Join CNN’s Marvel Concept science publication. Explore the universe with news on fascinating discoveries, scientific advancements and more.
Astronomers predict a “new star” to seem within the night time sky anytime between now and September in a celestial occasion that has been years within the making, in response to NASA.
“It’s a once-in-a-lifetime occasion that may create lots of new astronomers on the market, giving younger folks a cosmic occasion they will observe for themselves, ask their very own questions, and gather their very own knowledge,” mentioned Dr. Rebekah Hounsell, an assistant analysis scientist specializing in nova occasions at NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle in Greenbelt, Maryland, in an announcement. “It’ll gasoline the following era of scientists.”
The anticipated brightening occasion, generally known as a nova, will happen within the Milky Method’s Corona Borealis, or Northern Crown constellation, which is situated between the Boötes and Hercules constellations.
Whereas a supernova is the explosive loss of life of an enormous star, a nova refers back to the sudden, temporary explosion from a collapsed star generally known as a white dwarf. The dwarf star stays intact, releasing materials in a repetitive cycle that may happen for hundreds of years.
“There are a couple of recurrent novae with very quick cycles, however usually, we don’t usually see a repeated outburst in a human lifetime, and barely one so comparatively near our personal system,” Hounsell mentioned. “It’s extremely thrilling to have this front-row seat.”
T Coronae Borealis, in any other case generally known as the “Blaze Star,” is a binary system within the Corona Borealis that features a useless white dwarf star and an getting old purple large star. Crimson giants type when stars have exhausted their provide of hydrogen for nuclear fusion and start to die. In about 5 billion or 6 billion years, our solar will grow to be a purple large, puffing up and increasing because it releases layers of fabric and sure evaporating the photo voltaic system’s inside planets, though Earth’s destiny stays unclear, in response to NASA.
Each 80 years or so, T Coronae Borealis experiences an explosive occasion.
The celebrities within the orbiting pair are shut sufficient to one another that they work together violently. The purple large turns into more and more unstable over time because it heats up, putting off its outer layers that land as matter on the white dwarf star.
The trade of matter causes the environment of the white dwarf to step by step warmth till it experiences a “runaway thermonuclear response,” leading to a nova as seen within the animation beneath, in response to the area company.
Maintaining a tally of the altering sky
A nova was releasing from T Coronae Borealis within the fall of 1217 when a person named Burchard, abbot of Ursberg, Germany, famous his observance of “a faint star that for a time shone with nice mild,” in response to NASA. It was the primary recorded statement of the Blaze Star.
T Coronae Borealis final skilled an explosive outburst in 1946, and astronomers are protecting a watchful eye on the star system as soon as extra.
“Most novae occur unexpectedly, with out warning,” mentioned William J. Cooke, NASA Meteoroid Environments Workplace lead, in an e mail. “Nevertheless, T Coronae Borealis is one in every of 10 recurring novae within the galaxy. We all know from the final eruption again in 1946 that the star will get dimmer for simply over a 12 months earlier than quickly growing in brightness. T Coronae Borealis started to dim in March of final 12 months, so some researchers predict it to go nova between now and September. However the uncertainty as to when this can occur is a number of months — can’t do higher than that with what we all know now.”
The star system, situated 3,000 light-years from Earth and usually too dim to be seen with the bare eye, is anticipated to achieve a degree of brightness just like that of Polaris, or the North Star.
As soon as the nova peaks in brightness, will probably be as if a brand new star has appeared — one which’s seen for a couple of days with none tools and a bit over every week with binoculars earlier than it dims and disappears from sight for an additional 80 years or so.
The nova will seem in a small arc between the Boötes and Hercules constellations, and can be seen from the Northern Hemisphere.
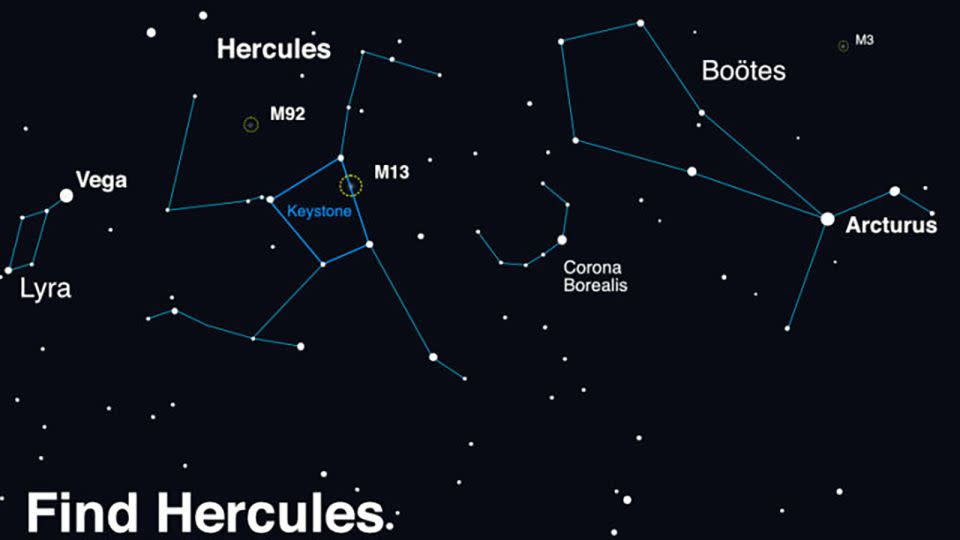

“The Northern Crown is a horseshoe-shaped curve of stars west of the Hercules constellation, ideally noticed on clear nights,” in response to a launch shared by NASA. “It may be recognized by finding the 2 brightest stars within the Northern Hemisphere — Arcturus and Vega — and monitoring a straight line from one to the opposite, which can lead skywatchers to Hercules and the Corona Borealis.”
Observations around the globe
The occasion guarantees to be an thrilling one for beginner astronomers, mentioned Dr. Elizabeth Hays, chief of the Astroparticle Physics Laboratory at NASA Goddard.
“Citizen scientists and area fanatics are all the time in search of these sturdy, vibrant alerts that establish nova occasions and different phenomena,” Hays mentioned. “Utilizing social media and e mail, they’ll ship out prompt alerts, and the flag goes up. We’re relying on that world neighborhood interplay once more with T CrB.”
Astronomers will observe the nova utilizing a variety of ground- and space-based telescopes, and knowledge from citizen scientists might assist astronomers piece collectively what occurs earlier than the eruption as properly, Hounsell mentioned.
Sometimes, nova occasions are so distant and faint that it’s troublesome to establish the complete image of the eruption, however “this one can be actually shut, with lots of eyes on it,” Hays mentioned.
“Learning recurring novae like T Coronae Borealis assist us perceive the mass switch between the celebrities in these techniques and supply insights into the thermonuclear runaway that happens on the floor of the white dwarf when the star goes nova,” Cooke mentioned.
Cooke recalled that the final nova he witnessed — Nova Cygni in 1975 — had an analogous brightness to what’s anticipated from T Coronae Borealis. Nova Cygni just isn’t anticipated to expertise one other explosion once more.
“I used to be a teenage astronomy geek about to start out faculty and was outdoors on the night time of August 29,” Cooke mentioned. “Glancing on the sky, I seen that the constellation of Cygnus was tousled; there was a star that shouldn’t be there. After enduring some feedback from buddies who thought I used to be loopy, I acquired them to look and we realized that we have been a nova! It was a really memorable expertise and strengthened my selection of astronomy as a profession. I used to joke {that a} star needed to explode with the intention to get me to undergo via undergraduate physics.”
Whereas it’s potential that T Coronae Borealis received’t explode by September, astronomers plan to watch it simply in case.
“Recurrent novae are unpredictable and contrarian,” mentioned Dr. Koji Mukai, an astrophysics researcher at NASA Goddard, in an announcement. “While you assume there can’t presumably be a motive they comply with a sure set sample, they do — and as quickly as you begin to depend on them repeating the identical sample, they deviate from it fully. We’ll see how T CrB behaves.”
For extra CNN information and newsletters create an account at CNN.com
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
