Antarctica’s Thwaites Glacier obtained its label the “Doomsday Glacier” for its prospective to flooding shorelines around the globe if it fell down. It is currently adding around 4% of annual sea-level rise as it sheds ice, and one concept recommends the glacier might quickly begin to collapse into the ocean like a row of dominoes.
However is that type of fast collapse truly as most likely as been afraid? A brand-new research study of Thwaites Glacier’s vulnerability to what’s referred to as marine ice cliff instability provides some hope. However the findings do not suggest Thwaites is secure.
Polar researcher Mathieu Morlighem, that led the research study, discusses the outcomes.
Why is the Thwaites Glacier so vital?
Thwaites Glacier drains pipes a significant location of Antarctica’s ice sheet– concerning 74,000 square miles (192,000 square kilometers), a stretch larger than Florida. If a snow drops within that drain system, it will ultimately wind up as component of an iceberg in the sea off Thwaites.
What we are seeing with Thwaites Glacier today is a catastrophe in sluggish movement.
The bedrock under Thwaites Glacier rests listed below water level and slopes downward going inland, so the glacier obtains much deeper towards the inside of the ice sheet. As soon as the glacier starts shedding much more ice than it gets from brand-new snowfall and begins to pull back, it’s extremely difficult to reduce it down as a result of this incline. And Thwaites is currently retreating at an accelerating rate as the environment warms.
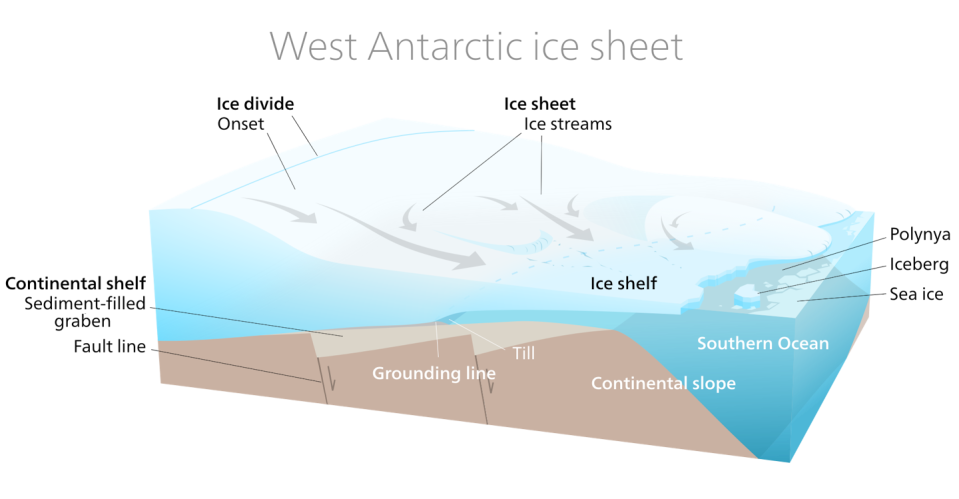

Thwaites Glacier holds sufficient ice to increase international water level by more than 2 feet (0.65 meters). As soon as Thwaites begins to undercut, it likewise will certainlydestabilize neighboring glaciers So, what takes place to Thwaites impacts every one of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, which impacts sea-level increase along shorelines anywhere.
What is aquatic ice high cliff instability?
Marine ice high cliff instability is a relatively new concept suggested by researchers in the previous years.
Most of the glaciers around Antarctica have significant drifting expansions called ice shelves that strengthen the glacier and reduce its ice circulation right into the sea. With the environment warming, we have actually seen a few of these drifting expansions collapse, sometimes very rapidly, in the period of a couple of weeks or months.
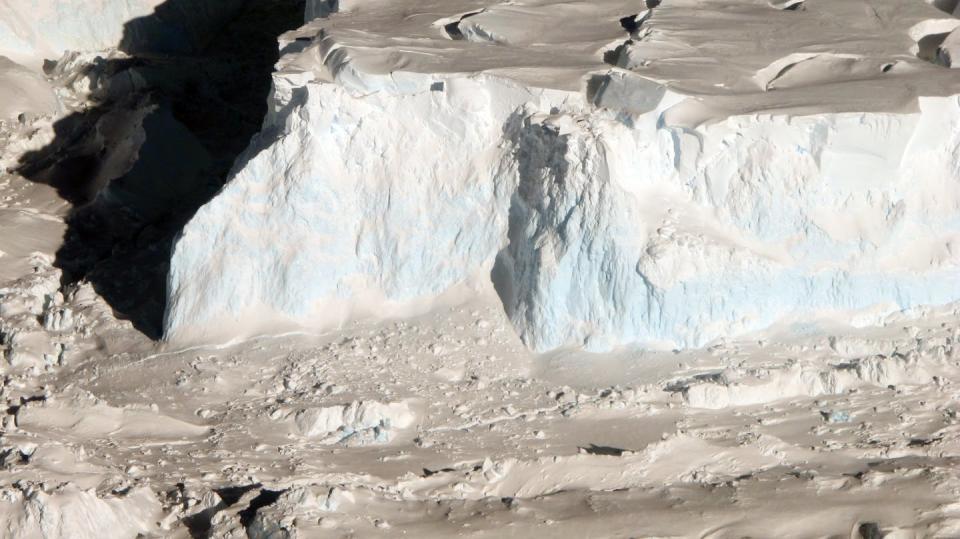


If Thwaites’ ice rack were to collapse, it would certainly subject an extremely high ice high cliff dealing with the sea along its75-mile (120-kilometer) front There is just a lot pressure that ice can maintain, so if the high cliff is as well high, it will certainly fall down right into the sea.
As soon as that takes place, a brand-new ice high cliff further back would certainly be subjected, and the brand-new high cliff would certainly be also taller due to the fact that it is further inland. The concept of aquatic ice high cliff instability recommends that if the high cliffs collapse promptly sufficient, that could have a domino effect of ever-higher ice high cliffs falling down together.
Nonetheless, nobody has actually observed aquatic ice high cliff instability at work. We do not understand if it will certainly take place, due to the fact that a whole lot relies on just how promptly the ice breaks down.
What did you uncover concerning the danger to Thwaites?
When the theory of marine ice cliff instability was very first presented, it utilized a harsh estimate of just how ice high cliffs may fall down as soon as the ice rack was gone.
Research Studies ever since have actually figured out that ice cliffs won’t fail systematically till the ice has to do with 442 feet (135 meters) high. Also then, they would certainly stop working much more gradually than forecasted till they ended up being much taller.
We utilized 3 high-resolution versions to discover what this brand-new physical understanding of ice high cliff instability would certainly suggest for Thwaites Glacier this century.
Our results show that if Thwaites’ whole ice rack fell down today, its ice front would certainly not swiftly pull back inland as a result of aquatic ice high cliff instability alone. Without the ice rack, the glacier’s ice would certainly move much quicker towards the sea, thinning the front of the glacier. Because of this, the ice high cliffs would not be as high.
We discovered that Thwaites would certainly stay rather secure at the very least with 2100. We likewise substitute an ice rack collapse in half a century, when the glacier’s grounding line— where its based ice fulfills the sea– would certainly have pulled away much deeper inland. Also after that, we discovered that aquatic ice high cliff instability alone would certainly not trigger a fast hideaway.
The outcomes bring into question some current price quotes of simply exactly how quick Thwaites may fall down. That consists of a worst-case circumstance that the Intergovernmental Panel on Environment Adjustment pointed out in its latest assessment report yet classified as “reduced probability.”
Thwaites is the glacier every person is fretted about. If you design the whole ice sheet, this is where aquatic ice high cliff instability begins andwhere it propagates far inland So, if Thwaites isn’t as at risk to ice high cliff failing as we believed, that’s an excellent indicator for the whole ice sheet.
However aquatic ice high cliff instability is just one system of ice loss. This searching for does not suggest Thwaites is secure.
What else is triggering glaciers to pull back at a speeding up price?
There are lots of procedures that make the Antarctic ice sheet unpredictable, a few of them extremely well recognized.
Ice-ocean communications clarify most of the recent ice mass loss until now. Antarctica is a very cold place, so climatic warming isn’t having a big impact yet. However cozy sea currents are obtaining under the ice racks, and they are thinning the ice from below, which deteriorates the ice racks. When that takes place, the ice streams move much faster due to the fact that there is much less resistance.
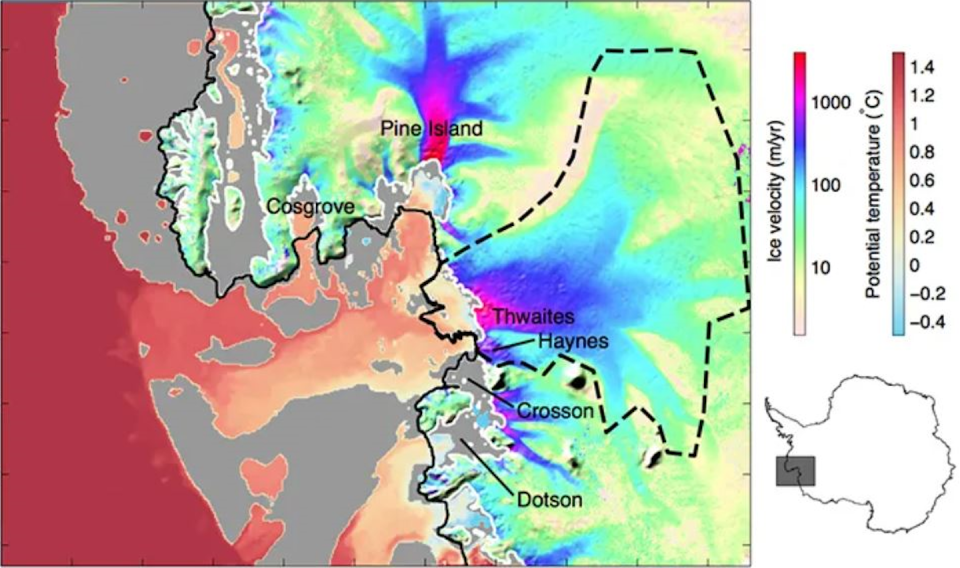

Over the past few decades, the Amundsen Sea field, where Thwaites and Pine Island glaciers lie, has actually seen a breach of cozy water from the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, which has actually been melting the ice from below.
What does environment modification involve it?
Antarctica can feel like a far location, yet human activities that warm the planet— such as melting nonrenewable fuel sources– are having significant impacts at the posts. Ice loss adds to sea-level increase, affecting coastal regions around the globe.
Individuals’s options today will certainly identify just how promptly the water climbs.
This short article is republished from The Conversation, a not-for-profit, independent wire service bringing you truths and reliable evaluation to assist you understand our complicated globe. It was composed by: Mathieu Morlighem, Dartmouth College
Learn More:
Mathieu Morlighem obtains financing from NASA, the National Scientific Research Structure, the Heising Simons Structure, and Dartmouth University.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
