Register For CNN’s Marvel Concept scientific research e-newsletter. Explore the universe with news on fascinating discoveries, scientific advancements and more.
An item of woolly massive skin dug deep into from the Siberian ice has actually been located to have fossil chromosomes in a first-of-its-kind exploration, according to a brand-new research study.
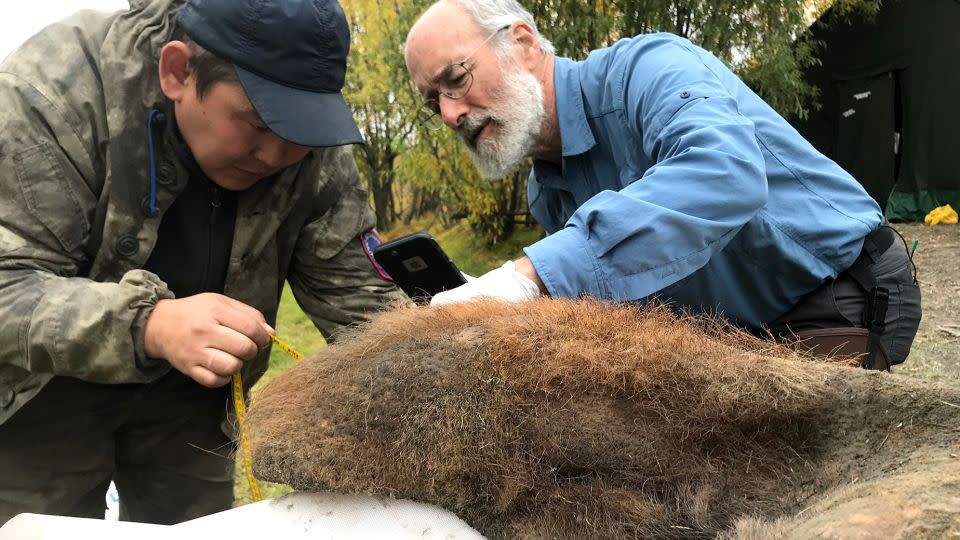
Scientist discovered the 52,000-year-old remains in 2018 near the town of Belaya Gora in northeastern Siberia, where freezing temperature levels assisted maintain the framework of the chromosomes– little threadlike frameworks that bring hereditary product, or DNA– in great information.
While old DNA examples have actually been located sometimes previously, they are usually very fragmented and have just thousands of letters of hereditary code. The fossil chromosomes have millions, using a much more full image of a pet’s hereditary code.
” Fossil chromosomes have actually never ever been located prior to,” stated Erez Lieberman Aiden, a teacher of molecular and human genes at the Baylor University of Medication and co-corresponding writer of the study released Thursday in the journal Cell.
In prior searchings for, the pieces were additionally doing not have an arranged framework, Lieberman Aiden included. “Below, the pieces are plainly set up in 3D– basically as they remained in the initial chromosomes in the living massive.”
The chromosomes, which the scientists mention are “non-mineralized fossils, or subfossils,” remain in a state of conservation sufficient to set up the genome, or the amount of all the hereditary product, of a vanished varieties, according to Olga Dudchenko, an assistant teacher of molecular and human genes at Baylor University of Medication and co-first writer of the research study.
” We highly think that this is not mosting likely to relate to simply the massive or this specific massive,” stated Dudchenko, that is additionally an elderly detective at the Facility for Theoretical Biological Physics at Rice College, “however is primarily opening a brand-new area that has remarkable possibility.”

DNA diffusion
DNA within various cell kinds is set out in unique and particular 3D frameworks that provide understanding right into the specific residential properties or attributes of that cell kind, stated Kevin Campbell, a teacher of ecological and transformative physiology at the College of Manitoba in Canada, that was not associated with the research study.
Upon fatality, body cells rapidly break down, and this 3D framework is shed within a couple of days or much less, he included. In Arctic pets such as the woolly massive, the deterioration is slower because of freezing temperature levels, however the DNA still ends up being broken, and over extended periods it is anticipated to shed the framework and the features that comprise the varieties’ biology.
” Nonetheless, this research study is the very first to show that this is not necessarily constantly the situation,” Campbell stated in an e-mail.
” DNA is a really, long particle, and when it rests there after a pet passes away, it begins to break down and obtains cut right into much shorter items,” Dudchenko stated.
” What you generally anticipate is that every one of these items will certainly begin moving about each various other and simply type of float away, shedding any kind of company that existed,” Dudchenko stated. “Yet plainly, in this specific example, that really did not occur.”
This loss of framework is called diffusion, and exactly how to avoid it is widely known to food researchers– and not different from the production of beef jerky, she included.


” Detaining diffusion is essential to maintaining foods, so if you intend to have something that is rack secure for a very long time, you primarily require a mix of dehydration and air conditioning,” she stated. “Any type of rack secure food that’s not tinned is most likely in a state of apprehension of diffusion.”
When the massive the skin example originated from passed away, problems could have been perfect to kick-start this procedure normally. “( The carcass) can have automatically gone through the exact same treatment that today we utilize readily at all times,” Dudchenko stated, “getting rid of significant quantities of water, apprehending diffusion inside and securing those items of chromosomes in position, permitting us to review them off 52,000 years after the truth.”
Yet although it was well protected, the DNA was not totally undamaged. “Each chromosome, initially one DNA particle, has actually fragmentized right into numerous DNA particles,” Aiden stated in an e-mail. “Yet the particles have actually or else stagnated extremely a lot, also at the nanometer range, which is why we call it a fossil chromosome.”
If this example were a publication, Lieberman Aiden stated, the binding would certainly be gone, leaving a multitude of unbound web pages, or DNA pieces. Diffusion resembles the wind blowing the web pages away, making it difficult to place them back in order. Yet in this example, the web pages never ever obtained surprised; they stayed in a cool stack, equally as they were prior to the binding was shed.
Capturing beef jerky
The scientists validated this concept of conservation by running some experiments on beef jerky to see exactly how severely they can abuse the meat treat prior to the chromosomes inside it shed their framework.
” We made a decision to check exactly how much this lovely particle can withstand tension and injury by having among the bottles from the Houston Astros toss a heater at it and shooting a shotgun at it,” stated Dr. Cynthia Pérez Estrada, co-first writer of the research study and a scientist at the Facility for Genome Design at Baylor and at Rice’s Facility for Theoretical Biological Physics.
” The beef jerky was damaging increasingly more, however the DNA framework was still there, informing us that DNA is very immune and much more so in this sort of glass-like state (like in the example), where the particles are primarily icy and acting like a crystal,” Pérez Estrada included.
With the freshly found hereditary info located in the skin examples, the scientists had the ability to identify for the very first time that the woolly massive had 28 sets of chromosomes, similar to modern-day elephants.
Yet the framework enabled them to go one action even more and see which private genetics were energetic in the pet. “Everyone needs to know exactly what made it woolly,” Dudchenko stated, “and we have some concepts many thanks to the manner in which these chromosomes were protected.”
Massive desires
The scientists had the ability to contrast private genetics from the massive example with the comparable ones in modern-day elephants, keeping in mind distinctions in the task of genetics that control hair roots. Yet the DNA from elephants was additionally required to set up the massive genome.
” Our desire and hope was to set up the massive genome totally, however today, this is not rather where we are– we still made use of some info from its closest about assist, due to the fact that the quantity of information that we had the ability to receive from the massive was less than what you usually require,” Dudchenko stated. “Yet the principles inform us that, as we proceed functioning in the direction of this, we will certainly have the ability to do it (without the assistance of elephant DNA).”
Could fossil chromosomes make the imagine resurrecting the woolly massive a fact? “The basic biology that we pick up from this is mosting likely to serve, there is no doubt concerning it,” Dudchenko stated. “Are we more detailed? One action more detailed, however there’s still many actions in advance and all kind of various other factors to consider that are past basic scientific research.”
The scientists additionally really hope that the exact same approach made use of on the massive example can be related to examples from various other varieties.


” We’re intending to locate chromosome frameworks in gallery samplings,” stated Marcela Sandoval-Velasco, a visitor scientist at the Facility for Evolutionary Hologenomics of the College of Copenhagen in Denmark and co-first writer of the research study. “Not just permafrost samplings, since that tightens it a whole lot, however additionally examples from gallery collections. There’s a massive possibility there,” she included, pointing out the woolly rhinocerous, vanished lions and the traveler pigeon as several of the vanished varieties that researchers could discover even more concerning by doing this.
That prospective unlocks to more explorations, according to Pérez Estrada.
” It will certainly take a tremendous initiative to locate ideal examples, so there will certainly be a great deal of job in advance– however I would not be shocked if we after that found something brand-new and totally various from what we have today,” she stated. “That is additionally an actually amazing open inquiry: What else and what various other physical features (of DNA) can be protected?”
Interesting searchings for
Scientists that were not entailed with the research study revealed interest concerning the searchings for.
This research study is the very first to rebuild the framework, or design, of a genome from a vanished varieties that lived throughout the last glacial period, stated Peter Heintzman, a paleogeneticist at Stockholm College in Sweden. “This architectural info offers understandings right into features of the woolly massive genome that were unseen utilizing previous genomic techniques,” Heintzman stated in an e-mail. “This breakthrough consequently assists to open a brand-new and amazing frontier in paleogenomics, the research study of old genomes, and will likely supply more understanding right into exactly how vanished varieties progressed, lived, and passed away out.”
As a result of exactly how significantly broken down and fragmented DNA from old examples generally is, it was unusual to see the top quality, chromosome-level restoration of the massive genome reported by this research study, stated Dmitry Filatov, a teacher of biology at the College of Oxford in the UK.
” It is much more unusual that the scientists took care of to presume which genetics were energetic and which were turned off in the massive example and contrast this with genetics expression in elephants,” Filatov stated in an e-mail. “This will definitely boost more paleo-genomic study in various other varieties.”
Hendrik Poinar, supervisor of the Old DNA Centre at McMaster College in Ontario, called the paper “incredibly amazing.” Usually with fossil stays scientists can not do anything from another location near to setting up a genome, Poinar stated.
” I do not recognize the number of cells examples will certainly have this degree of conservation,” he included an e-mail, “however I do assume the approach will certainly make us think of unique methods to obtain DNA out of cells in methods apart from what we are made use of to.”
For even more CNN information and e-newsletters produce an account at CNN.com
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
