
Simply outdoors Hiroya Yamaguchi’s workplace is a blackboard crowded with exploded stars, spaceship schematics and spectral strains. The A4 printouts obscure virtually all of the free area, apart from a tiny nook the place he generally scribbles in white chalk. Proper now, Yamaguchi, an affiliate professor at Japan’s Institute of House and Astronautical Science, is standing in entrance of this blackboard, going through me.
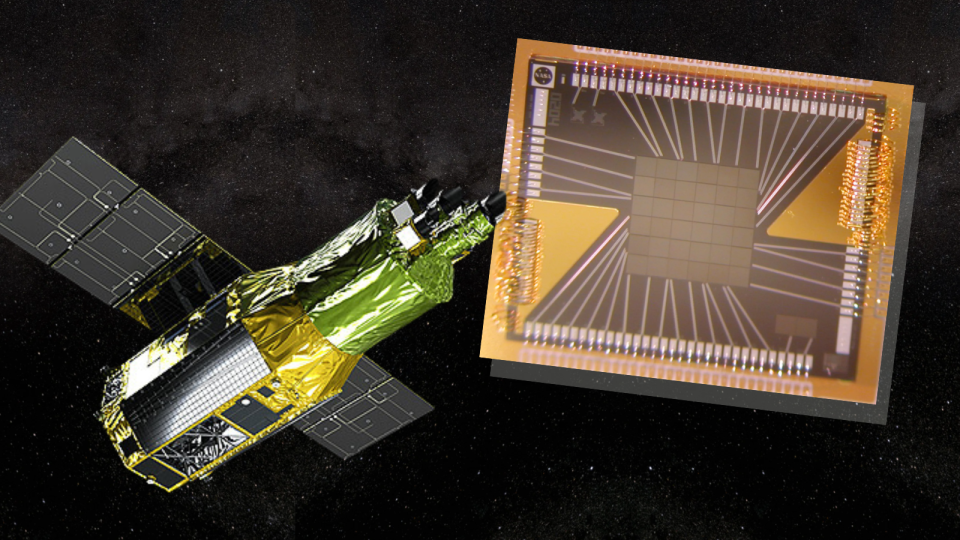
He is giving me a crash course on the X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission, or XRISM, a partnership between NASA, the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA) and the European House Company (ESA). The very first thing I be taught is I have been saying the telescope’s title flawed this complete time. Fortunately, I’ve principally been repeating the wrong “ex-riz-um” in my head. It is truly pronounced “criz-um.”
The second is that this area telescope was launched on September 6, 2023, carrying the heaviest weight of all: Expectation.
Associated: JAXA, NASA reveal 1st photographs from XRISM X-ray area telescope
JAXA’s two earlier X-ray telescopes, Suzaku and Hitomi, each skilled points after launch. Suzaku’s spectrometer malfunctioned after launch, however it was capable of perform a decade-long imaging mission. Hitomi was disastrous: After snapping its first gentle picture, the spacecraft went into an uncontrolled spin and broke aside. Up to now, XRISM has been performing effectively, Yamaguchi says, and has already supplied scientists with an abundance of information since first gentle in January — together with some discoveries nobody anticipated to search out.
“There are such a lot of surprises,” Yamaguchi laughs, glancing across the numerous printouts caught to the blackboard.
There may be, nevertheless, a little bit of an issue.
First, the excellent news: The telescope’s predominant instrument, a delicate X-ray spectrometer often called Resolve, is working as anticipated. The marginally worse information: An aperture door overlaying Resolve has not opened. A number of makes an attempt to open the door — or “gate valve” — have failed. Regardless of experiences suggesting JAXA and NASA have decided to “operate the spacecraft as is for at least 18 months,” Yamaguchi instructed me that “has not been formally determined.”
A NASA spokesperson confirmed “NASA and JAXA proceed to carry ongoing discussions about the very best path ahead to function XRISM; the present, main possibility is to gather science for the subsequent 18 months earlier than making one other try and open the gate valve, however the companies will proceed to evaluate options.”
With the door closed, an intriguing “What If?” scenario for mission specialists and X-ray astronomers presents itself. On one hand, the spacecraft is working fantastically and displaying it is able to delivering a heap of latest, thrilling knowledge. Attempting to open the door dangers damaging the spacecraft. However, opening the door may basically change our understanding of the universe.

Remedy for ‘X’
X-rays present a strategy to probe among the most energetic phenomena within the universe — however, as a result of Earth’s atmosphere blocks X-rays, space-based telescopes are a prerequisite.
“We’re unraveling the composition of the universe,” Aurora Simionescu, an astrophysicist on the Netherlands Institute for House Analysis, tells me. “That is what X-rays do.”
There are greater than a dozen X-ray telescopes at the moment in area, with NASA’s Chandra observatory, considered one of its so-called Nice Observatories, maybe essentially the most well-known due to the unbelievable views it has supplied of the X-ray universe. XRISM, with its skill to see essentially the most detailed X-ray spectra but, hopes to carve out the same legacy. Yamaguchi factors out, nevertheless, that though Chandra and XRISM observe the identical a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, they’re meant to take action in several methods. That comes all the way down to the instrumentation on board.
Resolve is what’s often called a microcalorimeter spectrometer. The detection equipment converts X-rays to warmth, measuring minute modifications in temperature — we’re speaking modifications in millikelvins — to find out the quantity and vitality of X-rays noticed coming from a selected area of area. Vitality is measured in electron volts (eV).
The instrument due to this fact needs to be cooled all the way down to only a few levels above absolute zero. That is colder even than the cosmic microwave background, which is leftover radiation from the start of time. This radiation is scattered throughout our universe, but hidden to the human eye due to how completely frigid it’s. “You’re mainly virtually 30 instances colder than the coldest a part of outer area,” says Simionescu. The acute cooling impact is achieved by chemical and mechanical means.
Chandra makes use of a unique fashion of X-ray detector, which options an array of charge-coupled units, or CCDs. This converts X-ray photons to electrons, slightly than to warmth.
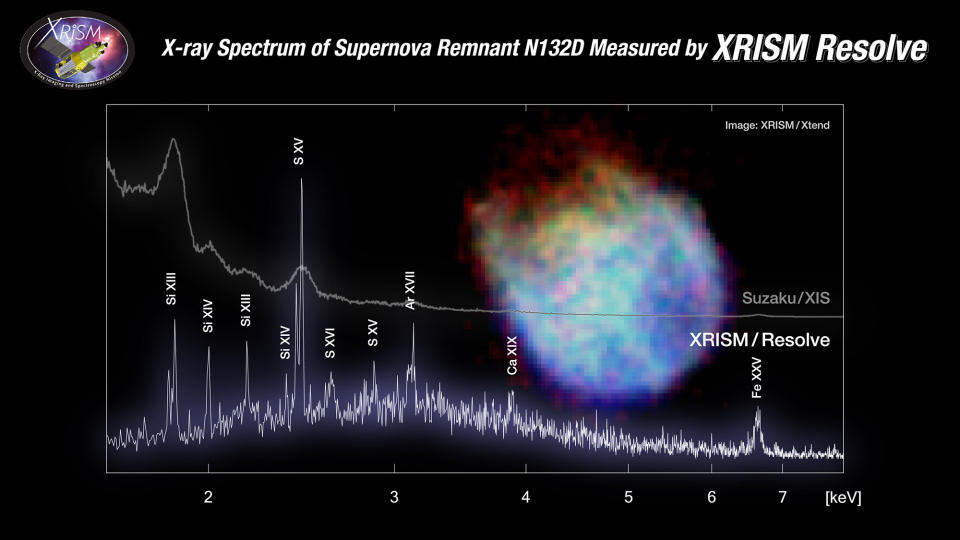
Measuring vitality is especially helpful, as a result of you possibly can plot the variety of X-rays that attain your telescope in opposition to their vitality stage — creating what researchers name a “spectrum.” XRISM’s Resolve has an edge on this case. It is capable of measure energies about 20 to 30 instances greater than Chandra can, and with larger decision. “This permits XRISM to check far more element in regards to the atomic physics and the speed construction of the X-ray sources,” says Patrick Slane, director of the Chandra X-ray Middle.

Chandra, nevertheless, has benefits of its personal. It is also constructed with the very best high quality X-ray mirrors ever constructed, Slane says, which implies its imaging high quality far exceeds XRISM’s. The important thing right here is the mirrors give Chandra an angular decision of 0.5 arcseconds, which basically permits Chandra to tell apart between objects within the sky which might be shut collectively. Evaluate that to XRISM, which has an angular decision of 1.7 arcminutes.
Because of that feat of engineering, Slane says Chandra can pick X-ray level sources about 200 instances extra simply than XRISM may. In follow, this makes NASA’s telescope extraordinarily helpful for specializing in these level sources — distant, smaller targets like neutron stars, planets and comets. XRISM is sweet for “prolonged” targets, just like the diffuse fuel between and inside galaxies.
Which, ultimately, brings us to XRISM’s gate valve: The closed door successfully blocking low-energy X-rays from reaching the detector. As of now, the telescope is continuous to discover the high-energy X-ray universe as a result of these wavelengths will not be affected by the gate dilemma — actually, Yamaguchi and Simionescu each say it is already returning unbelievable outcomes at greater energies.
But when the door is caught for good, scientists should deal with elements of our cosmos remaining inaccessible… at the very least, till one other X-ray telescope comes alongside, which is prone to be the Athena mission within the mid-2030s.
XRISMgate-gate
The gate valve was designed to keep up a near-vacuum inside the telescope’s cryostat — basically the fridge that ensures its devices stay extraordinarily chilly — whereas XRISM was stationed on Earth.
As soon as a telescope reaches orbit, sustaining this form of vacuum is not a difficulty. In area, area itself creates the vacuum. For that motive, the gate valve was designed to flip open in a two-step course of after launch, through a set of actuators. In brief, the actuators would slide again to permit the door — manufactured from a beryllium window and metal mesh — to flip open. That did not occur.
JAXA has tried to finesse the equipment open on three completely different events, however it hasn’t budged. The subsequent try can be a a lot riskier one, probably requiring the spacecraft to heat up from its extraordinarily low temperatures and be shaken about. The objective? Dislodging the actuators with drive. That is a danger the area companies working XRISM might want to weigh up. With the gate valve closed, they’re already banking knowledge. And it is superb knowledge.
“Essentially the most lovely factor is once you have a look at the info, and it appears nothing like what you anticipated — and that is taking place with the present XRISM knowledge,” says Simionescu.

Nonetheless, it is a powerful break for Simionescu. She’s significantly focused on learning X-rays from “galactic atmospheres” — the stuff XRISM was constructed to take a look at with an open gate valve. With the gate closed, that a part of the X-ray universe stays locked away. She absolutely agrees with the choice to not danger making an attempt to open the gate — at the very least for now. However that does not imply it is not painful, understanding what may very well be.
“I’m completely gutted that we won’t see under 2 keV,” Simionescu says.
And what may very well be?
Some X-ray area telescopes, just like the ESA’s XMM-Newton, can see decrease vitality X-rays, all the way down to under 2 keV. As an illustration, it has noticed the Coma Cluster, which accommodates over 1,000 galaxies, at energies as little as 0.3 keV. And XRISM’s different instrument, Xtend, can be capable of get all the way down to decrease energies. However these are CCD detectors too and never as helpful for acquiring spectra.
Exterior of XRISM, there isn’t any X-ray telescope orbiting the Earth with the aptitude to look throughout “prolonged” objects at low energies with excessive decision, which is especially necessary for Simionescu’s work.
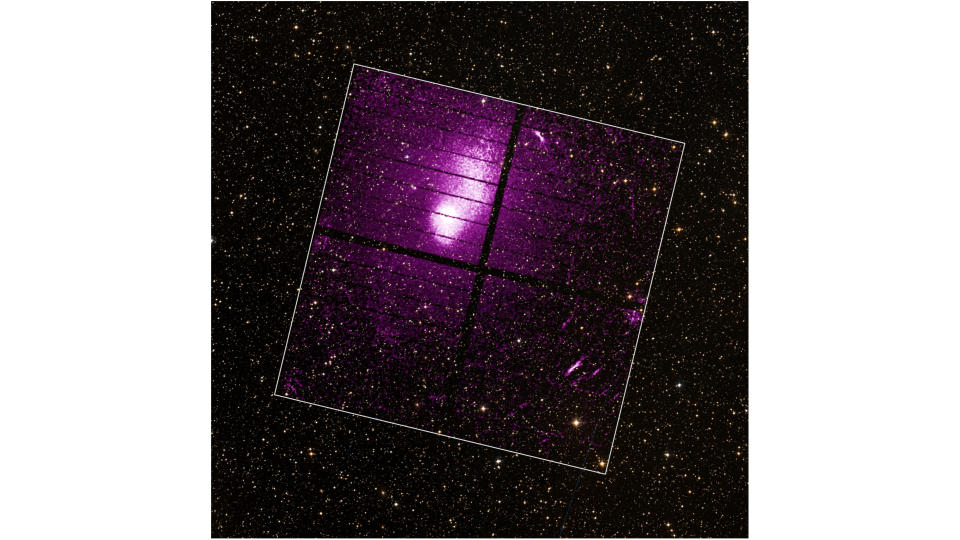
Throughout a web-based name, she shares a wide-field X-ray picture of M87, the primary black gap to be imaged by people in seen gentle. The picture was snapped by Chandra in 2019.
“That is my favourite object on this planet,” she says excitedly.
The area surrounding that black gap is a maelstrom. Simionescu’s cursor bounces across the sky as she factors out the big jet emanating from the black gap in addition to areas of dense fuel and an extended filament that stretches light-years into the cosmos. She describes a graph of the spectra noticed by Chandra at M87 — all under 2 keV — and notes the way it’s all “a mumbo jumbo” of emission strains from oxygen, neon, nickel and different gases.
With the gate open, that will change.
“You possibly can inform what’s the composition of the fuel, how is it being moved, how is it being pushed out by the black gap — which is all info that, proper now, you can not get,” she says.
It is attention-grabbing to think about the leap ahead with XRISM in opposition to the backdrop of uncertainty that surrounds NASA’s Chandra mission.
Sadly, the sector of X-ray astronomy may very well be with out Chandra within the close to future. The area telescope’s operations, which have lasted for 25 years, face excessive price range cuts in 2024. Astronomers say the proposed price range would end result within the mission’s cancellation.
“If Chandra had been to be canceled, we might lose an incredible useful resource for all of contemporary astrophysics,” Slane says.
Associated Tales:
— Most quasars are a ferocious drive of nature, however not this one
— X-ray picture of universe reveals virtually 1 million high-energy objects: ‘These are mind-blowing numbers’
— The Chandra X-ray spacecraft could quickly go darkish, threatening an excessive amount of astronomy
That will be an ignominious finish for the Nice Observatory, which stays invaluable for future discoveries, together with working in tandem with XRISM. If JAXA does unjam its door, Chandra will likely be an necessary software to observe up XRISM’s observations.
In the meantime, the ghosts of Suzaku and Hitomi will linger till the subsequent try at opening the door. For now, the sector of X-ray astronomy is happy about what’s to come back. The worst case situation is not all that unhealthy, relying the way you have a look at it.
“We’re taking unbelievable knowledge that no person has ever been capable of take earlier than,” Simionescu says. “The spectra are all completely spectacular.”
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
