When you acquire via web links on our posts, Future and its submission companions might gain a compensation.
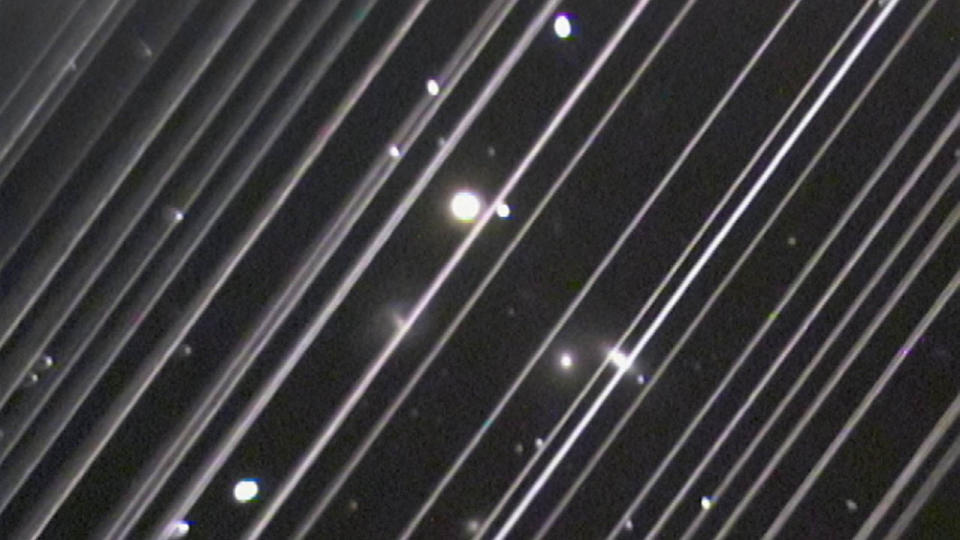

SpaceX Starlink satellites developed to link straight to smart devices radiate almost 5 times brighter overhead than typical Starlinks, according to current research study.
SpaceX intends to develop what it calls “a mobile phone tower precede” with countless direct-to-cell (DTC) satellites around Planet that use solution directly to unmodified smart devices “anywhere you can see the skies.” The greater luminance of these DTCs contrasted to routine Starlinks is partially since they circle Planet at simply 217 miles (350 kilometers) over the surface area, which is less than typical Starlink web satellites, whose elevation is 340 miles (550 kilometers), the research study reported.
In January 2024, simply a week after positioning the initial set of 6 Starlink DTC satellites in orbit, SpaceX utilized among them to send out sms message In Might, the business effectively demoed a video call, and stated it is dealing with T-Mobile to present such mobile solution to clients later on this year. There are currently over 100 DTC satellites in low Earth orbit, consisting of 13 that were released recently. Complying with effective screening of the initial set of DTCs, in March SpaceX requested an amendment to their certificate with the united state Federal Communications Compensation that would certainly permit them to run as much as 7,500 DTCs in LEO.
At the time the research study was carried out, SpaceX had actually not yet used its regular illumination reduction strategies to the DTCs, such as readjusting their framework and photovoltaic panels to decrease the section of spacecraft brightened by the sunlight, research study lead writer Anthony Mallama of the IAU Centre for the Security of Dark and Silent Skies from Satellite Constellation Disturbance (IAU-CPS) informed Space.com.
Associated: Blinded by the light: Just how negative are satellite megaconstellations for astronomy?
Kate Tice, SpaceX elderly supervisor for high quality systems design, recognized throughout the launch webcast in January that DTC satellites will certainly be brighter than routine Starlinks, and stated the business intends to deal with astronomers to analyze the effect on their monitorings prior to making equipment modifications that would certainly lower the DTCs, SpaceNews reported.
SpaceX started using illumination reduction strategies to routine Starlinks in 2020, after astronomers voiced serious concerns concerning the satellites’ routes streaking across telescope images, providing them pointless. Before launch, the business currently uses a mirror-like dielectric surface area to the bottom of each Starlink framework, to aid mirror sunshine right into area as opposed to spreading it towardsEarth Article launch, the business readjusts spacecraft framework and photovoltaic panels to better decrease luminance. With each other, these strategies are really reliable, lowering Starlink satellites’ illumination by an element of 10, Mallama stated.
If SpaceX uses these illumination reduction strategies to the DTCs, which are almost the very same dimension as the routine Starlinks, the DTCs would certainly still be 2.6 times brighter than their typical equivalents, Mallama and his associates reported in the recent study, which was evaluated inside by IAU-CPS and uploaded to the preprint web server arXiv last month.
Nevertheless, while DTCs are brighter things, they relocate at a much faster noticeable price and invest even more time in Planet’s darkness than routine Starlinks, which would certainly balance out several of their adverse effect on astronomy monitorings, the research study kept in mind.
” I see it as a tradeoff in specifications as opposed to an outright better/worse type of scenario,” John Barentine, a primary specialist at Arizona-based Dark Skies Consulting that was not included with the brand-new research study, informed Space.com.
ASSOCIATED TALES:
— SpaceX’s Starlink web satellites ‘leakage’ a lot radiation that it’s harming radio astronomy, researchers claim
— Starlink satellites: Facts, tracking and impact on astronomy
— Starlink satellite train: How to see and track it in the night sky
Barentine presumes that radio discharges beamed by the DTCs’ antennas might be interfering with radio bands protected for astronomy, as the satellites connect with Planet by means of radio signals yet do not have a specialized range to do so.
While researchers concur that offering connection to remote areas worldwide is a worthwhile objective, the rate at which satellites are being released to orbit concerns most of them– and not even if of their image-scarring illumination. Over a million satellites might quickly get in a room around Planet currently crowded with countless abandoned spacecraft, invested rocket bodies and numerous millimeter-sized items of scrap that zip over us at broadband. This particles populace positions a risk to satellites that supply web solution, navigating and climate tracking, and often also to astronauts onboard the International Spaceport station
Associated: Astronomers advised to combat ‘with every available resource’ to safeguard dark skies
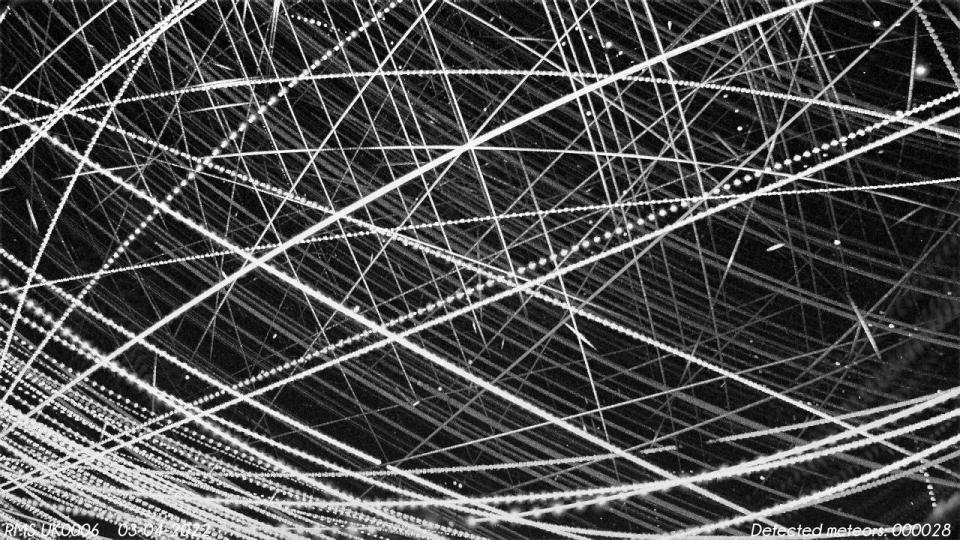


Also if we can evade a calamity in orbit by sensibly de-orbiting abandoned satellites, several researchers are worried that the variety of things circling our world might still do injury: When they deorbit, they might transfer a substantial change of steels that might change the chemical make-up of Planet’s ambience.
” Results on astronomy are simply the idea of the iceberg,” stated Barentine, that claims we might be quick coming close to a transforming factor where disaster comes to be brewing, either precede because of a crash or on the ground from dropping particles. “Room policy-making relocates much as well gradually to efficiently take care of every one of this.”
” Today, there’s not a great deal to anticipate that declares,” he included. “If the New Room Age goes terribly in the long run, background will certainly not look positively on it.”
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
