Register For CNN’s Marvel Concept scientific research e-newsletter. Explore the universe with news on fascinating discoveries, scientific advancements and more
A fossilized ear bone discovered in a collapse Spain has actually exposed a Caveman youngster that coped with Down disorder up until the age of 6, according to a brand-new research.
The locate recommended that participants of the neighborhood looked after and cared for the prone youngster, that lived at the very least 146,000 years back. The study is at chances with the photo of Neanderthals, old human loved ones that went vanished around 40,000 years back, as brutish neanderthals.
” The person would certainly require constant and extensive treatment,” claimed paleoanthropologist Mercedes Conde-Valverde, the lead writer of a study on the bone that showed up Wednesday in the journal Scientific research Breakthroughs.
The youngster “dealt with serious loss (of) hearing and had significant equilibrium problems and episodes of vertigo,” clarified Conde-Valverde, that is an assistant teacher of physical sociology at the College of Alcalá in Spain.
Muscular tissue weak point would certainly have likewise made breastfeeding and motion tough, she included.
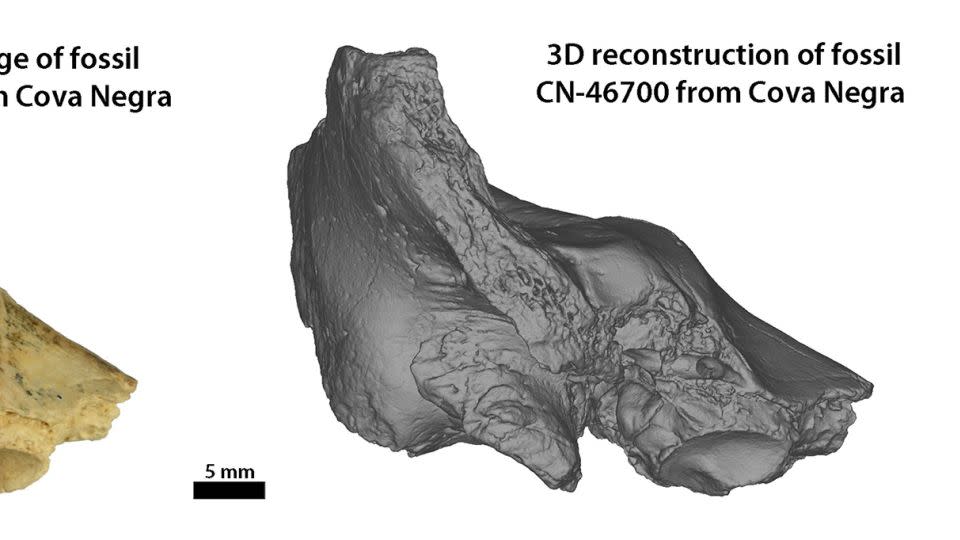
The little fossil was dug deep into in 1989 from the Cova Negra historical site in Spain’s Valencia district. Nevertheless, excavators just just recently uncovered the sampling when they brushed with faunal pieces collected at the website throughout a testimonial of the product.
” We have actually had the ability to determine it as a Caveman because of the strange percentages of its semicircular canals, which are particular of Neanderthals,” Conde-Valverde claimed, describing the internal tubes of the ear.
The research did not consist of accurate dating of the bone, which would certainly need removal of old DNA, yet Neanderthals inhabited the website 146,000 to 273,000 years back. The study group has actually not identified the sex of the young Caveman.
A shocking life-span
Individuals with Down disorder can lead a lengthy life today, yet it was unexpected the youngster lived past the age of 6, Conde-Valverde claimed.
Life in the Rock Age would certainly have been requiring. The research kept in mind that Neanderthals were extremely mobile, routinely relocating from area to area. The treatment needed for the youngster to endure for a prolonged time period most likely entailed the mom’s dependence on the participation and assistance of various other participants of the team.
Also in the current the past, it prevailed for individuals with Down disorder to pass away in youth. According to the research, life span in 1929 for youngsters with Down disorder, a problem brought on by an added partial or complete chromosome, was 9 years. By the 1940s, the anticipated life-span had actually boosted to 12 years.
Today, regarding 1 in 772 children in the USA are birthed with Down disorder, and life span currently surpasses 60 years, according to the National Down Syndrome Society in the USA.
The earliest recognized instance of Down disorder in Humankind, our very own varieties, go back at the very least 5,300 years. Making use of old DNA, the writers of a study published in February determined 6 instances in primitive populaces. None of the youngsters lived longer than 16 months.
Down disorder has actually likewise been recorded in primates. A January 2016 study highlighted the case of a chimp with Down disorder that endured to 23 months many thanks to the treatment obtained by the mom, with support from the oldest little girl.
Nevertheless, when the little girl quit assisting to take care of her very own spawn, the mom was incapable to offer the needed treatment, and the spawn passed away, the research claimed.

Problems in the internal ear
Conde-Valverde and her coworkers think the bone came from a kid with Down disorder as a result of a collection of problems in the internal ear framework.
These consist of an unusual form of the side semicircular canal (the quickest ear canal); a bigger vestibular aqueduct, a slim, bony canal that goes from the internal ear to deep inside the head, and a decrease of the total dimension of the cochlea bone chamber.
” A few of these pathologies typically show up in numerous disorders, yet the mix existing in the Cova Negra fossil has actually just been defined in modern individuals with Down disorder,” she claimed.
Conclusive evidence that the youngster had Down disorder would certainly need the healing of old DNA from the fossil, yet that had not yet been feasible, she claimed.
Previous researches of historical finds have actually recommended that Neanderthals looked after prone participants of their team.
One Neanderthal man buried in Shanidar Cave in what’s currently Iraq was deaf and had a paralyzed arm and head injury that possibly provided him partly blind, yet he lived a long period of time, according to October 2017 study.
A Caveman skeletal system called the “Old Male of La Chapelle” discovered in current-day main France had degenerative joint inflammation and may have been fed by other members of his team, a February 2019 research located.
A youngster cared for ‘like any kind of various other’
Conde-Valverde claimed that the exploration of the Cova Negra fossil sustained the presence of real selflessness amongst Neanderthals.
” For years, it has actually been recognized that Neanderthals looked after and cared for their prone buddies,” Conde-Valverde claimed.
” Nevertheless, all recognized instances of treatment entailed grown-up people, leading some researchers to think that this actions was not authentic selflessness yet just an exchange helpful in between equates to,” she claimed.
” What was not recognized previously was an instance of a person that had actually obtained extra-maternal treatment from birth, despite the fact that it might not reciprocate.”
The majority of moms and dads today do not watch child care as an “assumption of reciprocity,” and it was not likely to be the instance amongst Neanderthals, claimed Cent Spikins, a teacher of archaeology at the College of York in the UK and writer of “Hidden Midst: The Beginnings of Human Link.”
Human beings most likely progressed an instinctive and psychological feedback to look after babies to guarantee they endured, claimed Spikins, that had not been associated with the study.
” This locate earns exactly how like us Neanderthals remained in numerous means, specifically in our typical human need to look after the prone,” she claimed.
” We can envision that this youngster was enjoyed and cared for like any kind of various other.”
For even more CNN information and e-newsletters develop an account at CNN.com
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
