niño to La Niña has actually affected exactly how much north this area has actually relocated this summertime Haustein claimed. El Niño– an all-natural environment pattern noted by warmer than ordinary sea temperature levels in the equatorial Pacific– usually causes drier than typical problems in the damp sections of West and Central Africa. La Niña, or perhaps a budding one, can have the contrary impact.
A warming up globe is the various other substantial variable.
” The Intertropical Merging Area, which is the factor for (Africa’s) greening, relocates further north the warmer the globe obtains,” Haustein described. “A minimum of, this is what a lot of versions recommend.”
A research study released in the journal Nature this June discovered further northward changes in this area might occur much more often in the following pair years as co2– a result of fossil fuel pollution— degrees raise and the globe warms.
A damaging indication of points to find
The change isn’t simply transforming deserts eco-friendly, it has actually interrupted the Atlantic hurricane season and had significant repercussions over the previous couple of months for numerous African nations.
Nations that ought to be obtaining even more rains are obtaining much less as tornados change north. Components of Nigeria and Cameroon usually obtain saturated with at the very least 20 to 30 inches of rainfall from July to September, however have actually just obtained in between 50 and 80% of their common rainfall given that mid-July, according to CPC information.
Further north, usually drier locations, consisting of components of Niger, Chad, Sudan, Libya and southerly Egypt have actually obtained greater than 400% of their common rains given that mid-July, according to CPC information.
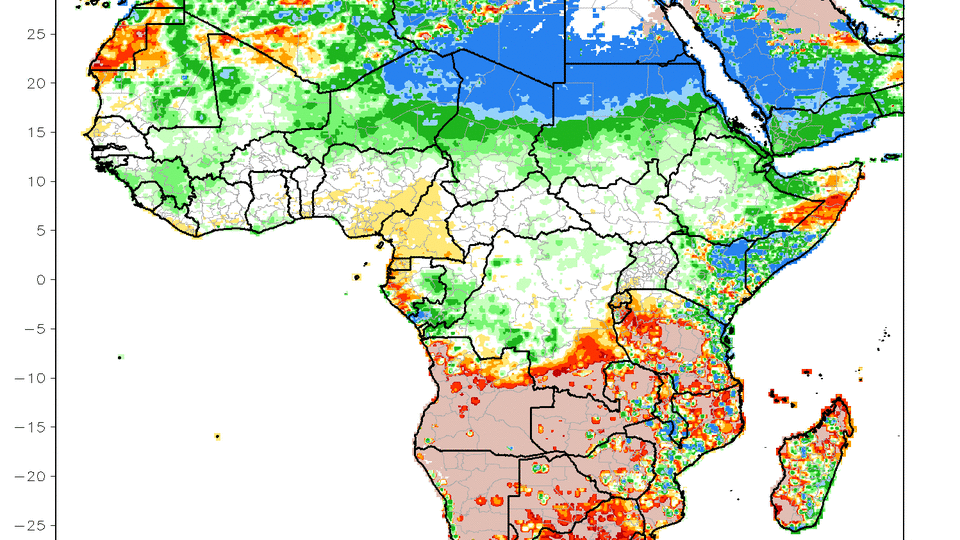

Take the north part of Chad, which becomes part of the Sahara Desert. Just as much as an inch of rainfall usually drops right here from concerning mid-July to very early September. However anywhere from 3 to 8 inches of rainfall has actually dropped in the exact same duration this year, according to CPC information.
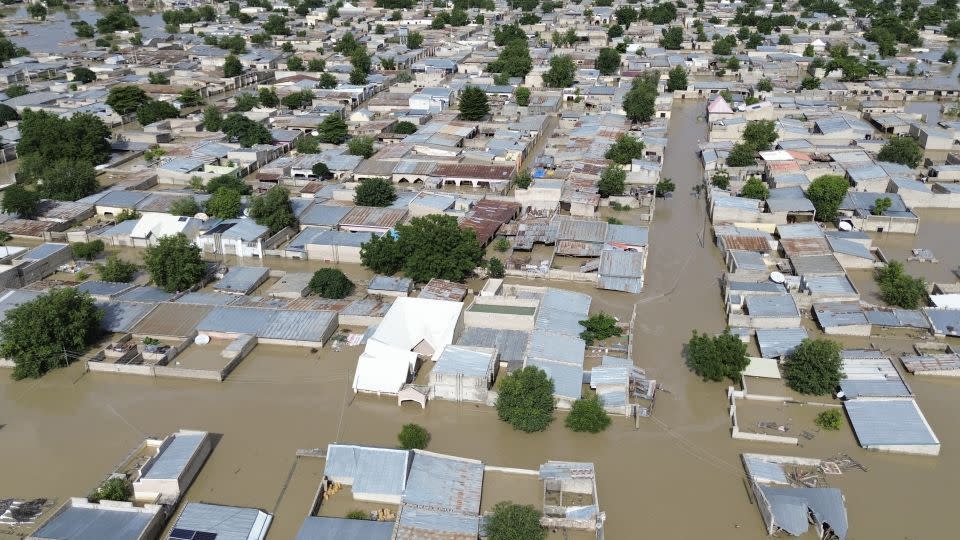
This extreme rains triggered disastrous flooding in Chad. Virtually 1.5 million people have actually been affected and at the very least 340 have actually been eliminated by flooding in the nation this summertime, according to a United Nations rundown.
Dreadful flooding has actually likewise eliminated greater than 220 individuals and displaced numerous thousands in Nigeria, mostly in the usually drier north part of the nation, CNN previously reported.
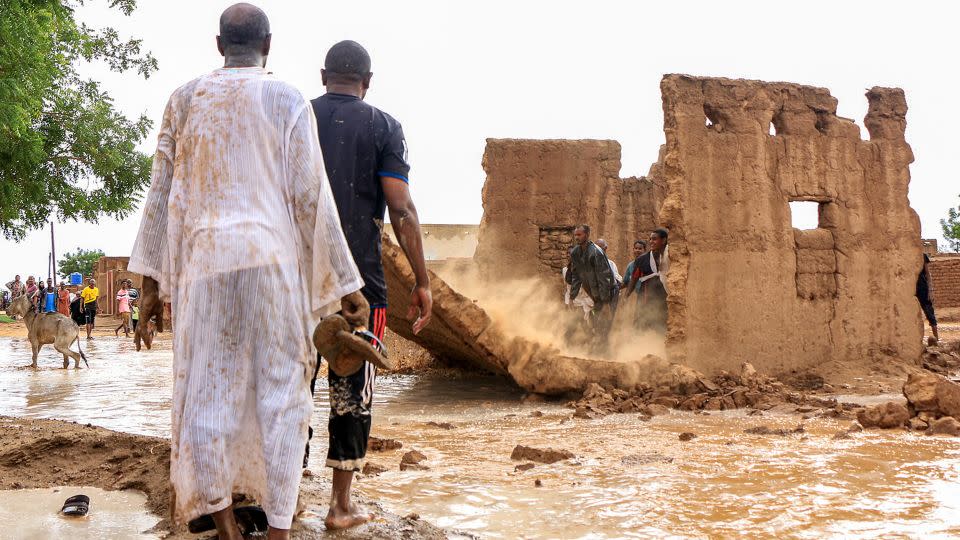




Fatal flooding likewise shook Sudan in late August, eliminating at the very least 132 individuals and ruining greater than 12,000 homes.
Flooding occasions like these most likely have the finger prints of environment modification, according to Haustein, that services attribution studies to figure out to what degree environment modification has actually affected a certain weather condition occasion.
As the globe warms, it will certainly have the ability to hold even more dampness, Haustien described. This might result in wetter total gales and even more disastrous flooding similar to this period.
Extra study will certainly be required to figure out simply just how much of function environment modification played in each flooding occasion, however maybe an indication of points to find, Haustien claimed.
” Each and every single occasion is influenced by environment modification,” Haustein claimed. “( Also if) no solitary flooding is (straight) triggered by environment modification, it has actually been made most likely.”
For even more CNN information and e-newsletters produce an account at CNN.com
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
