Great voids are impressive huge things with gravity so strong that absolutely nothing, not also light, can leave them. One of the most big ones, called “supermassive” great voids, can consider millions to billions times the mass of the Sunlight.
These titansusually live in the centers of galaxies Our very own galaxy, the Galaxy, contains a supermassive black hole in its heart also.
So, just how do these supermassive great voids end up being very large? To address this inquiry, our team of astrophysicists recalled in time throughout deep space’s 13.8 billion-year background to track just how supermassive great voids have actually expanded from the very early days to today.
We built a version of the overall growth history of supermassive great voids covering the previous 12 billion years.
Exactly how do supermassive great voids expand?
Supermassive great voids expand largely in 2 methods. They can take in gas from their host galaxies in a process called accretion, and they can likewise merge with each other when 2 galaxies clash.
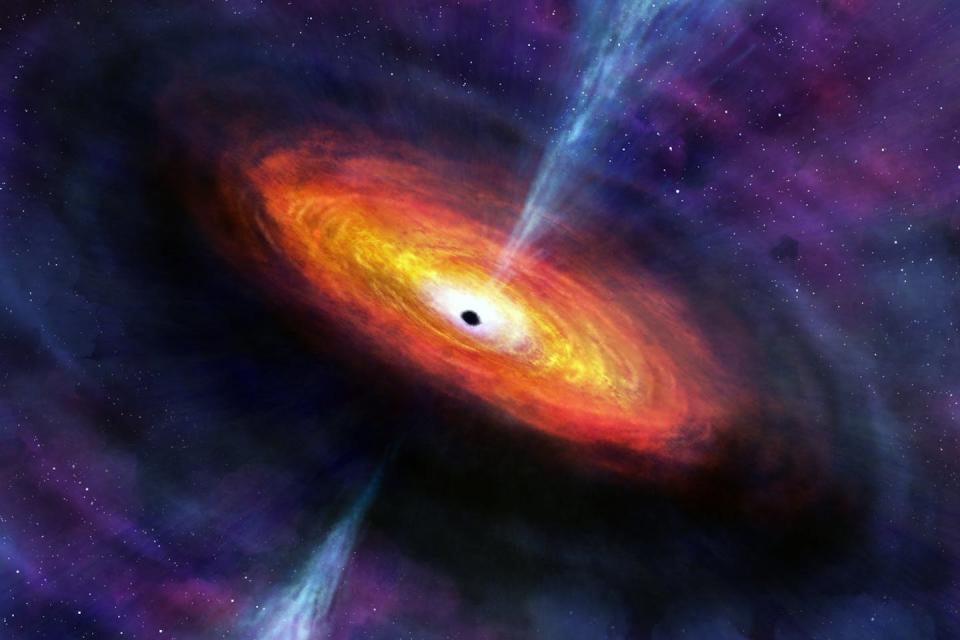


When supermassive great voids take in gas, they almost always emit strong X-rays, a kind of high-energy light unseen to the nude eye. You have actually possibly come across X-rays at the dental professional, where they are in some cases utilized to analyze your teeth. The X-rays used by astronomers typically have reduced powers than clinical X-rays.
So just how can any kind of light, also unseen X-rays, getaway from great voids? Purely talking, the light is not originating from the great voids themselves, yet from the gas simply outside them. When gas obtains drawn towards a great void, it warms up and radiates to create light, like X-rays. The even more gas a supermassive great void takes in, the even more X-rays it will certainly create.
Many thanks to the information collected over greater than two decades from 3 of one of the most effective X-ray centers ever before introduced right into room– Chandra, XMM-Newton and eROSITA— astronomers can record X-rays from a multitude of accreting supermassive great voids in deep space.
This information permits our research study group to approximate just how quick supermassive great voids expand by taking in gas. Typically, a supermassive great void can take in sufficient gas to total up to around the mass of the Sun yearly, with the precise worth relying on different elements.
For instance, the data shows that a great void’s development price, balanced over numerous years, is highly linked to the mass of all the celebrities in its host galaxy.
Exactly how usually do supermassive great voids combine?
Besides eating gas, supermassive great voids can likewise expand by combining with each various other to create a solitary, extra large great void when galaxies clash.
Supercomputer cosmological simulations can forecast concerning just how usually these occasions occur. These simulations intend to design just how deep space expands and advances with time. The numerous galaxies flying with room are sort of like blocks, developing deep space.
These simulations show that galaxies and the supermassive great voids they hold can go through several mergings throughout the period of planetary background.
Our group has actually tracked these 2 development networks– gas usage and mergings– making use of X-rays and supercomputer simulations, and after that integrated them to create this general development background, which maps the development of great voids throughout deep space over billions of years.
Our growth history revealed that supermassive great voids expanded a lot quicker billions of years earlier, when deep space was more youthful.
Back in the very early days, deep space included extra gas for supermassive great voids to take in, and supermassive great voids maintained arising. As deep space aged, the gas was slowly diminished, and supermassive great void development reduced. Regarding 8 billion years earlier, the variety of supermassive great voids maintained. It hasn’t enhanced significantly ever since.

When there isn’t sufficient gas readily available for supermassive great voids to expand by augmentation, the only means for them to obtain bigger is with mergings. We really did not see much situations of that in our development background. Typically, one of the most large great voids can collect mass from mergings at a price approximately the mass of the Sunlight every a number of years.
Looking ahead
This research study has actually assisted us recognize just how over 90% of the mass in great voids has actually collected over the previous 12 billion years.
Nonetheless, we still require to check out just how they expanded in the very early universe to clarify the continuing to be couple of portions of the mass in great voids. The huge area is beginning to make progression discovering these very early supermassive great voids, and we want to locate even more solutions quickly.
This write-up is republished from The Conversation, a not-for-profit, independent wire service bringing you truths and evaluation to aid you understand our intricate globe.
It was composed by: Fan Zou, Penn State and W. Niel Brandt, Penn State.
Learn More:
Follower Zou obtains financing from the united state National Scientific Research Structure, the Chandra X-ray Facility and Penn State.
W. Niel Brandt obtains financing from the united state National Scientific Research Structure, the Chandra X-ray Facility, and Penn State.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
