AMD’s Radeon RX 7000-series and the RDNA 3 design released in late 2022, beginning with theRX 7900 XTX and RX 7900 XT Ove the following year and a fifty percent, various various other cards have actually signed up with the collection, powering several of the most effective graphics cards. You can see exactly how the GPUs rate versus various other generations and rivals in our GPU standards pecking order, and we’re currently eagerly anticipating the future RDNA 4 GPUs.
However allow’s not prosper of ourselves. AMD’s complete schedule of RDNA 3 cards includes 7 various designs. We have actually evaluated and evaluated them all, from the fastest RX 7900 XTX to the lowly RX 7600 and whatever in between. Allow’s reach the information.
AMD RDNA 3/ Navi 3x at a Look
-
As Much As 96 CUs/ 12,288 shaders
-
50% far better efficiency per watt than RDNA 2
-
Double the ALU matter per CU
-
GPU chiplet design
-
As Much As 96MB of Infinity Cache
AMD RX 7000-series requirements
With all the AMD RDNA 3 GPUs currently released and readily available globally, below are the core requirements.
The previous generation RDNA 2 and RX 6000-series GPUs had 4 GPU layouts expanded throughout a complete loads various graphics card designs– which’s not counting incorporated graphics remedies. AMD RDNA 3 trims points down rather, with 3 main GPUs and 7 various graphics card designs (plus some incorporated variations).
The 3 GPU layouts are called Navi 31, Navi 32, and Navi 33, going from greatest efficiency to cheapest efficiency. The biggest die has 3 various designs, while the various other 2 just have 2 designs. However there are some substantial distinctions in exactly how AMD arrives.
AMD RDNA 3 makes use of GPU chiplets for the very first time, a minimum of on the leading 2 arrangements. Navi 31 and 32 each have a huge GCD (Video Compute Pass Away), with anywhere from 3 to 6 MCD (Memory Cache Pass away) chiplets. The tiniest die, Navi 33, maintains the standard monolithic die.
Each MCD supplies a 64-bit memory user interface and 16MB of L3 cache. The MCDs connect to the primary GCD using AMD’s Infinity Textile, utilizing what AMD calls the Infinity Fanout Bridge. It makes use of much less power per little bit than various other outside user interfaces, though there’s absolutely a power charge about monolithic layouts. Basically, AMD conserved cash on the expenses of making the MCDs on a previous generation procedure node, which subsequently diminishes the dimension of the GCD.
While future layouts might gain from separating the GPU pass away right into numerous chiplets, for this initial generation of GPU chiplets it’s generally a cost-saving procedure. The Navi 33 pass away on the other hand still makes use of N6, an improvement of the N7 node made use of with RDNA 2, since it’s little sufficient it had not been worth the initiative of damaging it right into a GCD plus 2 MCDs.
Clock rates have not altered a lot from RDNA 2, though AMD has a 2 various clock domain names this moment– one for the shaders and one for the front-end. AMD’s specified clock rates are rather traditional this round, indicating you’ll typically see greater appear the majority of video games. However there are video games where you might not strike the increase clock, which is what we have actually detailed– AMD additionally has a “Video game Clock” that’s a lot more traditional, however in technique it’s not as significant.
The CUs and shader cores have actually obtained a large upgrade this generation, however strangely enough AMD does not straight call each of the possible ALU cpus a shader. Rather, it provides a base worth that’s fifty percent of the reliable price. So as an instance, the 6,144 GPU sahders in the RX 7900 XTX can sometimes act even more like 12,288 shaders. That’s where the a lot greater calculate originates from, greater than increasing what was readily available with RDNA 2.
The leading version has 61.4 teraflops of calculate, and dual that for FP16 work. Also the mid-tier 7800 XT has 37.3 teraflops of calculate, which nearly increases what the RX 6800 XT supplied. Nonetheless, real pc gaming efficiency does not range straight symmetrical to the academic calculate. So, as an instance, the RX 7800 XT winds up carrying out rather in a similar way to the RX 6900 XT.
Memory transmission capacity on the 7900 XTX raised by over 50% about the RX 6950 XT. That’s many thanks to the transfer to a 50% bigger user interface, plus running the GDDR6 memory at 20 Gbps (versus 18 Gbps on the 6950). Efficient memory transmission capacity additionally boosts many thanks to the 2nd generation Infinity Cache, which for the majority of designs lowered in dimension contrasted to RDNA 2. However that’s primarily countered by greater throughput and various other tweaks to the caching pecking order.
AMD Radeon 7000 Efficiency


As we saw with the previous 2 generations of AMD equipment, AMD targeted a minimum of a 50% renovation in efficiency per watt with RDNA 3. While that may appear sensibly certain, it leaves lots of shake area. For instance, RDNA 2 supplied 50% far better efficiency per watt than RDNA. Allow’s provide some concrete instances of exactly how that played out.
According to our GPU standards pecking order, the RX 6900 XT takes in 308W of power while supplying 130 fps at 1080p ultra, 106 fps at 1440p ultra, and 63 fps at 4K ultra. A lower-tier RX 6700 XT makes use of 215W and standards 96 fps, 71 fps, and 39 fps, while the RX 5700 XT takes in 214W while supplying 74 fps, 53 fps, and 29 fps at those very same resolutions.
Do the mathematics, and the 6900 XT offers a 22% to 50% renovation in efficiency per watt, while the 6700 XT just offers a 29% to 34% renovation. If we include all the various other RDNA and RDNA 2 GPUs as recommendation factors, the possible spread for performance-per-watt renovations comes to be also bigger.
AMD has actually additionally gone over some building renovations. The ray mapping equipment boosted, however not as high as we would certainly have suched as. The largest adjustment architecturally was the transfer to double CUs with dual the implementation sources. AMD additionally included AI Accelerators that enhance the throughput of FP16 and INT8 estimations– these share sources with the shader implementation cores however maximize the information circulation.
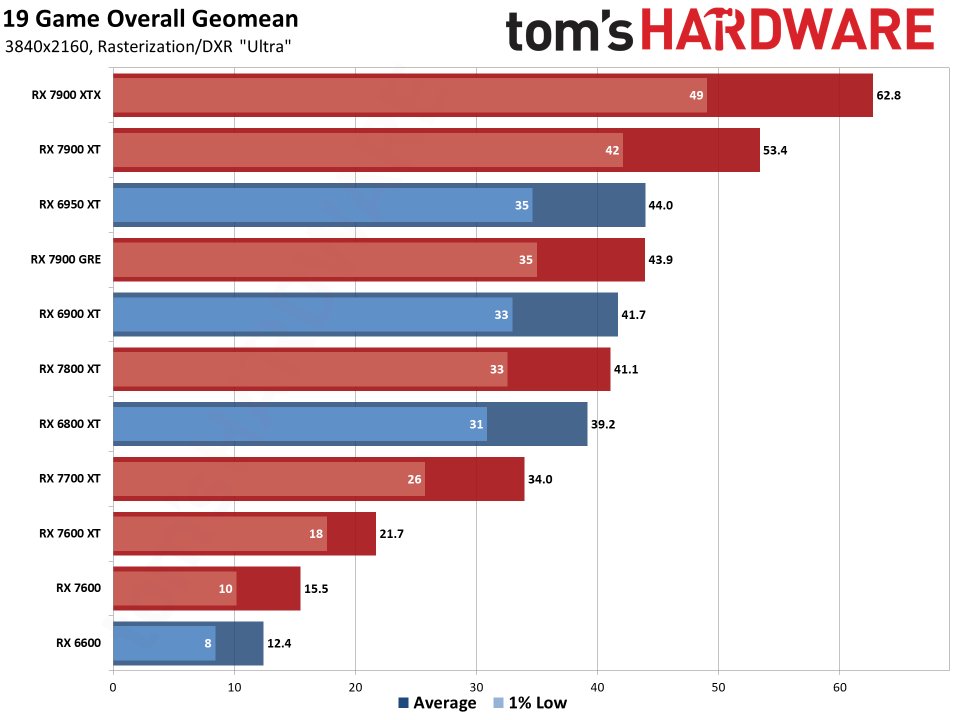

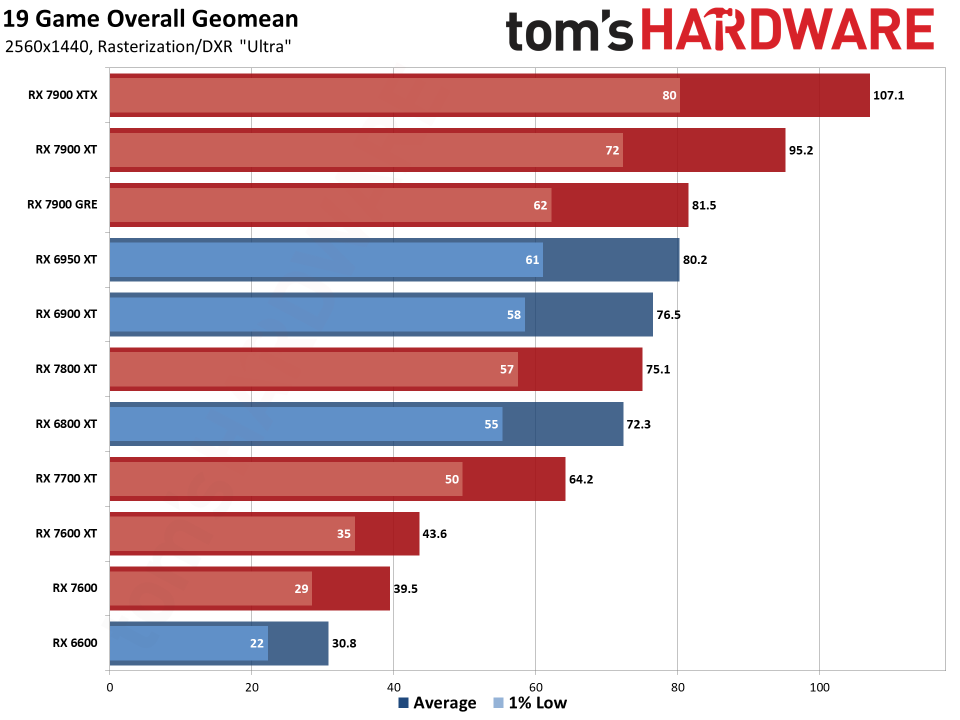

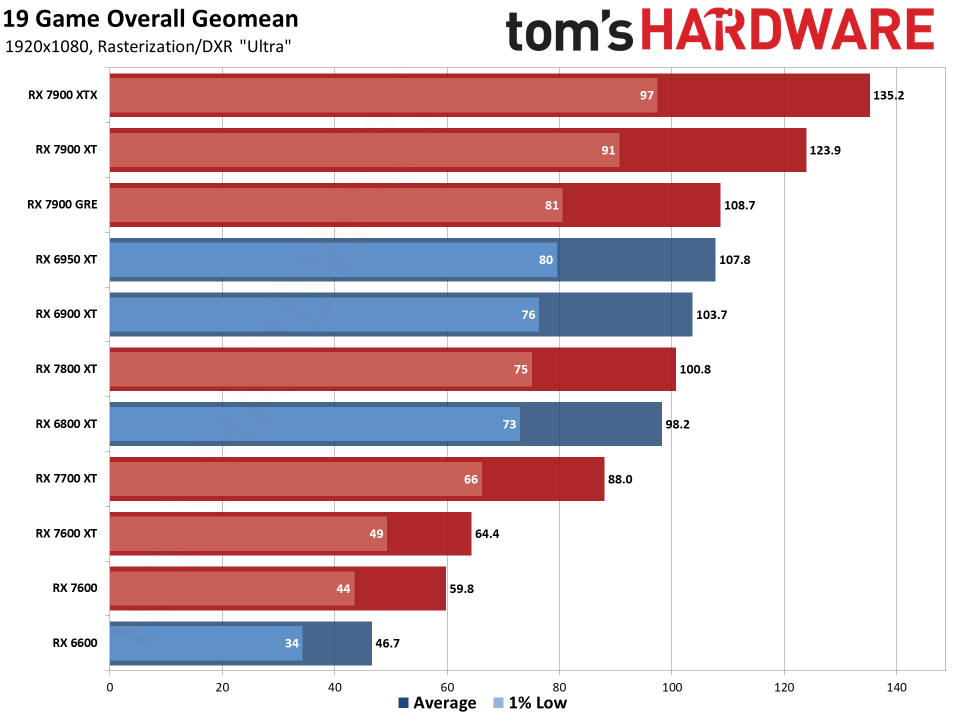

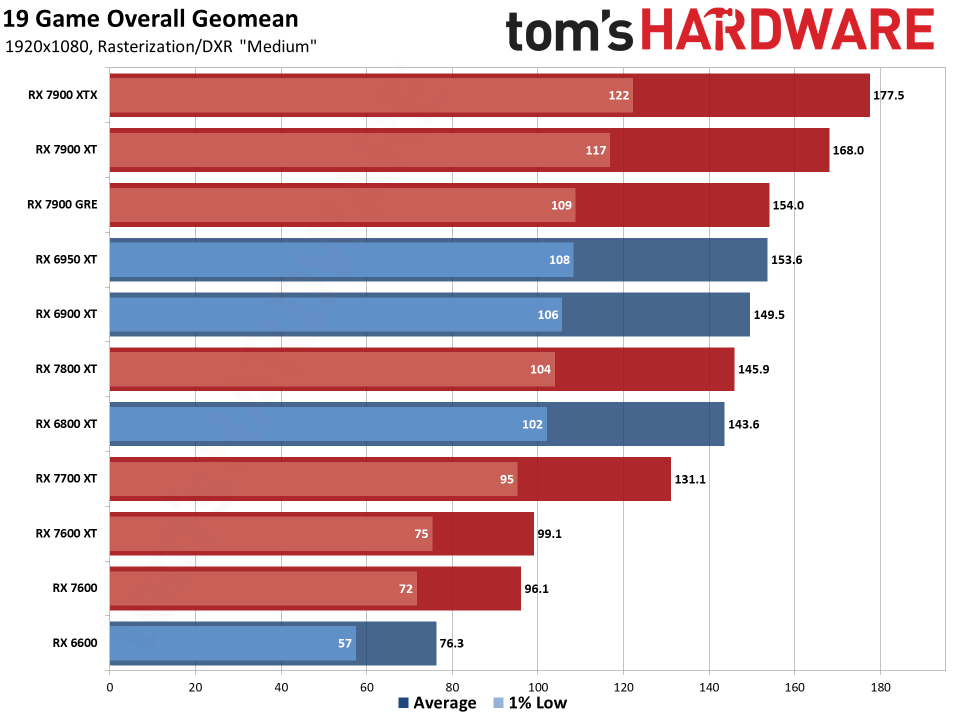

Since all the RDNA 3 GPUs have actually released, we can obviously offer independent analyses of exactly how they accumulate– both in efficiency along with efficiency per watt. The above graphes reveal the general arise from our 19-game examination collection. Listed below, we have tables of the specific examination outcomes. Concerning fifty percent of the 6000-series GPUs are ‘missing out on’ since we do not have actually upgraded examination outcomes (yet), however we have actually supplied sufficient information to place the 7000-series right into context.
The leading 2 GPUs, the 7900 XTX and 7900 XT, go beyond the efficiency of anything supplied by AMD’s previous generation. That’s mainly many thanks to both having even more CUs, even more VRAM, and even more memory transmission capacity than anything the previous gen supplied. The 7900 XTX has 96 CUs and 24GB of memory with 960 GB/s of transmission capacity; 7900 XT has 84 CUs and 20GB of memory with 800 GB/s of transmission capacity. Contrast that to the 6950 XT with 80 CUs, 16GB of memory, and 576 GB/s of transmission capacity and it’s very easy to see why efficiency boosted on top.
Listed below that mark, points come to be much less remarkable. The 7900 GRE professions strikes with the 6950 XT while the 7800 XT and 6800 XT land extremely close with each other. This reveals the huge interest in RDNA 3: Breaking short the memory controllers and cache to develop GPU chiplets had not been actually regarding enhancing efficiency.
Comparable CU counts wind up supplying reasonably comparable efficiency, gen-on-gen. RX 7800 XT has 60 CUs and the 6800 XT has 72 CUs, so the older GPU had 20% even more CUs. Nonetheless, the brand-new GPU additionally has greater clocks– 8% greater by requirements, however extra like 5% in our examination outcomes. Generally, the 7800 XT winds up having to do with 5% faster, indicating the building renovations show up to just offer regarding a 10% renovation in general efficiency.
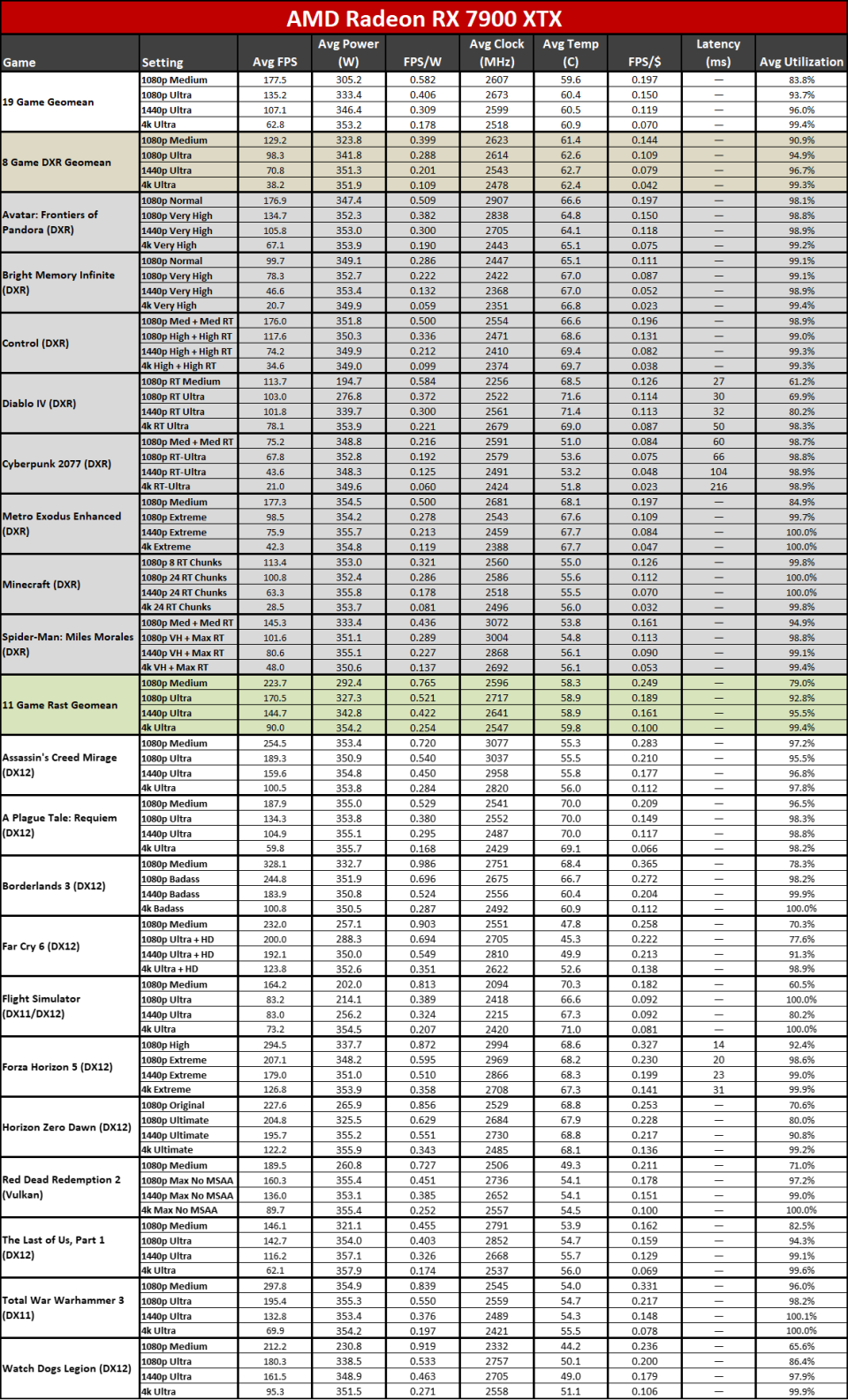

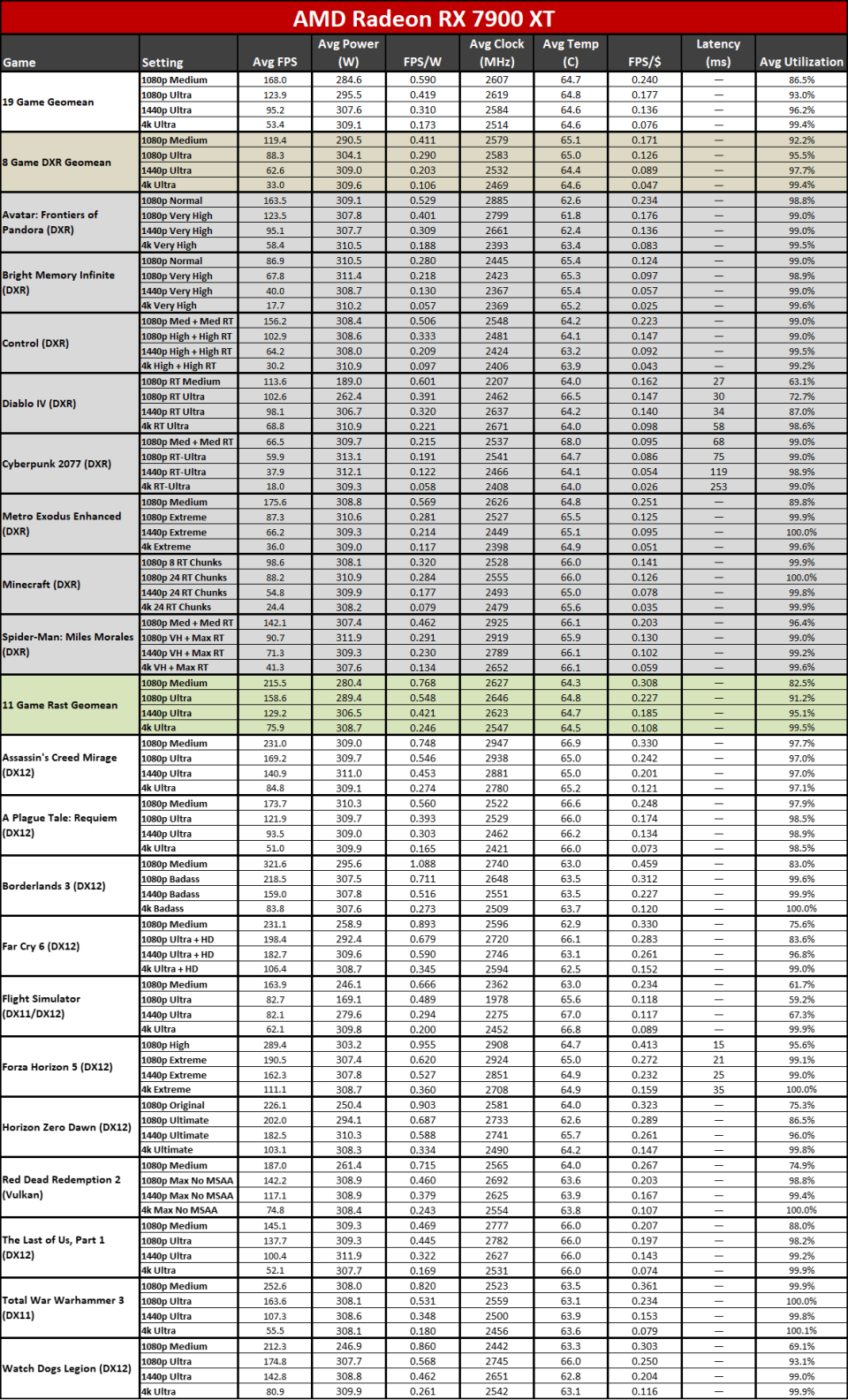

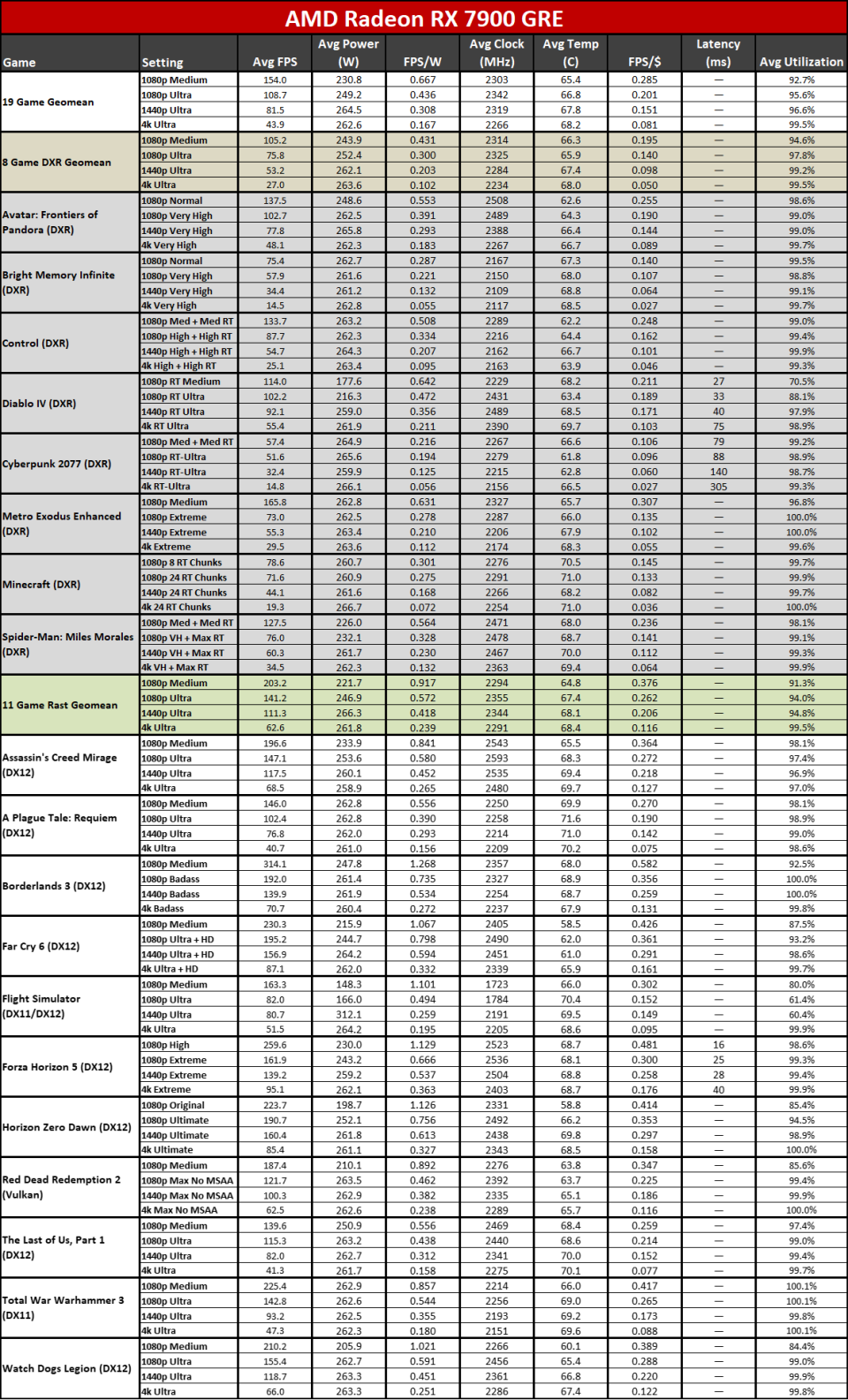

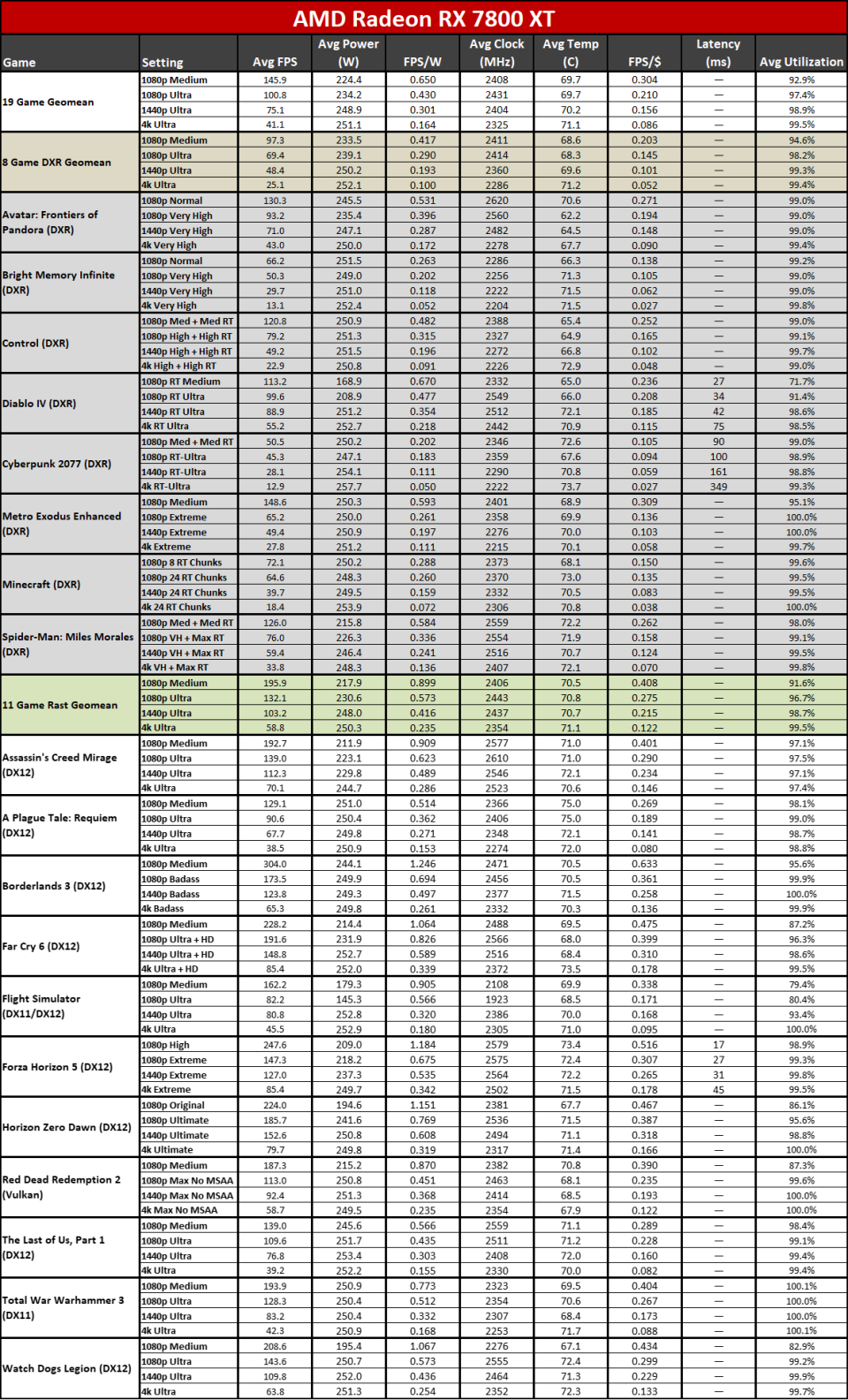

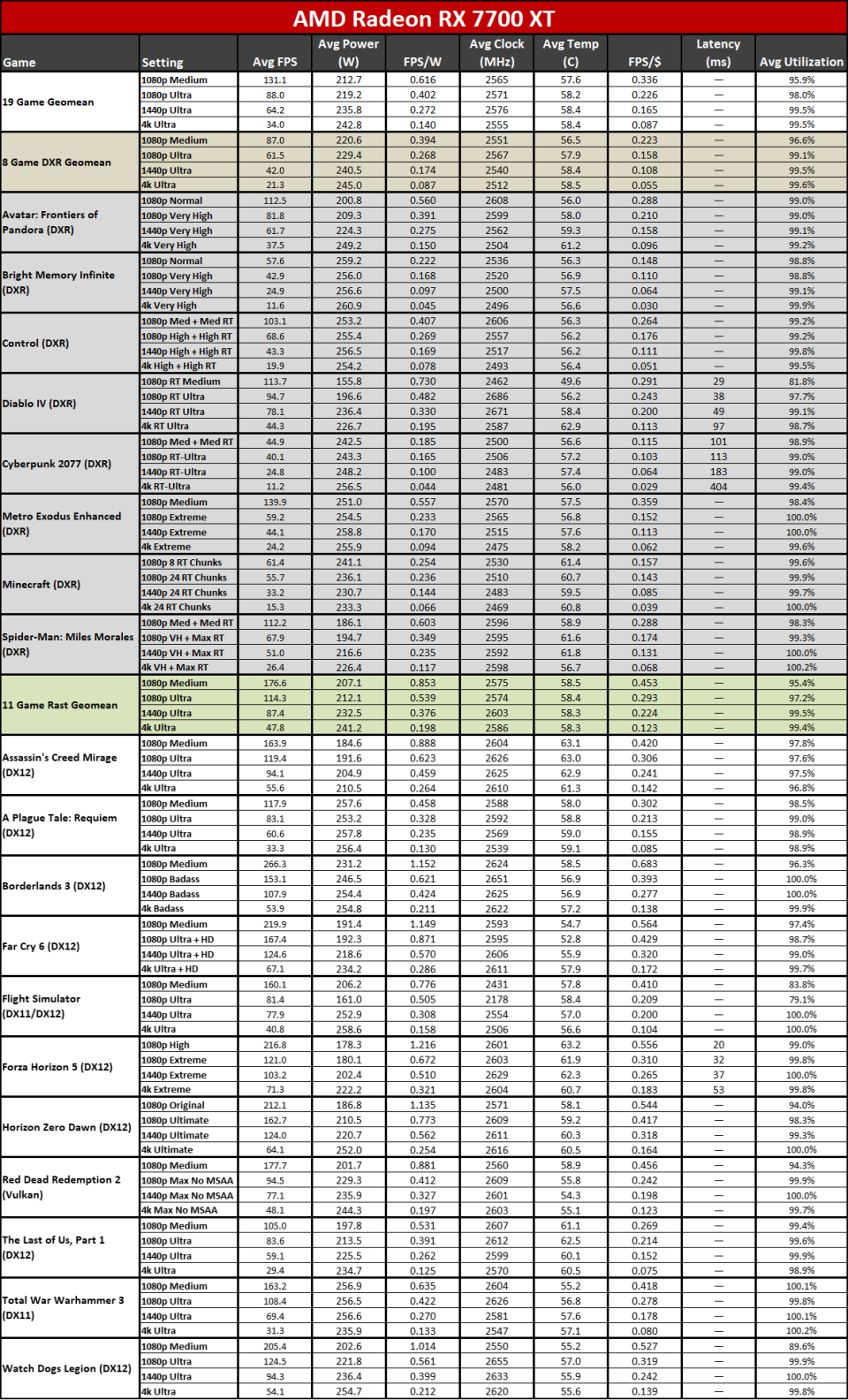

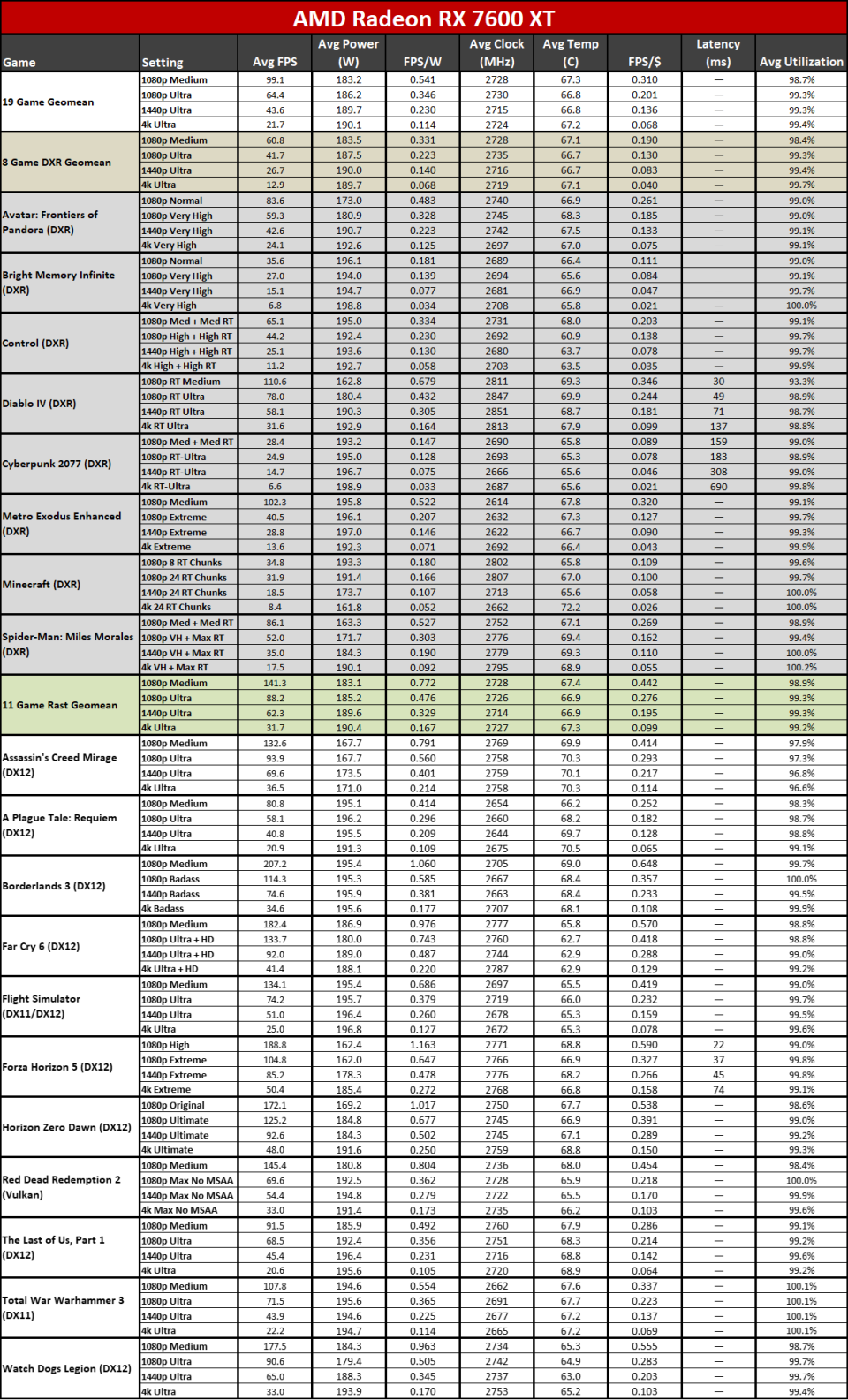

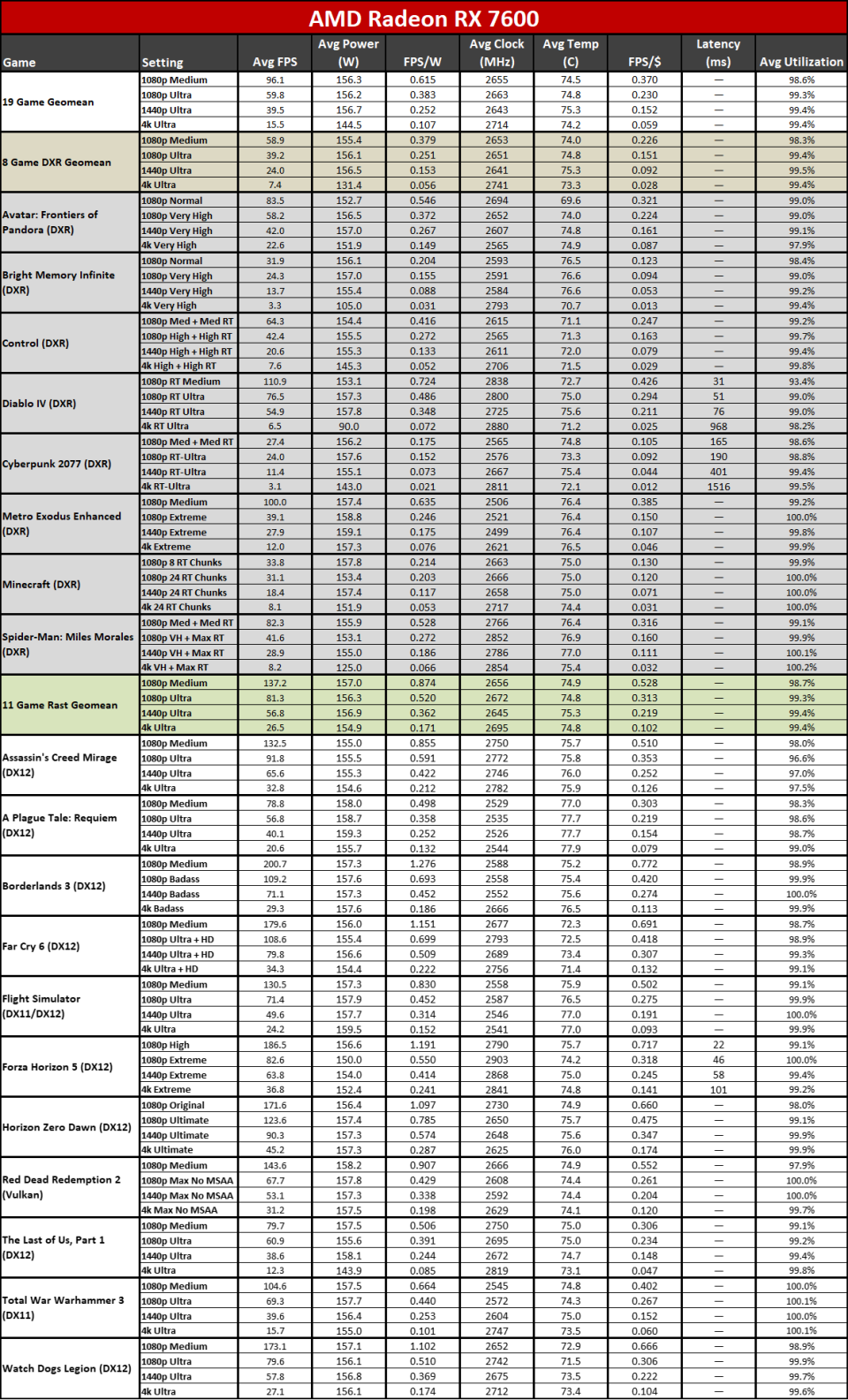

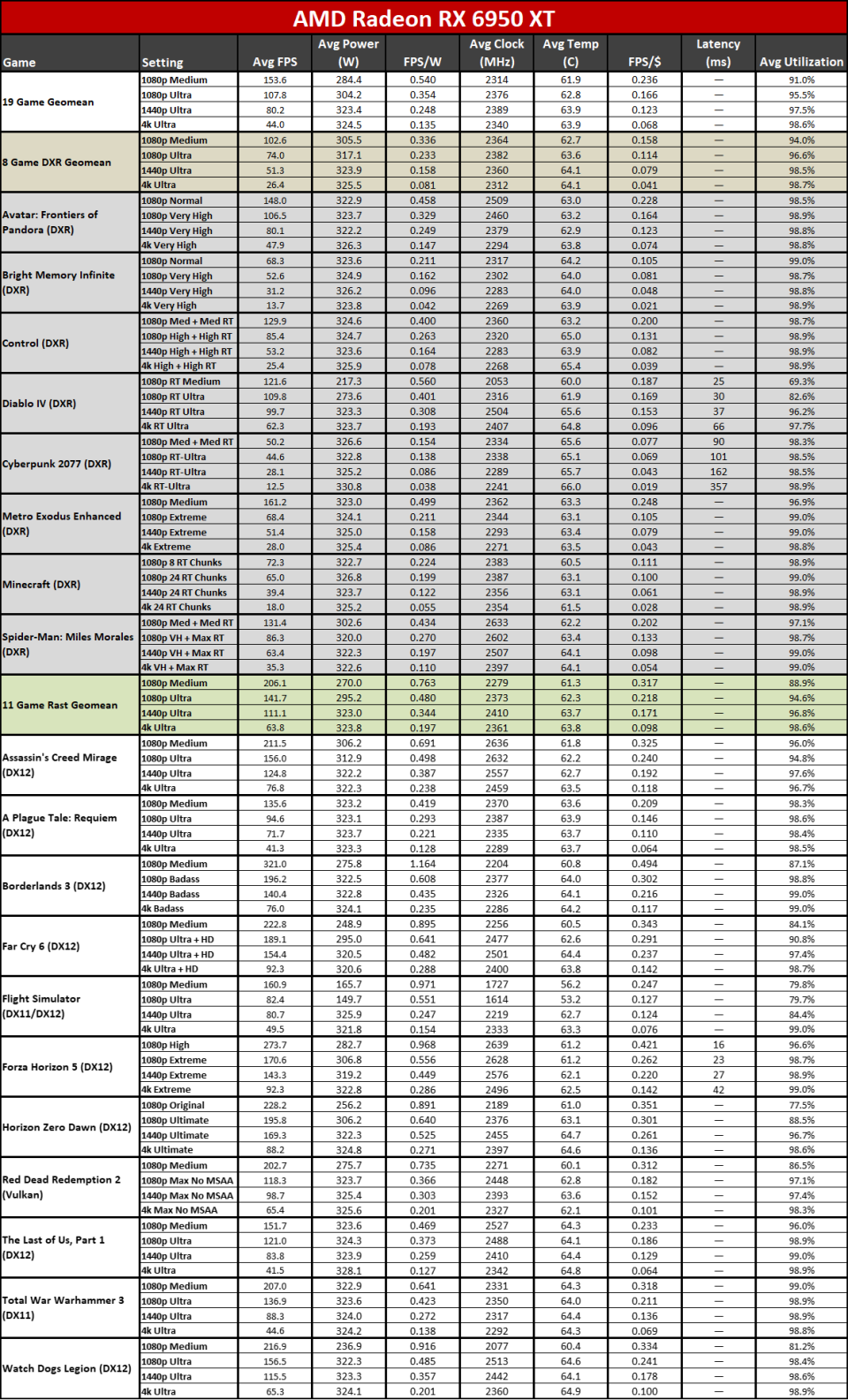

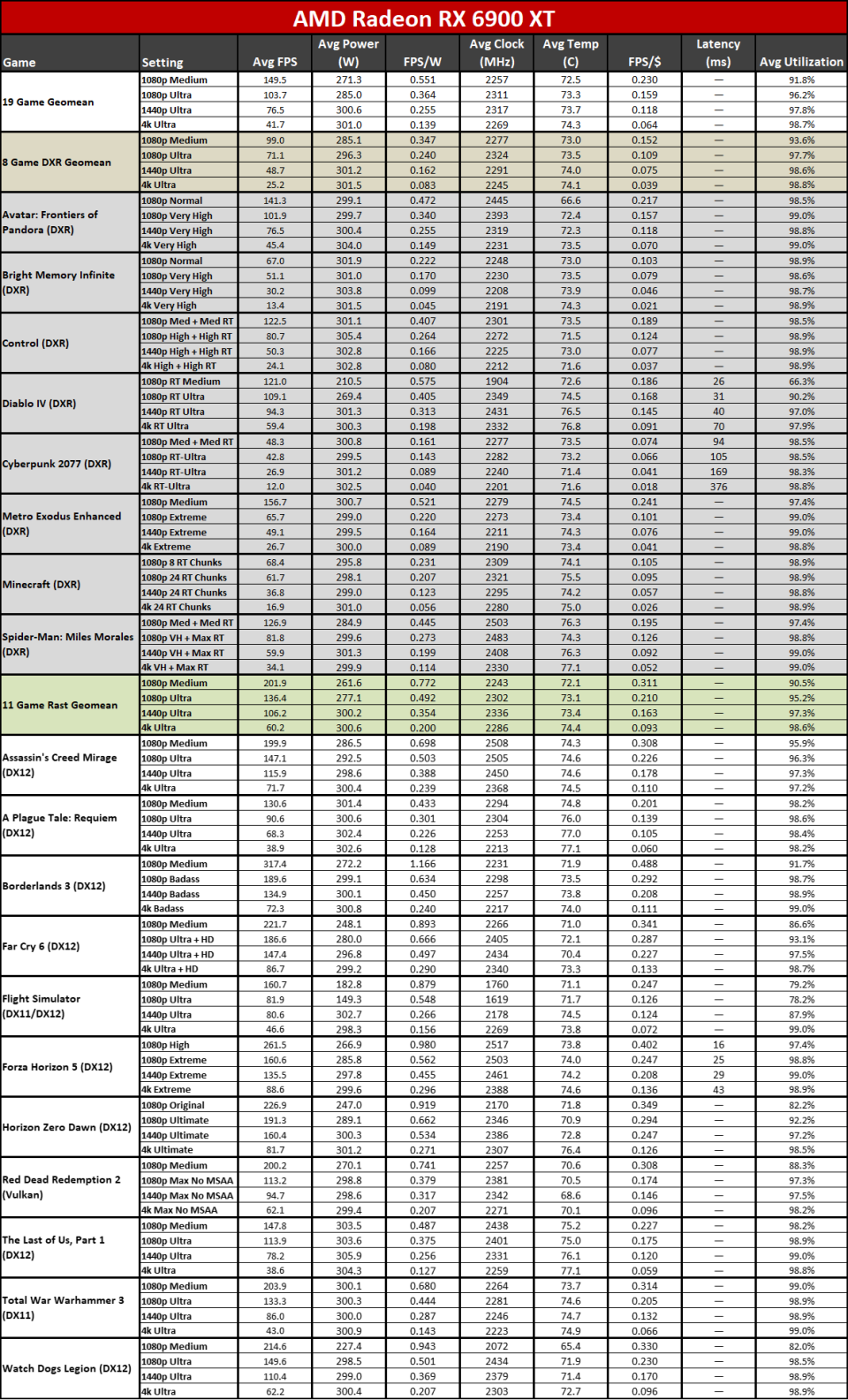

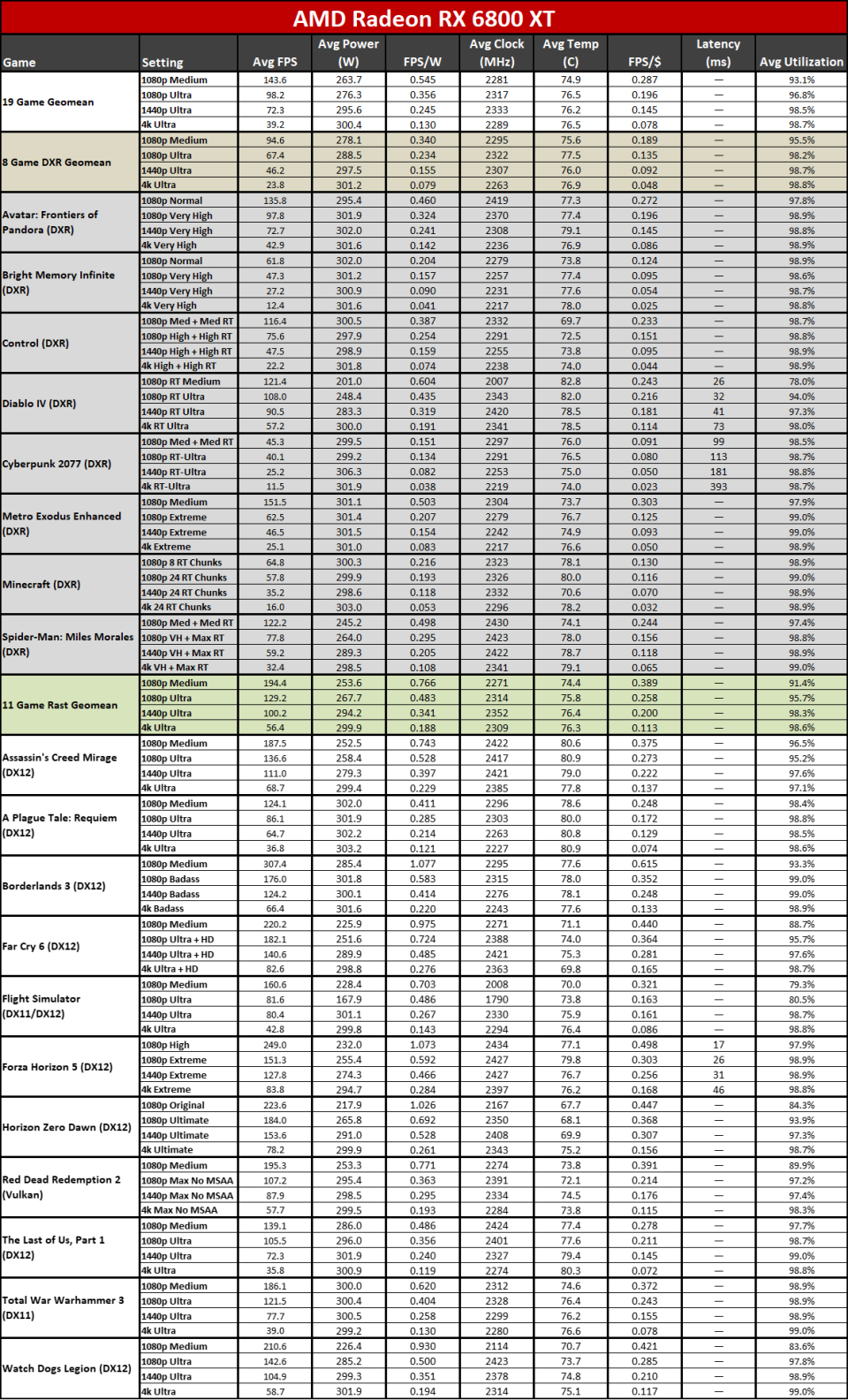

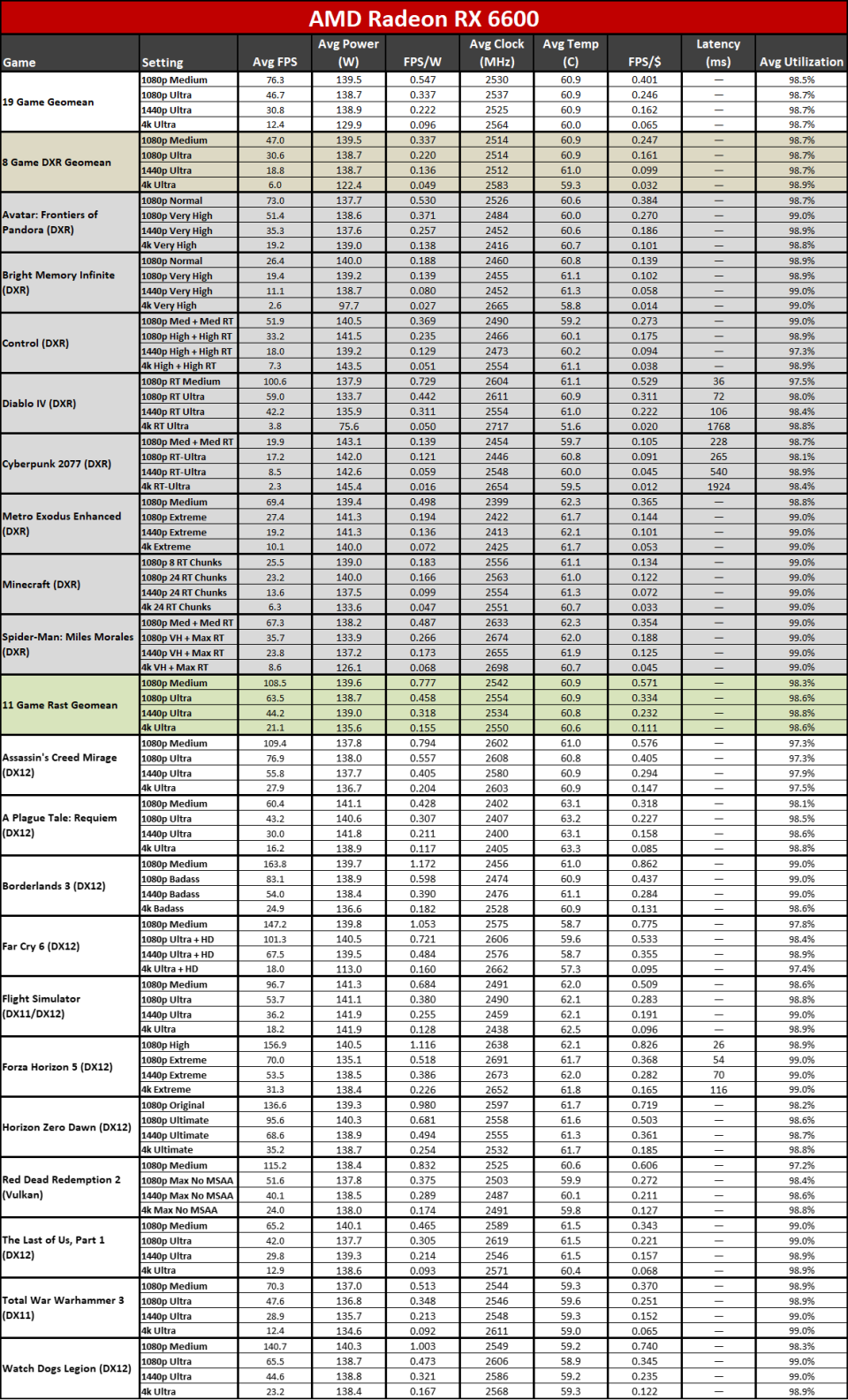

Right here you can see the efficiency per watt metrics from our complete screening collection. AMD asserts approximately a 50% renovation in perf/W, and if you select the ideal GPUs to compre, you can arrive … however it needs some major cherry-picking of outcomes.
The 7800 XT versus 6800 XT as an example reveals a gen-on-gen efficiency per watt renovation of simply 19– 25 percent on the whole. The 7900 XT versus 6900 XT renovation varies from 7% (at 1080p tool) to 25% (at 4K ultra). If you desire greater than a 50% renovation, you require to do something like contrast the RX 6600 with the RX 7700 XT at 4K ultra. Other than the RX 6600 was never ever planned to be a 4K pc gaming card, to ensure that’s a rather suspicious contrast.
It’s not that the RDNA 3 design stands for a go back from RDNA 2; it’s that it does not offer the huge advance that lots of wished to see. RDNA 2 had far better efficiency per watt than Nvidia’s completing RTX 30-series, a minimum of in rasterization video games, however it additionally had a procedure node benefit. Nvidia leapfrogged AMD on procedure nodes and performance this round with the RTX 40-series, typically offering around 30 ~ 60 percent greater efficiency per watt.
AMD RDNA 3 Style: GPU Chiplets
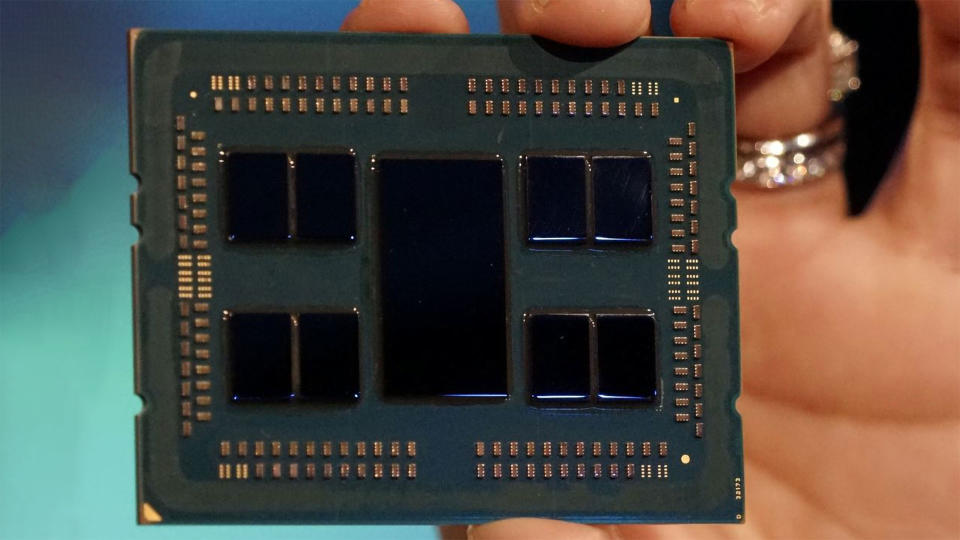

Among the largest building updates for RDNA 3 is something we have actually currently pointed out– the transfer to GPU chiplets. There are excellent factors for transferring to numerous chiplets, though the general internet advantage greatly relies on application. For this initial generation of customer GPU chiplets, AMD primarily appears to be concentrated on lowering expenses.
Previous GPU layouts were monolithic, indicating whatever required for the GPU to operate originated from a solitary item of silicon. Due to that, GPUs construct in a great deal of redundancy, and chips obtain marketed in “collected” arrangements. Navi 21 was made use of in the 6950 XT, 6900 XT, 6800 XT, and 6800, with approximately 80 calculate systems (CUs) or as couple of as 60 CUs.
Remarkably, the Navi 21 pass away additionally has 8 32-bit memory user interfaces, however AMD really did not launch any type of Navi 21 versions with less memory networks. The very same primarily relates to Navi 22, Navi 23, and Navi 24– memory and cache dimensions appear to have actually been an all-or-nothing point. Maybe returns on the memory controller were simply actually excellent, as the only GPU that really did not make use of all the memory networks feasible was Navi 22 in the RX 6700 (non-XT), with a 160-bit user interface as opposed to the complete 192-bit user interface.
With Navi 31 and 32, AMD will certainly draw every one of the memory user interface and Infinity Cache shuts out of the primary die and relocate them right into different passes away. Each MCD has a 64-bit GDDR6 user interface and a 16MB portion of Infinity Cache. There were reports that the MCDs had the alternative to make use of 3D chip piling with one more 16MB pass away in addition to the primary MCD, however if that report held true, AMD never ever applied such an arrangement. The MCDs relate to the GCD using AMD’s Infinity Textile, which will certainly see some updates to the previous versions made use of in Ryzen CPUs.
Bursting Out the Infinity Cache and GDDR6 memory user interface has some clear benefits. Transistor thickness range best with reasoning circuits, much less so with cache, and analog user interfaces (i.e., for memory controllers) scale the most awful. The on-package Infinity Textile web links on both the GCD and MCDs still call for some pass away area, however any type of defective memory controllers or cache blocks will certainly no more be an issue– they simply obtain thrown.
On The Other Hand, the MCDs will certainly be made on TSMC’s existing N6 procedure, which sets you back much less than the more recent N5 node, and pass away dimension will not also be a major worry. The MCDs are just 38mm ^ 2, indicating a 300mm N6 wafer must have sufficient area for regarding 1,600 MCDs, provide or take. There’s no genuine trouble in just throwing every defective chip as opposed to stressing over structure in redundancies.
The GCDs for Navi 31 and Navi 32 subsequently diminish a fair bit contrasted to the previous generation, and on the more expensive N5 node, that might be extremely useful. AMD can still navigate 180 of the bigger Navi 31 GCD per wafer or almost 300 of the smaller sized Navi 32. And it can still make use of collected chips with less calculate systems or perhaps MCDs to develop lower-tier items– which is why we have actually 3 cards based upon the Navi 31 GCD, and 2 making use of the Navi 32 GCD.
Had AMD stuck to monolithic layouts, it likely would have wound up with Navi 31 making use of closer to 550mm square and obtaining possibly 100 chips per wafer. Given that N5 wafers most likely expense greater than two times as high as N6, this must be a simple internet win from a price point of view. It additionally provides AMD extra versatility with cache dimensions, a minimum of on the higher-tier items. The piled cache is just on the MCDs, leaving the GCD complimentary to dissipate warm right into the air conditioning configuration– that’s something 3D V-cache dealt with on its CPUs.
AMD RDNA 3 Style: Core Enhancements

AMD will certainly have lots of various other modifications in the core design of RDNA 3. AMD has actually specified that it will certainly have a rearchitected calculate device and maximized shader design, though the last does not offer much in the method of information.
The calculate systems were revamped, and in a method that looks comparable to what Nvidia performed with Ampere, RDNA 3 CUs to have two times as lots of FP32 implementation systems. This produces a huge increase to academic calculate, as AMD went from 80 RDNA 2 CUs and approximately 5,120 GPU shaders to an optimum of 96 RDNA 3 CUs with 6,144 GPU shaders that are each two times as effective as their precursors. Also if the real-world advantage does not range straight with academic calculate, this must boost efficiency.
AMD’s Ray Accelerators remain to drag what Nvidia and also Intel deal (per GPU handling collection). Sharing the structure systems with the BVH traversal equipment might have been all right for the preliminary of ray mapping equipment, however the 2nd generation required to be far better. And it is … however not by a lot.
Generally, the optimizations and renovations made with RDNA 3 did supply greater efficiency, however AMD remains to focus on pure GPU shader calculate with ray mapping and AI equipment relatively a second thought.
AMD RDNA 3 Style: AI Accelerators
We asked throughout our interview with AMD’s Sam Naffziger whether we would certainly see tensor cores or their equal in AMD’s customer GPUs. To rapidly summarize, tensor cores are calculate cores maximized for raw throughput, with a much more minimal guideline collection than GPU shaders. Nvidia’s RTX cards have tensor cores for DLSS and various other equipment finding out applications. Intel has actually done the same with the Arc design’s XMX cores (Xe Matrix expansions) made use of for XeSS and various other deep discovering software program.
AMD isn’t averse to offering such equipment in its GPUs, and it has tensor cores in the Reaction MI250X and MI300 information facility GPUs. That’s where most applications that will genuinely gain from tensor cores run now, however while there’s a possible usage instance on customer equipment, AMD appears material to primarily miss including additional AI equipment in the meantime.
What AMD did offer with RDNA 3 is what it’s calling an AI Accelerator with WMMA (Wave Matrix Multiply Accumulate) guidelines. These show up to repurpose the existing FP16 implementation sources, so the raw academic throughput does not alter, however the performance of running a number of FP16 estimations boosts. We have actually seen this in our Secure Diffusion screening.
AMD Radeon 7000 Power Needs

Moore’s Regulation has actually greatly concentrated on enhancing optimum transistor thickness by lowering transistor dimensions. While we remain to see development, we have actually time out of mind passed the factor of increasing transistor matters every 2 years. In addition to that, we have actually additionally seen a remarkable downturn in power performance renovations.
It made use of to be that you would certainly obtain smaller sized transistors performing at greater clocks making use of reduced voltages and hence much less power. Today, we obtain unclear declarations regarding 30% much less power at the very same efficiency or 15% even more efficiency at the very same power. Do the mathematics and you’ll see that those 2 points are not equal.
No business is unsusceptible to the adverse effects, and all indications suggest raised power usage from the next-gen GPUs. The PCIe 5.0 power user interface and upcoming power materials that sustain it can provide approximately 600W over a solitary 16-pin port, as an example, hinting a more comprehensive sector change to higher-power GPUs. Nvidia’s RTX 4090 bumped power draw to 450W for the base version, and some manufacturing facility overclocked cards also presumed regarding consist of double 16-pin adapters. AMD chose to totally miss the 16-pin port, which wound up being a terrific relocation regarding we’re worried.
AMD’s RDNA 3 pressed TBP (Overall Board Power) somewhat greater than RDNA 2, however just on top of the range. RX 7900 XTX has a 355W TBP, contrasted to 335W for the 6950 XT and 300W on the 6900 XT. The 7900 XT goes down that to 315W, while the reduced rate applications are commonly reduced or comparable TBPs to their precursors. Strangely enough, also the RX 7600 has a 165W TBP, so there are no spending plan or low-power components.
AMD’s Sam Naffziger discussed this with us. “It’s actually the principles of physics that are driving this,” Naffziger discussed. “The need for pc gaming and calculate efficiency is, if anything, simply speeding up, and at the very same time, the underlying procedure modern technology is reducing quite substantially– and the renovation price. So the power degrees are simply mosting likely to maintain increasing. Currently, we have actually obtained a multi-year roadmap of extremely substantial performance renovations to balance out that contour, however the pattern exists.”
AMD has actually had the ability to drive somewhat greater clocks with RDNA 3 while staying as effective as RDNA 2. AMD has actually long reviewed its approach of ‘cross-pollinating’ CPU and GPU style groups, bringing the most effective technology from both sides of your house per brand-new CPU and GPU style. The brand-new RDNA 3 GPU cores are intended to be “inherently even more power effective,” however a service choice still requires to be made.
” Efficiency is king,” specified Naffziger, “however also if our layouts are extra power-efficient, that does not imply you do not press power degrees up if the competitors is doing the very same point. It’s simply that they’ll need to press them a great deal greater than we will.”
AMD Radeon 7000 Launch Dates
The initial RDNA 3 and RX 7000-series GPUs shown up in December 2022 with the 7900 XTX and XT designs. The RX 7600 was the 2nd distinctive RDNA 3 die with Navi 33, introducing in Might 2023. We really did not see the middle-tier RDNA 3 cards till September 2023 when the RX 7800 XT and RX 7700 XT got here. There was additionally a 7900 GRE in China in July 2023, which at some point got here in the united state in February 2024, together with the RX 7600 XT that increased the VRAM of the base non-XT card in January 2024.
There was likely a large hold-up in presenting several of the RDNA 3 GPUs while AMD waited to clean out existing RDNA 2 stock. Also almost 2 years after the initial cards released, there are still RX 6000-series GPUs drifting around the marketplace offering suitable worth options. RX 6700 XT and 6750 XT as an example still typically outshine the more recent RX 7600/7600 XT.
AMD Radeon 7000 Costs
Just how much do AMD’s RX 7000-series graphics cards expense? The initial designs appeared to adhere to Nvidia’s lead with greater rate factors than ever before. The RX 7900 XTX gone for $999, with the step-down RX 7900 XT going for $899. The latter had not been a terrific worth, and in time it has actually gone down $200 to simply $699.
The spending plan RX 7600 on the other hand successfully took control of the very same rate factor– with incredibly comparable efficiency– as the existing RX 6650 XT. As kept in mind over, RX 7800 XT and 7700 XT really did not appear till 9 months after the Navi 31 components, possibly to permit the existing Navi 21 GPUs to clean out of the marketplace. Rates resembled the existing road costs on the older GPUs too, with $499 and $449 rate factors, however AMD did reduce the RX 7700 XT rate to $399 6 months after launch.
Several of the rates still shows up to have actually been influenced by the GPU-based cryptocurrency mining of the previous generation. Ethereum mining has actually finished, so GPUs aren’t actually being made use of much for cryptocurrency currently (earnings remain in the bathroom), however after seeing the previous generation GPUs typically costing two times their main MSRPs, AMD and Nvidia appear to have actually been extremely hoggish with the brand-new costs. That additionally suggested possible scalpers really did not actually influence costs or schedule, so there goes to the very least a little a positive side.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
