When you purchase via web links on our short articles, Future and its submission companions might gain a compensation.
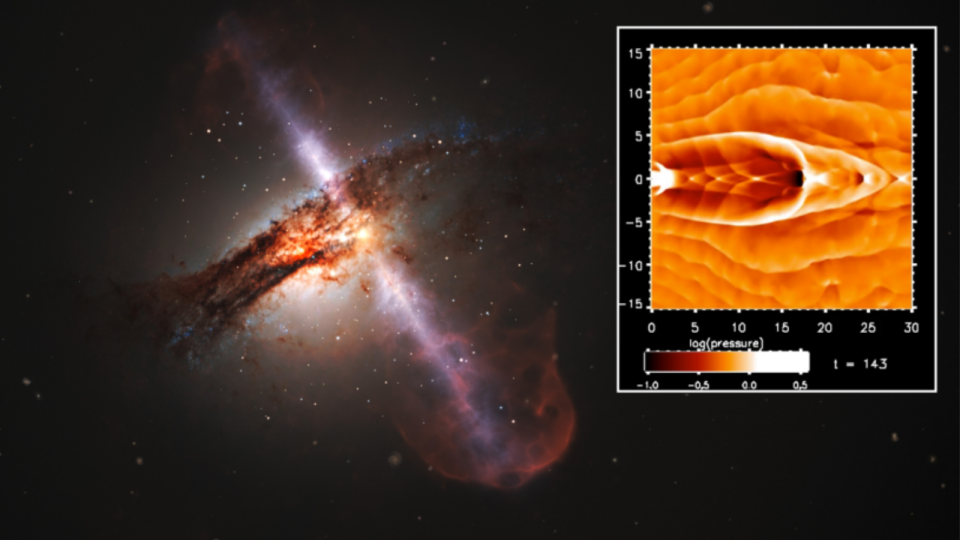

The lives of galaxies can be prolonged if their supermassive great voids that supply them with “hearts and lungs” to sustain their “breathing” and avoid them from expanding as well big.
That is the idea of brand-new study showing deep space would certainly have matured much faster and would certainly today be full of “zombie” galaxies including dead or passing away celebrities were it except the supermassive black holes believed to rest at the hearts of all big galaxies. The astrophysicists behind the searchings for contrast jets of gas and radiation that supermassive black holes strike from their posts to the air passages that feed our lungs.
The College of Kent staff assumes pulses from each great void “heart” trigger shock fronts that oscillate backward and forward throughout both jets. This resembles just how a component of our body called the thoracic diaphragm goes up and down inside our breast dental caries to pump up and decrease our lungs.
In galaxies, this respiratory-like activity transfers the power of the supermassive black hole-blown jets to the surrounding tool, like just how on a cool wintertime early morning you can breath out cozy air right into the chillier air. Stars type when interstellar gas clouds awesome and are enabled to condense. That implies this “breathing out” can slow down celebrity development, reducing galaxies’ development.
Connected: James Webb Area Telescope sees an old great void dancing with clashing galaxies
The group got to this final thought after examining simulations made to reproduce the influence supersonic supermassive black hole-blown jets may play in hindering galaxy growth. The simulations revealed that the supermassive great void heart can pulse, developing high stress in the jets– nearly like a human struggling with hypertension, or “high blood pressure.”
When this happened, the group saw the jets starting to imitate bellows, introducing soundwaves that splashed via bordering product of stellar gas and dirt.
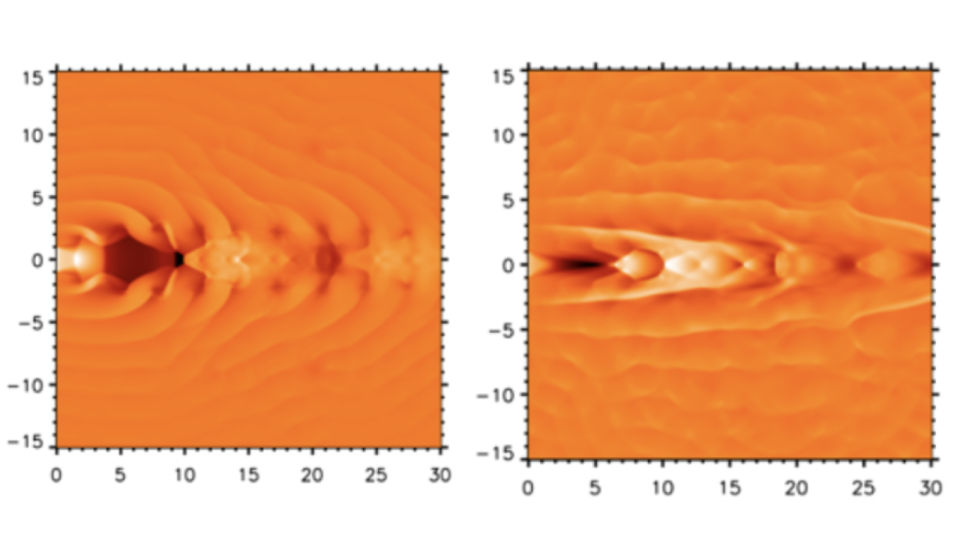

” We recognized that there would certainly need to be some methods for the jets to sustain the body– the galaxy’s bordering ambient gas– which is what we uncovered in our computer system simulations,” employee Carl Richards, a Ph.D. trainee at the College of Kent, said in a statement. “The unanticipated habits was exposed when we assessed the computer system simulations of high stress and enabled the heart to pulse.”
This sent out a stream of pulses right into the high-pressure jets, triggering them to alter form as an outcome of the bellows-like activity of the oscillating jet shock fronts. The scientist included that these jets increased “like air-filled lungs.” In doing so, they sent out surges of stress right into the stellar product around them, with this quiting the development of galaxies in the simulations.
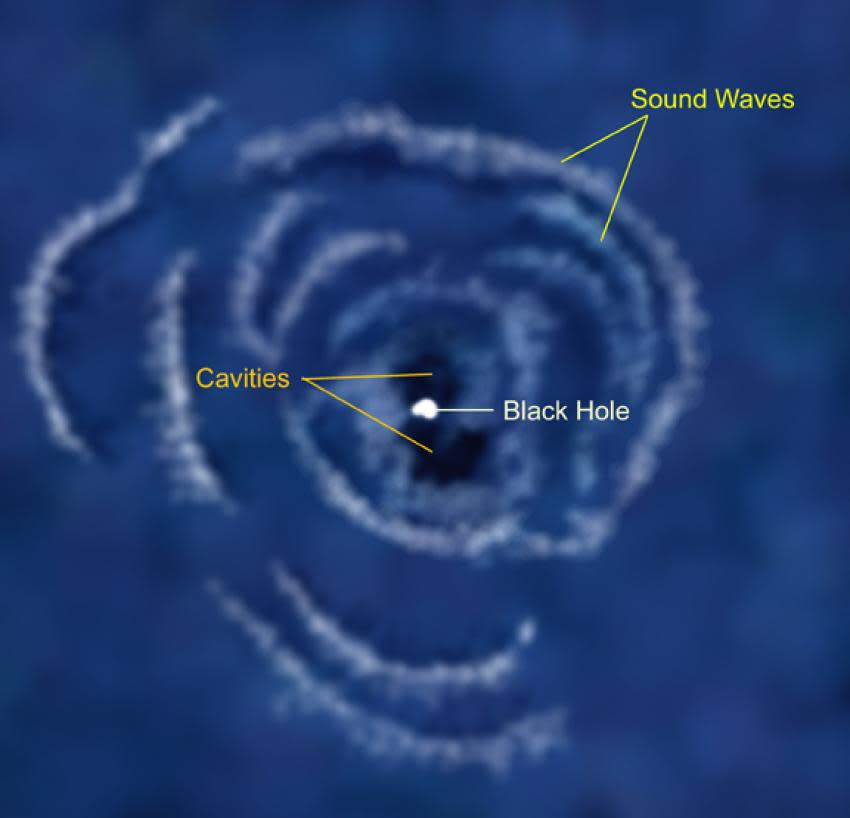


Far from the group’s simulations, there is a few other proof of this sensation in actual galaxies. For example, around 240 million light-years from Planet in the Perseus galaxy cluster, astronomers have actually seen proof of big gas bubbles in this collection of countless galaxies submersed in a huge cloud of multimillion-degree gas. These are thought to be the outcome of soundwaves splashing via the stellar tool in this collection.
The balance in between great void task and the circulation of gas right into galaxies is incredibly hard to attain– nonetheless, as supermassive great voids call for a stable supply of gas and dirt to develop jets.
” Breathing as well quickly or as well sluggish will certainly not supply the life-giving shakes required to keep the galaxy tool and, at the very same time, maintain the heart provided with gas,” employee and College of Kent scientist Michael Smith claimed in the declaration. “To do this is challenging, nonetheless, and we have restrictions on the kind of pulsation, the dimension of the great void, and the high quality of the lungs.”
RELEVANT TALES:
—The giant black hole of galaxy M87 shoots jets at nearly light speed
— Brightest quasar ever before seen is powered by great void that consumes a ‘sunlight a day’
— first great void ever before imaged by people has actually turned electromagnetic fields and researchers are delighted
The group ended that a galaxy’s life expectancy can be prolonged with the aid of its supermassive great void “heart” which great void’s jet “lungs” blowing from its core as they hinder development by restricting the amount of gas collapsing into stars from a beginning.
Without this system, several galaxies would certainly have tired their gas products required for celebrity development now in our 13.8-billion-year-old world. Consequently, they would certainly have “died,” with many galaxies appearing like supposed “red and dead” zombie galaxies now, full of old burnt celebrities.
The group’s study is released on July 12 in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
