When you get via web links on our posts, Future and its submission companions might make a compensation.

Seasonal modifications can have a remarkable result on exactly how swiftly Mars sheds its water to area, a joint research in between the Hubble Space Telescope and NASA’s Mars Environment and Volatile Advancement (MAVEN) objective has actually revealed.
Over 3 billion years earlier, Mars was cozy and damp, with huge bodies of water on its surface area and a thicker ambience. Today, nonetheless, Mars is barren, cold and completely dry. So, what occurred to all the water?
” There’s just 2 locations water can go,” John Clarke of the College of Boston claimed in astatement “It can ice up right into the ground, or the water particles can get into atoms, and the atoms can get away from the top of the ambience right into area.”
A Lot Of Mars’ water is still on the Red Earth. Huge tanks seem secured deep underground at midsts in between 11.5 and 20 kilometers (7.1 and 12.4 miles). There suffices water inside Mars for an international comparable layer (GEL, which basically describes exactly how deep a planet-wide sea it would certainly develop) in between 1 and 2 kilometers (0.62 and 1.24 miles).
Associated: Mars rock examples reveal indicators of water in Jezero Crater– could life have when existed there?
Reasonably percentages of water-ice are likewise secured in superficial ice and in Mars’ polar ice caps. Throughout the Martian summer season, this ice can sublimate, disposing water vapor right into theatmosphere A lot of that water vapor distributes from post to post, cold out in the hemisphere in which it is wintertime, however some locates itself in the top ambience where solar ultraviolet light can photodissociate H2O water particles, damaging them apart right into their element atoms. The oxygen in water winds up either oxidizing products externally (thus, why Mars shows up rust-red) or bonding with carbon to develop co2. At the same time, the hydrogen atoms (or their much heavier isotopic equivalent, deuterium) can get away right into area (if they are energised sufficient to get to retreat speed) and obtain lugged away with the solar wind.
VIRTUOSO, which reached Mars in 2014, is entrusted with determining this hydrogen retreat.


Due to the fact that deuterium, a hefty type of hydrogen, does not get away Mars’ ambience so quickly, it indicates that the proportion of deuterium to hydrogen (D/H) in Mars’ ambience is essential, with the wealth of deuterium about hydrogen expanding gradually as it sheds hydrogen quicker. As Earth and Mars are assumed to have got their water from the very same resources, the prehistoric D/H proportion of water on Mars 3 billion to 4 billion years ago must have coincided as it gets on Planet today. The D/H proportion on Mars today is someplace in between 8 and 10 times bigger than in the world. There are specific uncertainties in the dimensions, however by contrasting that prehistoric Mars water proportion to today’s proportion while considering the price of hydrogen and deuterium loss to area, it is feasible to theorize in reverse and determine just how much water Mars most likely shed over its background.
Based upon wizard’s previous monitorings, Mars has actually shed sufficient water to area to develop a GEL of in between 10s and numerous meters deep. Integrated with the substantial quantity of water lately located hidden inside Mars, this indicates the Red Earth was water-rich in its far-off past.
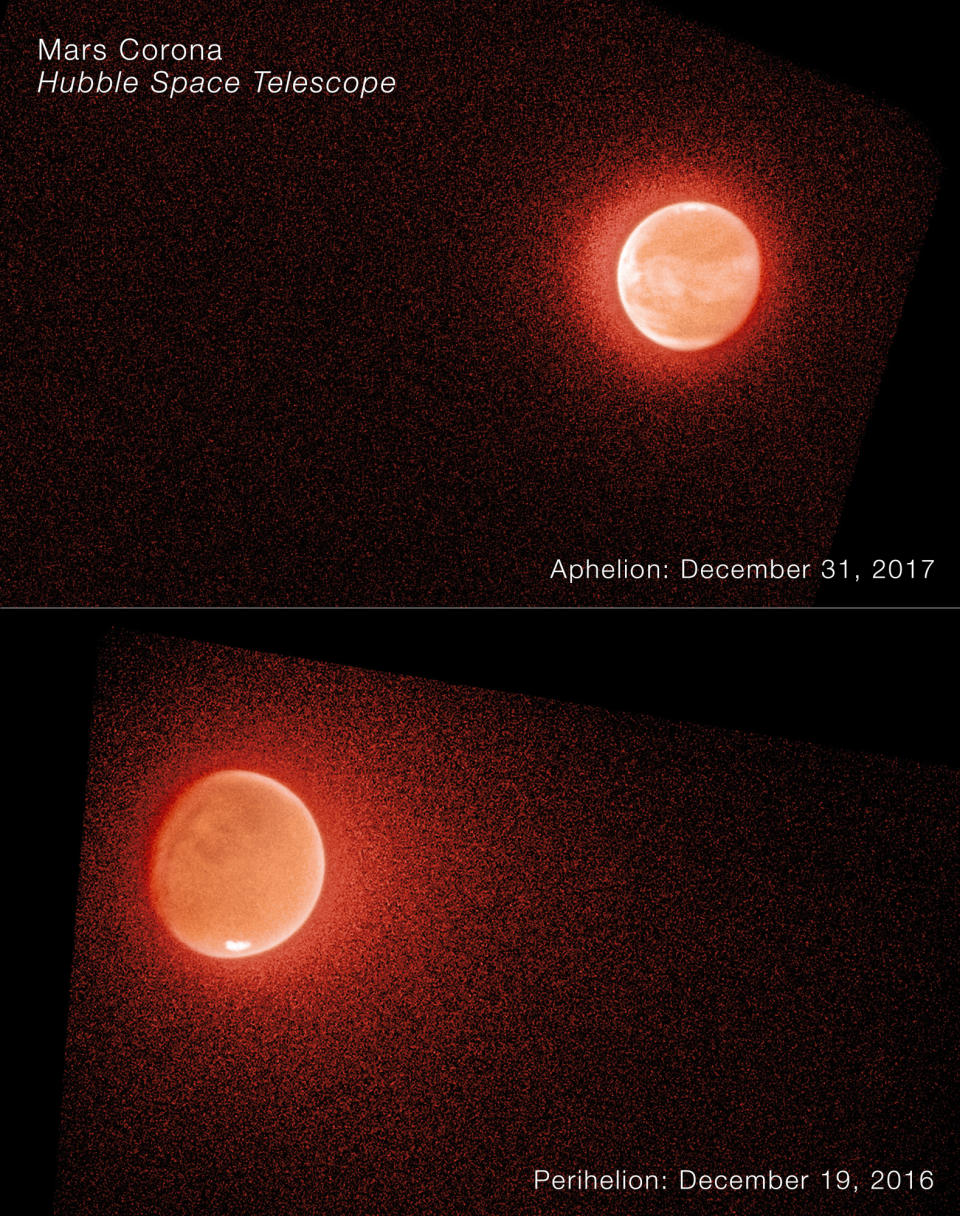
Nonetheless, VIRTUOSO, with the Hubble Room Telescope’s aid, has actually currently located some unexpected intricacy to the tale of Mars’ water loss. With each other, the tools have actually revealed that the price of hydrogen loss is seasonal, with huge boosts in the retreat price at perihelion, which is Mars’ closest factor in its orbit aroundthe sun This accompanies a solid upwelling of water vapor right into the center ambience, brought on by seasonal home heating. When at perihelion, Mars’ southerly hemisphere is slanted in the direction of the sunlight and the Red Earth is swallowed up in its yearly dust storm period; the air-borne dirt can add to climatic home heating and water vapor web content.
At perihelion, wizard determined thickness of deuterium and hydrogen in the top ambience that are specifically regarding 5 and 20 times more than at aphelion, which is Mars’ farthest factor from the sunlight in its elliptical exerciser (extended, instead of round) orbit. At aphelion, the deuterium loss is so weak that wizard is not also delicate sufficient to find it. This is where the Hubble Room Telescope needs to can be found in, completing the spaces. The monitorings likewise revealed that the retreat prices are 10 to 100 times greater for deuterium and hydrogen specifically at perihelion than at aphelion. Certainly, both deuterium and hydrogen are running away so quickly at perihelion that the only point restricting them is the quantity of water vapor offered in the ambience.
Associated Stories:
— Sea’s well worth of water may be hidden within Mars– however can we reach it?
— ‘We assumed it was difficult:’ Water frost on Mars uncovered near Red Earth’s equator
— Exists actually a substantial subsurface lake near Mars’ south post?
” Over the last few years researchers have actually located that Mars has a yearly cycle that is a lot more vibrant than individuals anticipated 10 or 15 years earlier,” claimed Clarke. “The entire ambience is extremely stormy, warming up and cooling on brief timescales, also to hours. The ambience increases and gets as the illumination of the sunlight at Mars differs by 40% throughout a Martian year.”
This does establish a quandary when discussing the deuterium loss, which shows up higher than what would certainly be anticipated totally from average thermal retreat, where a deuterium atom is cozy sufficient to have actually the power required to miss right into area. To enhance the price of deuterium loss to make sure that it matches the observed D/H proportion on Mars, an additional shot of power right into the ambience is needed from someplace. This can originate from protons on the solar wind going into the ambience and ramming deuterium atoms, or chain reactions from solar ultraviolet light that can provide the deuterium an additional kick.
The searchings for were published on July 26 in the journal Scientific research Breakthroughs.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
