New pictures released by the European Space Agency have actually caught a 600-kilometer-long (373-mile-long) snaking mark on Mars’ surface area in higher information than in the past. The Red Earth contains scrapes and marks, and this set, called Aganippe Fossa, is one more of these ditch-like grooves with high wall surfaces– even more especially, nevertheless, Aganippe Fossa is what’s called a “graben.”
” We’re still unclear of exactly how and when Aganippe Fossa happened, yet it promises that it was created as lava increasing below the gigantic mass of the Tharsis volcanoes created Mars’s crust to stretch and split,” ESA authorities composed in a recent press release.
As prevails in worldly classification, the name “Aganippe Fossa” has its origins in timeless folklore. Aganippe, child of the river Termessos, was a fairy connected with a springtime discovered at the base of Mount Helicon in Greece. In tribute to its calling beginnings, Aganippe Fossa shows up at the base of among Mars’ biggest volcanoes,Arsia Mons “Fossa” is after that originated from the Latin term for ditch or trench, and describes a long, slim anxiety externally of an earth or moon.
The just recently released pictures owe themselves to ESA’s Mars Express, Europe’s initial goal to the Red Earth, which has actually been orbiting Mars considering that 2003. Although its lander, Beagle 2, was shed, the orbiter continues to be performing an international examination ofMars It maps minerals, research studies the environment, probes underneath the crust and checks out the earth’s blob-shaped moons, Phobos and Deimos.
Associated: Largest canyon in the solar system revealed in stunning new images
Mars Express caught the brand-new pictures of Aganippe Fossa with its high resolution stereo video camera and disclosed the diverse surface area attributes of Mars in terrific information, revealing both gathered, unequal hillsides and smooth, delicately sloping high cliffs covered in particles– described as hummocky and lobate surfaces, specifically.
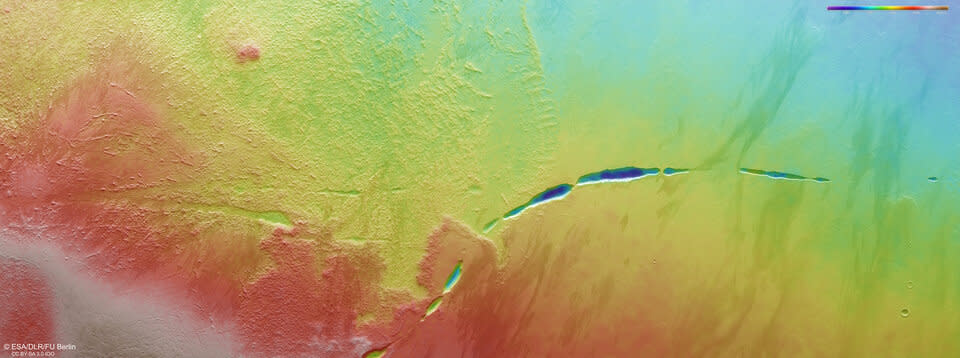

These surfaces are particular of Arsia Mons’s ring-shaped “aureole,” the ESA news release states, of a 100,000-square-kilometer (38,610-square-mile) disk around the base of the volcano, perhaps connected with old glaciers. “Intriguingly,” the declaration proceeds, “this aureole has actually just developed on the northwestern flank of the volcano, likely as a result of dominating winds from the contrary instructions regulating where ice worked out over time.”
The group additionally explains windblown dirt and sand characteristics of this area of Mars, which produce “zebra-like” patterns on earth’s surface area as an outcome of darker product obtaining transferred on lighter ground. “The surface area right here additionally reveals proof of lava circulations, dating from when the volcano was energetic.” the researchers composed.
Associated Stories:
—Mars may still be volcanically active, study finds
—Ancient Mars was rocked by violent, climate-changing volcanic eruptions
—Mars images shows ‘fingernail’ gouging-like features on surface
Aganippe Fossa is among numerous timeless albedo attributes on Mars, which describes the light and dark attributes that can be seen on earth via also an Earth– based telescope. With space– based orbiters, astronomers have actually been provided extraordinary sights of the earth’s surface area and its appealing topography.
” The goal has actually been exceptionally effective over its life time, developing a much fuller and a lot more exact understanding of our worldly next-door neighbor than in the past,” ESA researchers stated.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
