When you purchase with web links on our posts, Future and its submission companions might make a payment.
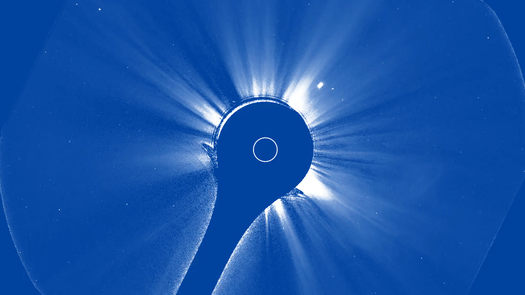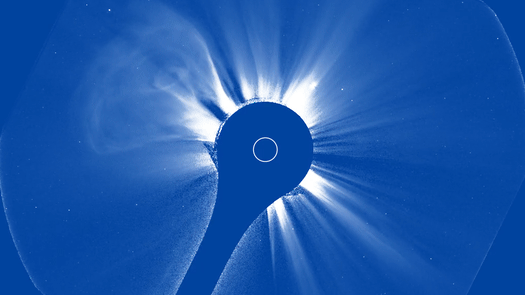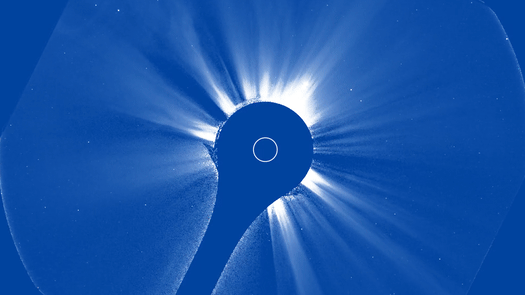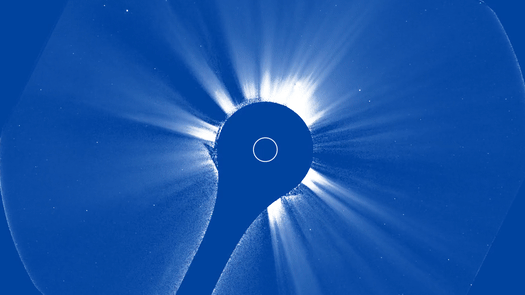

The initial photos from a brand-new space-based telescope released right into Planet’s orbit to keep an eye on the sunlight recorded a striking solar tornado outburst.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Management ( NOAA) shared the initial photos taken by its Compact Coronagraph (CCOR-1), the globe’s initial functional space-based coronagraph. CCOR-1 is placed on NOAA’s latest geostationary satellite, GOES-19, which released right into orbit over Planet on June 25.
CCOR-1 started its goal to observe the sunlight’s corona– the pale outer layer of the solar atmosphere— on Sept. 19. The effective solar telescope makes use of an occulting disk, noticeable as a dark blue circle in the photos, to obstruct the light from thesun This tool, called a coronagraph, permits the telescope to observe the sunlight’s corona, which would certainly or else be covered up by the intense light of the sunlight’s surface area.

CCOR-1 notes a substantial innovation precede weather condition surveillance. Contrasted to ground-based tools, space-based coronagraphs do not need to manage Earth’s atmosphere, which can spread light and influence the quality of monitorings. That implies CCOR-1 has a continuous sight of the sunlight’s corona.
CCOR-1 is developed to record brand-new pictures of the sunlight’s corona every 15 mins, supplying earlier cautions of coronal mass ejections (CMEs)– big expulsions of plasma and electromagnetic fields tossed right into room from the sunlight– that can cause geomagnetic tornados in the world. While various other space-based coronagraphs have actually been utilized in the past, NOAA states these previous tools were utilized for clinical study while CCOR-1 “will certainly be utilized operationally for normal, real-time tasks and surveillance.”
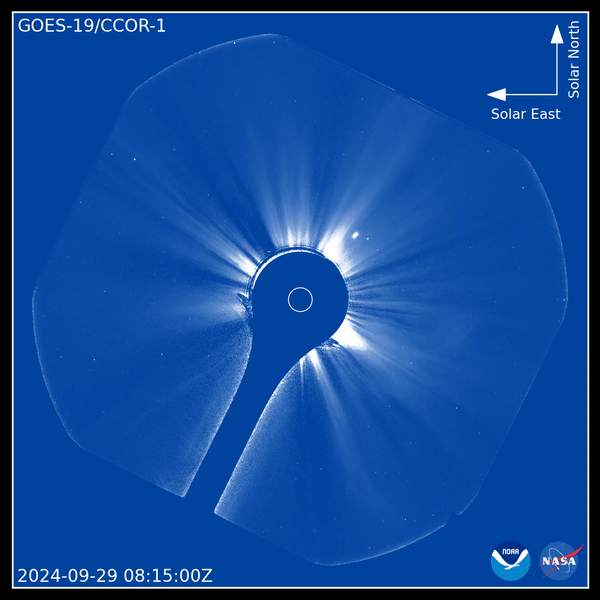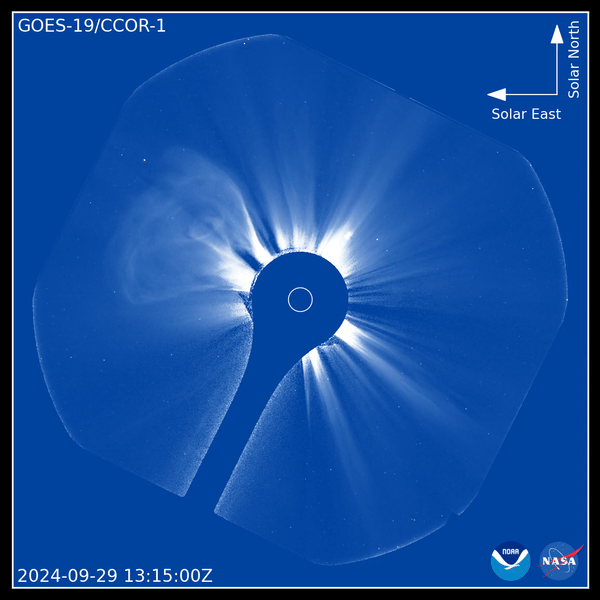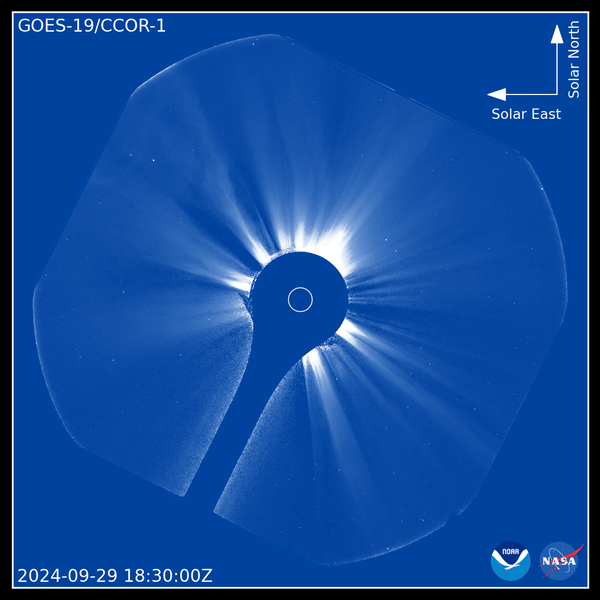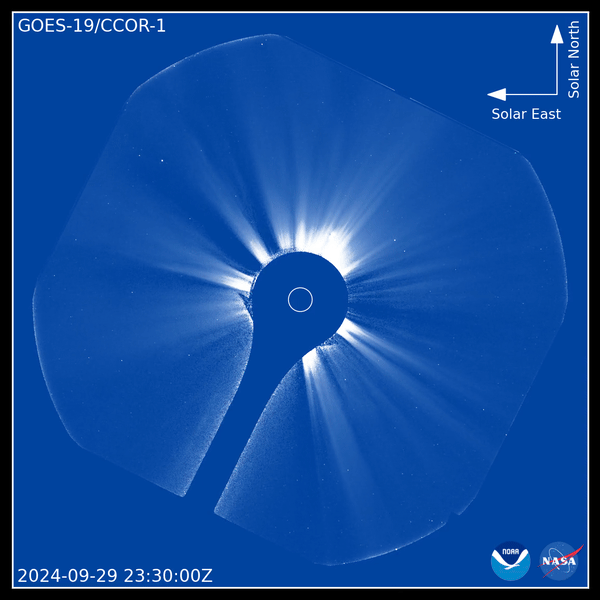
Utilizing the brand-new tool, CCOR-1 lately recorded a CME outburst on Sept. 29. Video clip video from the coronagraph reveals a “plainly specified” CME arising from the eastern arm or leg (left side) of the sunlight at 8:15 a.m. EDT (1200 GMT), according to a statement from NOAA.
” The sunlight likewise impresses with its little and big banners, intense radial frameworks along which the solar plasma takes a trip gradually exterior,” NOAA authorities claimed in the declaration. “The CME surges bend and in some cases interrupt the streaming plasma, humming past it at rates of hundreds to countless miles per secondly.”
The Good News Is, this CME was routed far from our earth. When a solar tornado is routed towards Earth, it can interrupt the earth’s electromagnetic field, bring about power interruptions, radio and interaction power outages and position higher danger to astronauts on the spaceport station. Enhanced surveillance of the sunlight’s corona will certainly consequently make it possible for researchers to much better anticipate the effects of CMEs.
ASSOCIATED TALES:
— Effective GOES-U weather condition satellite releases to orbit atop SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket (video clip)
— Just How the GOES U satellite will certainly transform Planet and room weather prediction permanently
— Coronal mass ejections: What are they and how do they form?
The GOES-19 satellite released on June 25, 2024 atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket. It was the 10th launch of SpaceX’s heavy-lift car.
GOES-19 is still going through post-launch screening to guarantee its tools and systems are running as anticipated. While the current CCOR-1 monitorings are initial, they demonstrate how the tool will certainly assist in space weather projecting and readiness as soon as the room telescope is totally functional in springtime 2025.
NOAA strategies to release added coronagraphs to keep an eye on the sunlight from room as component of the company’s Climate Follow-On and Area Climate Next campaigns.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
