When you acquire with web links on our write-ups, Future and its submission companions might gain a compensation.
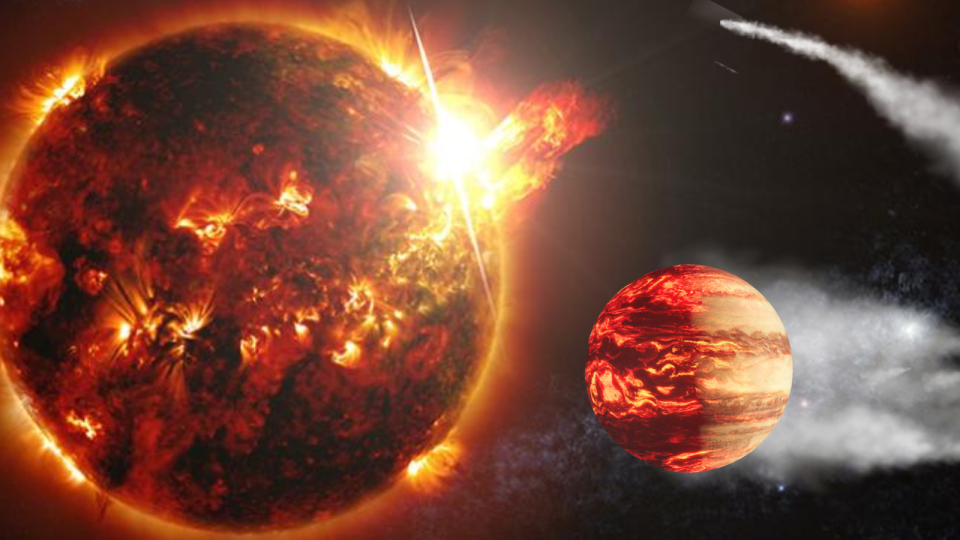


One of the most typical celebrities in the Galaxy might be also much less pleasant to life than formerly presumed.
Brand-new study recommends that red dwarf stars, excellent bodies smaller sized and much less enormous than the sunlight, might blast their worlds with extreme ultraviolet (UV) light radiation flares that significantly decrease their possible habitability.
A group of researchers reached this final thought by assessing information gathered by the now-decommissioned NASA goalGalaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX) Introduced in April 2003, GALEX checked deep space in UV light, searching for flares from around 300,000 close-by celebrities till it was closed down in 2013.
That study exposes that these dangerous flares might be much more typical than presumed, the scientists state. “Couple of celebrities have actually been believed to create adequate UV radiation with flares to effect earth habitability. Our searchings for reveal that much more celebrities might have this ability,” group leader and College of Cambridge scientist Vera Berger said in a statement.
The group refined the GALEX historical information utilizing modern-day computer system strategies, resulting in all brand-new red dwarf understandings.
” Incorporating modern-day computer system power with gigabytes of decades-old monitorings permitted us to look for flares on thousands and hundreds of close-by celebrities,” employee Michael Tucker from Ohio State College stated.
Relevant: Earth-size earth uncovered around trendy red dwarf celebrity shares its name with a biscuit

Researchers were currently mindful that there are a variety of manner ins which high-energy light in the kind of UV radiation from a celebrity can be harmful to life. These consist of removing an earth’s environment and damaging down complicated particles that develop the foundation of biology.
This brand-new study tests what we understand regarding the habitability of extrasolar worlds or “exoplanets” by recommending that present stellar flare designs have actually minimized the danger. The group discovered that far-UV exhausts from flares have to do with 3 to 12 times as energised as anticipated.
” An adjustment of 3 coincides as the distinction in UV in the summertime from Anchorage, Alaska to Honolulu, where unguarded skin can obtain a sunburn in much less than 10 mins,” employee Benjamin J. Shappee from the College of Hawaii stated.
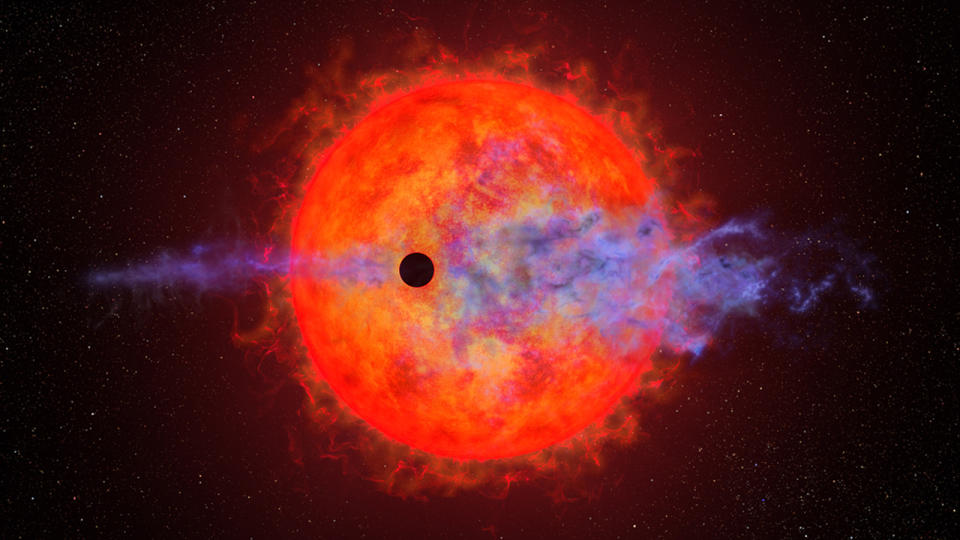

” This research study has actually transformed the image of the atmospheres around celebrities much less enormous than our sunlight, which send out extremely little UV light beyond flares,” stated employee Jason Hinkle, PhD prospect at the College of Hawai’i.
The group isn’t presently certain what creates the extra-strong UV flare exhausts, yet they believe they can be focused at details wavelengths of light. Due to the fact that components take in and send out light at particular wavelengths, this can show the visibility of carbon and nitrogen atoms.
Relevant Stories:
— This ruby exoplanet shed its environment– after that it expanded one more
— Some exoplanets are reducing. Right here’s why
— Celebrity impacts large exoplanet’s environment away, leaving enormous tail in its wake
Berger stated that even more room telescope information will certainly be required prior to the resource of the UV exhausts in these red dwarf flares can be determined.
” Our job places a limelight on the demand for additional expedition right into the results of excellent flares on exoplanetary atmospheres,” he wrapped up. “Utilizing room telescopes to acquire UV ranges of celebrities will certainly be critical for much better comprehending the beginnings of this exhaust.”
The group’s study was released in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
