When you get via web links on our short articles, Future and its submission companions might gain a compensation.
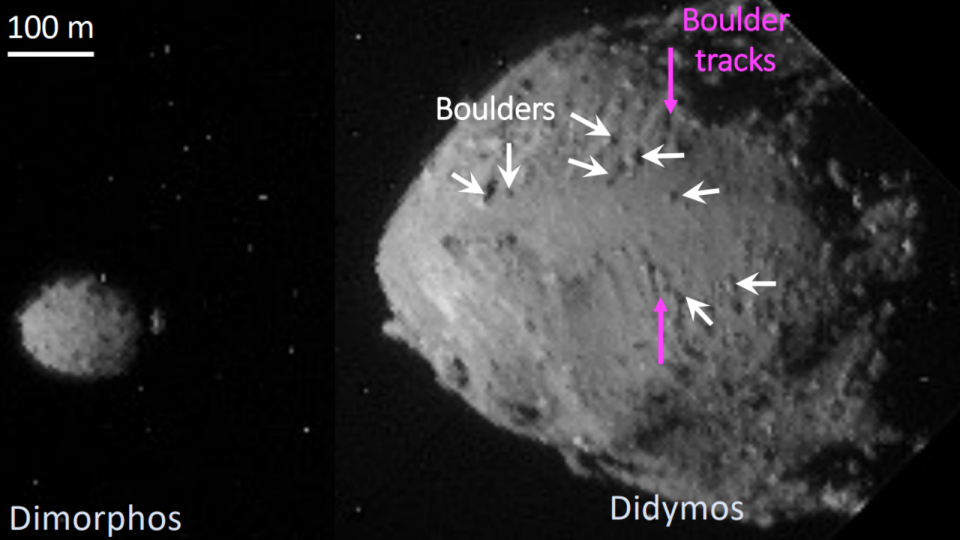

Researchers have actually made use of pictures accumulated by NASA’s DART planet effect goal to repaint a much more thorough photo of its planet targets Didymos and Dimorphos. The study might assist much better comprehend the development and development of binary planets such as these.
DART, which represents “Dual Planet Redirection Examination,” just affected the smaller sized body in this double-asteroid double star, the moonlet Dimorphos, which orbits the bigger room rockDidymos Still, the goal was to see what affect such an effect would certainly carry both bodies. The information accumulated throughout this effective goal might assist researchers far better strategy a planetary defense mission to draw away a planet on a clash with Planet.
Prior to collapsing right into Dimorphos on Sept. 26, 2023, DART had the ability to take pictures of bothnear-Earth asteroids Together with information from the Light Italian Cubesat for Imaging of Asteroids (LICIACube) goal, scientists had the ability to figure out a few of Didymos and Dimorphos’s geological attributes and physical homes.
The group, led by Olivier Barnouin from the Johns Hopkins College Applied Physics Research laboratory, examined the surface area of Didymos, the bigger of both planets. The scientists located that at high altitudes, Didymos is harsh and hosts big rocks in between 33 and 525 feet (10– 160 meters) long and numerous craters. At reduced altitudes, this planet’s surface area ends up being smoother, with less big rocks and craters.
Its smaller sized moonlet friend, Dimorphos, has rocks throughout its surface area that have a bigger series of dimensions. While the surface area of Dimorphos is mainly craterless, it is riven with numerous splits or “mistakes.”
The searchings for assisted Barnouin and associates figure out that Dimorphos most likely developed from product flung far from Didymos and afterwards clumped with each other intoxicated of gravity.
The group made use of the variety of craters on both planets to evaluate the ages of both planets. they established that the moms and dad body Didymos is 12.5 million years of ages, in between 40 to 130 times older than Dimorphos. They approximated the age of the moonlet to be around 0.3 million years.
Associated: NASA’s asteroid-impacting DART goal totally transformed the form of its target
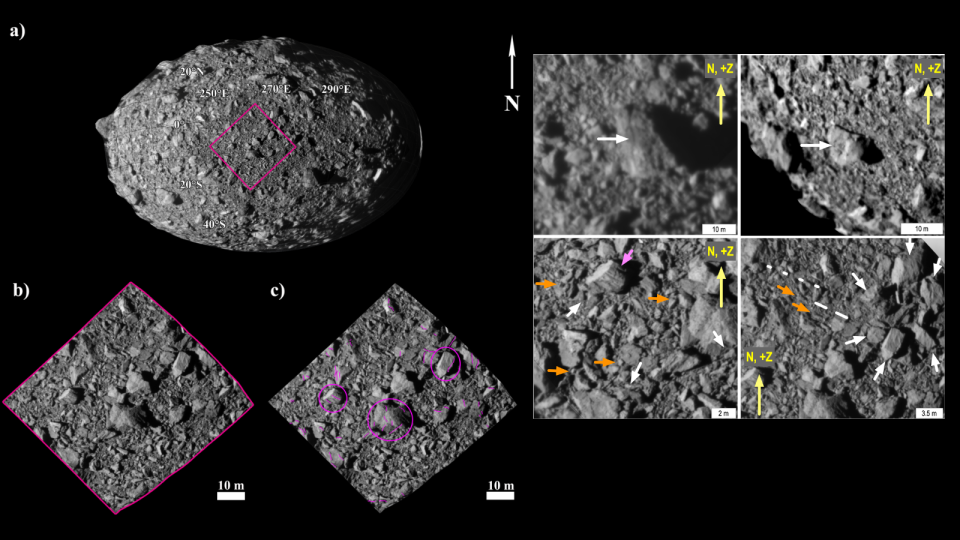

Checking out the dimension of rocks and their circulation throughout Dimorphos, a different group of researchers led by Maurizio Pajola from the INAF – Expensive Observatory of Padova established that they developed at various times instead of simultaneously.
This suggests that the rocks externally of Dimorphos are straight acquired from Didymos, more sustaining the concept that the moonlets in binary asteroid systems type from product shed by their bigger companions. This procedure would certainly additionally discuss an unique ridge at the equator of the moms and dad body, Didymos.
One more group of scientists led by Naomi Murdoch from the Université de Toulouse checked out rock tracks mapped throughout the surface area of Didymos. They located the surface area of Didymos is made up of extremely loosened product, efficient in sustaining a lot less weight than completely dry sand in the world or lunar dirt on the moon.
On The Other Hand, Alice Lucchetti, from the INAF-Astronomical Observatory of Padova additionally and associates located that rocks at the surface area of Dimorphos are being fractured over a duration of around 100,000 years by a procedure called “thermal exhaustion,” which arises from transforming temperature levels creating micro-fractures in the rock.
Though 100,000 years might appear like an unbelievably very long time to us, in geological terms, it is a brief duration, particularly in a planetary system that is around 4.6 billion years of ages. This indicates that the thermal exhaustion experienced by Dimorphos is quick. This is the very first time that quick thermal exhaustion has actually been seen on a rocky asteroid composed of silicate products and nickel-iron.
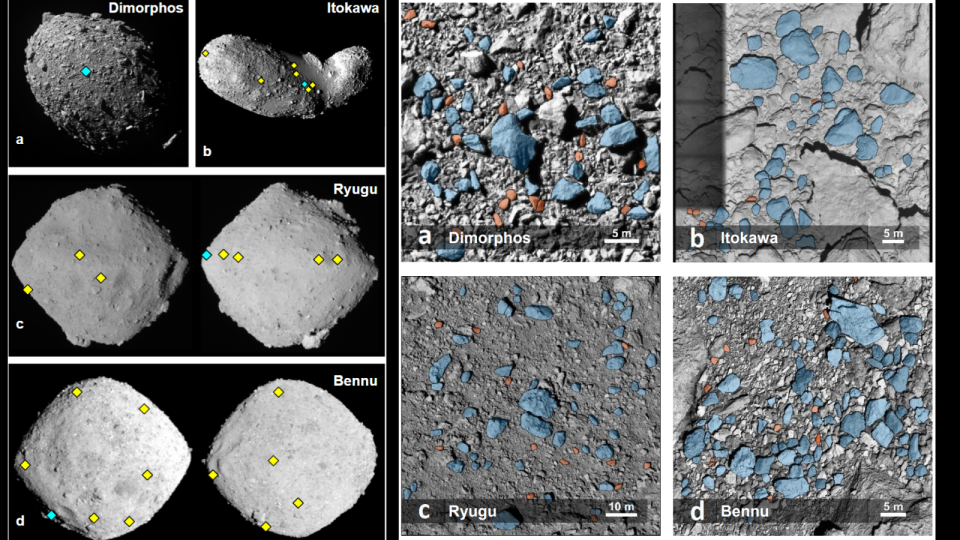

A 3rd group, led by Université de Toulouse scientist Colas Robin, contrasted 34 rocks externally of Dimorphos that varied from 5.5 feet (1.67 meters) to 22 feet (6.7 meters) to rocks located free “rubble-pile” planets Itokawa, Ryugu, and Bennu.
They located resemblances in between the morphology of the rocks of every one of these planets and recommended to Robin and associates a typical development and development device.
Associated tales:
— Asteroid impact: Here’s the last thing NASA’s DART spacecraft saw before it crashed
— DART asteroid crash seen by James Webb, Hubble space telescopes (photos)
— DART impact gave asteroid Dimorphos a debris tail thousands of miles long (stunning photo)
The groups’ outcomes develop a comprehensive photo of the Didymos system as it was prior to the effect of the DART on Dimorphos. The searchings for might assist educate the approaching Hera mission from the European Area Firm (ESA).
Ready to introduce in October this year, Hera will certainly satisfy Didymos and Dimorphos in September 2026. One at the Didymous double star, Hera, will certainly record higher-resolution information that permits a much more extensive evaluation of the system as it desires the DART effect. This need to assist researchers much better figure out the aftermath of DART’s collision with Dimorphos.
The 3 group’s research papers were published on Tuesday (July 30) in the journal Nature.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
