Making Use Of the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST), astronomers have actually observed the significant “dancing” in between a supermassive great void and 2 satellite galaxies. The monitorings might aid researchers much better comprehend exactly how galaxies and supermassive great voids expanded in the very early cosmos.
This specific supermassive black hole is eating bordering issue and powering an intense quasar that is so far-off that JWST sees it as it was much less than a billion years after theBig Bang The quasar, assigned PJ308-21, is local to an active galactic nucleus (AGN) in a galaxy that remains in the procedure of combining with 2 enormoussatellite galaxies
Not just did the group figure out that the black hole has a mass matching to 2 billion sunlight, however they additionally discovered that both the quasar and the galaxies associated with this merging are extremely progressed, a shock considering they existed when the 13.8-year-old universes was simply a baby.
The merging of these 3 galaxies is most likely to provide to the supermassive great void substantial quantities of gas and dirt, which will certainly promote its development and enable it to maintain powering PJ308-21.
Connected: James Webb Area Telescope locates ‘incredibly red’ supermassive great void expanding in the very early cosmos
” Our research study exposes that both the great voids at the facility of high-redshift [early and distant] quasars and the galaxies that hold them undertake incredibly reliable and troubled development currently in the initial billion years of planetary background, helped by the abundant stellar setting in which these resources are developed,” group leader Roberto Decarli, a scientist at Italy’s National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), said in a statement.
The information was gathered in September 2022 by JWST‘s Near InfraRed Spectrograph (NIRSpec) tool as component of the 1554 Program, which intends to observe the merging in between the galaxy organizing PJ308-21 and 2 of its satellite galaxies.
Decarli included that the job stood for an actual “psychological rollercoaster” for the group, which created ingenious services to get over the first troubles in information decrease and generate pictures with an unpredictability of much less than 1% per pixel.
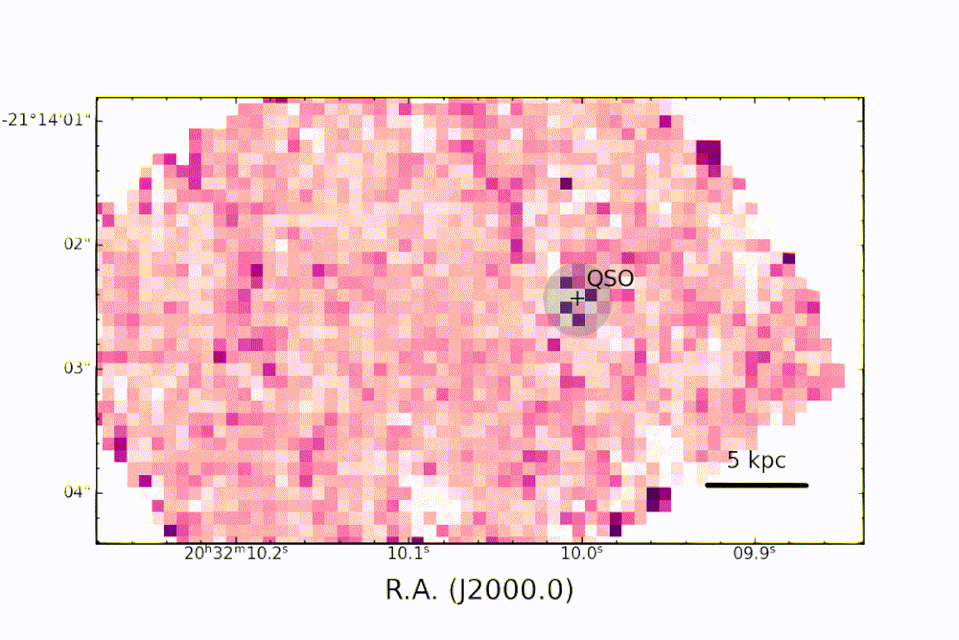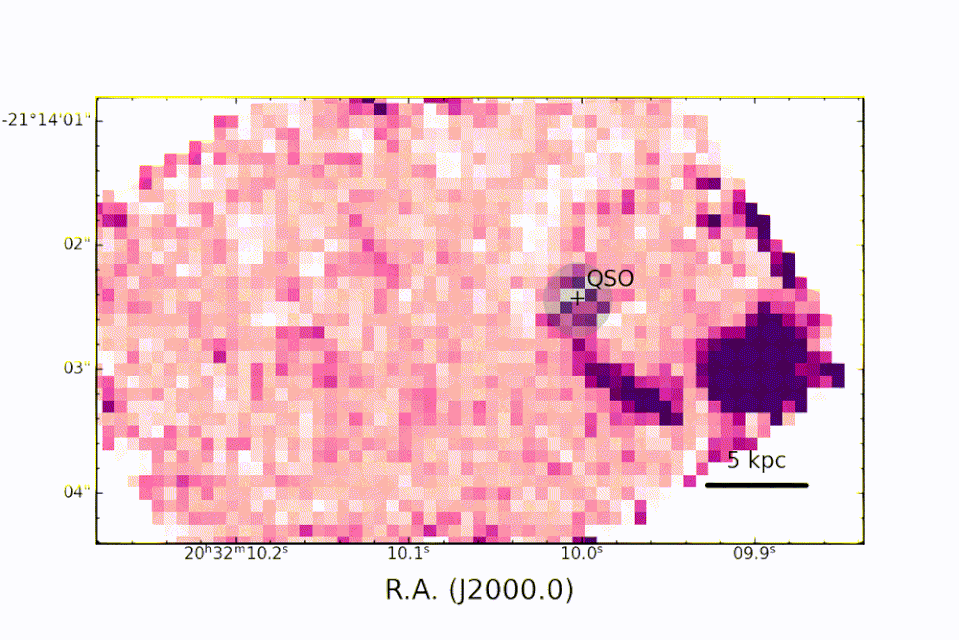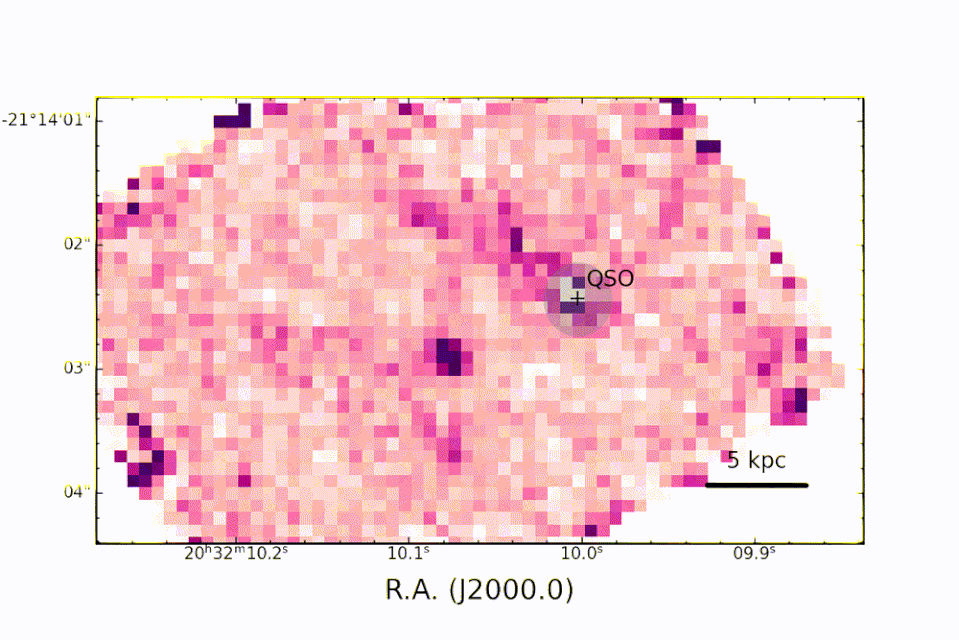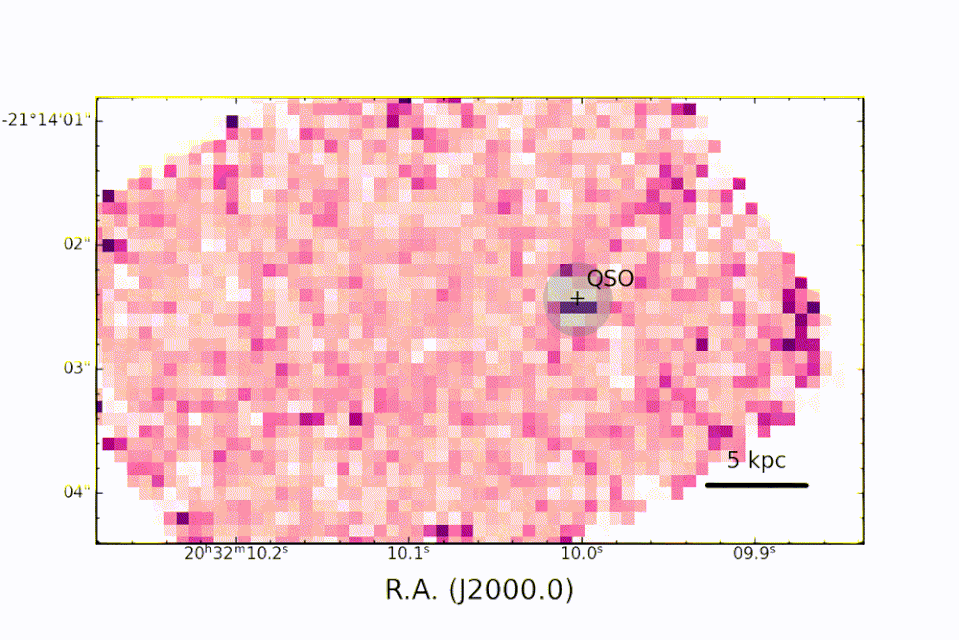

A really metal quasar
Quasars are birthed when supermassive great voids with masses millions or billions of times that of the sunlight that rest at the heart of galaxies are bordered by a wide range of gas and dirt. This issue develops a squashed cloud called an accretion disk that swirls around the great void and progressively feeds it.
The tremendous gravitational forces of the great void produce effective tidal forces in this accumulation disk, which warm this gas and dirt temperature levels as excellent as 120,000 levels Fahrenheit (67,000 levels Celsius). This triggers the accumulation disk to release light throughout theelectromagnetic spectrum This exhaust can usually be brighter than the consolidated light of every celebrity in the bordering galaxy, making quasars like PJ308-21 a few of the brightest items in the universes.
While great voids do not have features that can be made use of to figure out exactly how progressed they are, their accumulation disks (and hence quasars) do. As a matter of fact, galaxies can be “aged” similarly.


The very early cosmos was loaded with hydrogen, the lightest and easiest aspect, and a little helium. This developed the basis of the initial celebrities and galaxies, however throughout the life of these outstanding bodies, they created components larger than hydrogen and helium, which astronomers phone call “steels.”
When these celebrities finished their lives in enormous supernova surges, these steels were spread throughout their galaxies and took place to be the foundation of the future generation of celebrities. This procedure saw celebrities, and with them galaxies, coming to be gradually “steel abundant.”
The group discovered that, like a lot of AGNs, the energetic heart of PJ308-21 is metal-rich, and the gas and dirt around it are being “photoionized.” This is the procedure whereby fragments of light, called photons, offer the power that electrons requirement to leave atoms, developing electrically billed ions.
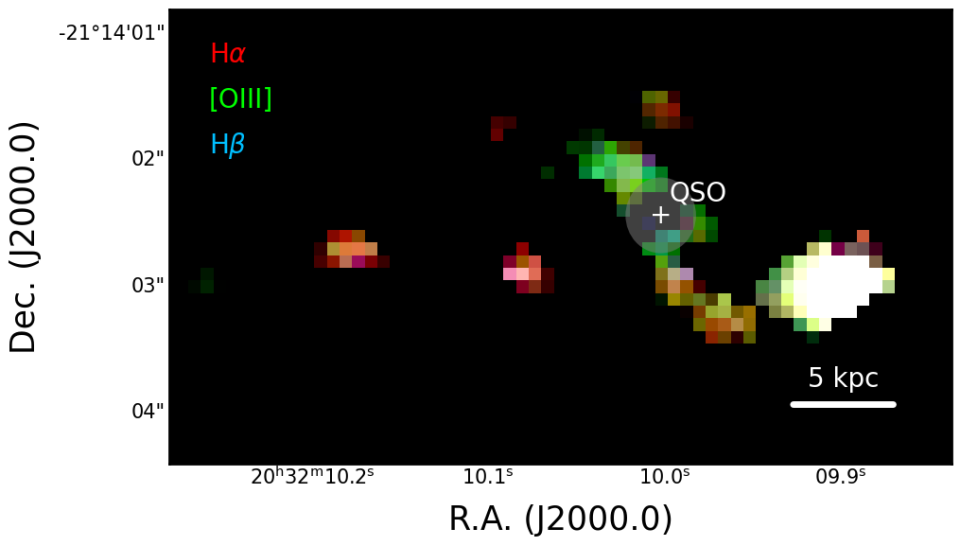

Among the galaxies that’s combining with the host galaxy PJ308-21 is additionally metal-rich, and its issue is additionally being partly photoionized by electro-magnetic radiation from the quasar.
Photoionization is additionally occurring in the 2nd satellite galaxy, however because instance, it is being triggered by a round ofrapid star formation This 2nd galaxy additionally varies from the initial and the AGN, as it seems metal-poor.
” Many Thanks to NIRSpec, for the very first time, we can research, in the PJ308-21 system, the optical band abundant in priceless analysis information on the residential or commercial properties of the gas near the great void in the galaxy organizing the quasar and in the bordering galaxies,” claimed employee and INAF astrophysicist Federica Loiacono. “We can see, as an example, the exhaust of hydrogen atoms and contrast it keeping that of the chemical components created by the celebrities to develop exactly how abundant the gas remains in steels.”
ASSOCIATED TALES:
—The giant black hole of galaxy M87 shoots jets at nearly light speed
— Brightest quasar ever before seen is powered by great void that consumes a ‘sunlight a day’
— first great void ever before imaged by human beings has actually turned electromagnetic fields and researchers are delighted
Though light fallen leaves this early-universe quasar throughout the wide variety of the electro-magnetic range, consisting of optical light and X-rays, the only means to observe it remains in infrared.
That’s because, as the light has actually taken a trip for over 12 billion years to get to JWST, the growth of deep space has actually “extended” its wavelengths significantly. That “changes” the light towards the “red end” of the electro-magnetic range, a sensation naturally called “redshift,” which is represented as “z” by astronomers.
JWST is skilled at seeing “high red-shift” or “high-z” items and occasions like PJ308-21 as a result of its level of sensitivity to infrared light.
” Many thanks to the level of sensitivity of the JWST in the close to and mid-infrared, it was feasible to research the range of the quasar and friend galaxies with unmatched accuracy in the distant universe,” Loiacono ended. “Just the superb ‘sight’ used by JWST has the ability to make certain these monitorings.”
The group’s research study was approved for magazine in June 2024 in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
