When you get via web links on our write-ups, Future and its submission companions might gain a compensation.
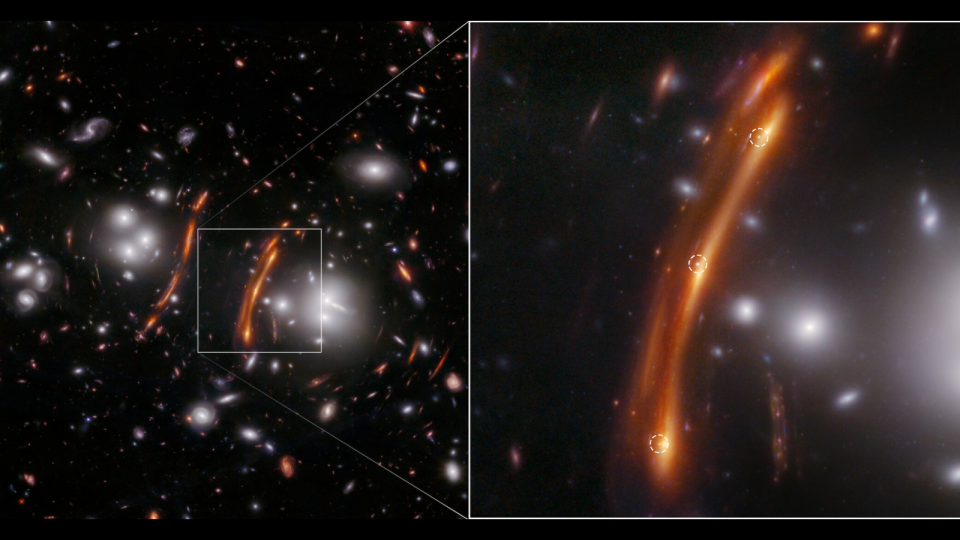


Making Use Of the James Webb Area Telescope, astronomers have actually caught a sensational picture of a remote supernova in a galaxy that resembles it’s being extended like cozy taffy.
Nevertheless, the gold smear concealing this gravitationally lensed supernova, which has actually been nicknamed “supernova Hope,” isn’t simply amazing for its visual worth. The supernova, which took off when the 13.8-billion-year-old world was simply around 3.5 billion years of ages, informs us something regarding a substantial trouble in cosmology called the “Hubble stress.”
The Hubble stress originates from the reality that researchers can not settle on the specific price of expansion of the universe, determined by the Hubble constant. Essentially, the price can be determined beginning with the regional (and as a result current) world, after that going further back in time– or, it can be computed beginning with the far-off (and as a result very early) world, after that functioning your method up. The concern is both approaches provide worths that do not concur with each various other. This is where the James Internet Area Telescope (JWST) is available in.
Gravitationally lensed supernovas in the very early universes the JWST is observing can give a 3rd method of determining the price, possibly assisting solve this “Hubble difficulty.”
” The supernova was called ‘supernova Hope’ because it provides astronomers intend to much better recognize deep space’s altering growth price,” Brenda Frye, research group leader and a College of Arizona scientist, stated in a NASA statement.
This examination of supernova Hope started when Frye and her worldwide group of researchers located 3 interested factors of light in a JWST picture of a remote, largely jam-packed cluster of galaxies. Those factors of light in the photo were not noticeable when the Hubble Space Telescope imaged the very same collection, called PLCK G165.7 +67.0 or, much more just, G165, back in 2015.
Associated: Unusual physics beside great voids might aid fix sticking around ‘Hubble difficulty’
” Everything began with one concern by the group: ‘What are those 3 dots that weren’t there prior to? Could that be a supernova?'” Frye stated. “Preliminary evaluations validated that these dots represented a blowing up celebrity, one with unusual top qualities.”
The area bordering G165 was picked for the PEARLS program since it remains in the middle of “starburst,” a duration of extreme celebrity development, and spawning 300 solar masses of celebrities each year. Such high celebrity development prices are associated with greater circumstances of supernova surges.
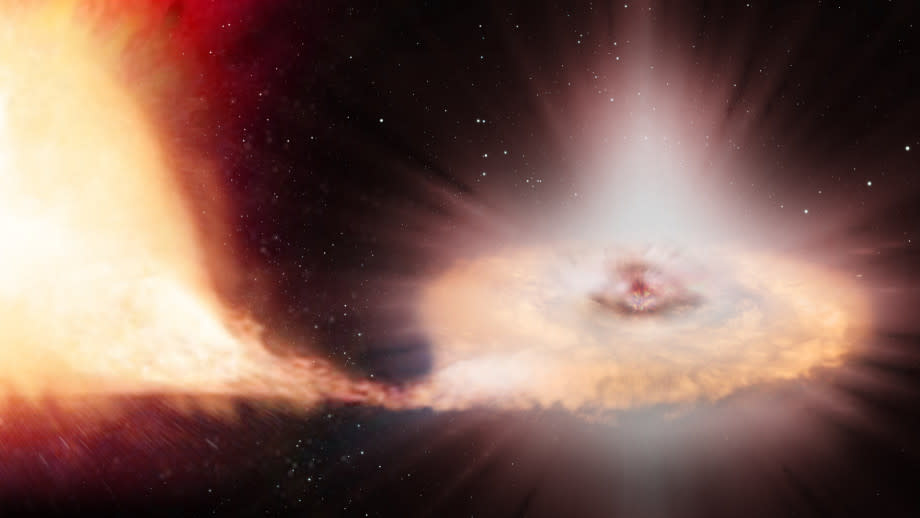


Supernova Hope is a details kind of supernova called aType Ia supernova These supernovas happen in binaries which contain a primary series celebrity, like the sunlight, and a celebrity that has actually tired its gas for nuclear combination and has actually ended up being a dead husk, called a white dwarf.
If these excellent bodies are close sufficient, after that the dead celebrity can imitate a planetary vampire, attracting plasma from the living, or “contributor,” celebrity. As this proceeds, the product accumulates till it sets off an atomic surge– surges we view as Kind Ia supernovas. As a result of exactly how consistent their flashes of light are, these supernovas are an exceptional device that astronomers can make use of tomeasure cosmic distances Astronomers, as a result, describe Kind Ia supernovas as “standard candles“
One method of obtaining a worth for the Hubble constant is to take a look at Kind Ia supernovas in the regional world to gauge their ranges from us, and from each other, and afterwards gauge exactly how rapid they are declining. The various other major method of determining deep space’s growth includes taking monitorings of the far-off world, after that computing exactly how quickly the universes is broadening via reduction.
However, once more, these approaches aren’t in contract. Supernova Hope, nonetheless, can serve as a bridge in between both strategies.
Einstein aids
Gravitational lensing is a result forecasted in Albert Einstein’s magnum piece concept of gravity, which was developed in 1915 and is called “general relativity“
General relativity recommends that items with mass create the bending of spacetime, the four-dimensional marriage of area and time, with gravity emerging from this curvature. The higher the mass of the item, the much more severe the bending of area and, hence, the higher the gravitational impact that object has. This is what triggers moons to orbit worlds, worlds to orbit celebrities, and stars to orbit supermassive great voids.
This bending of spacetime has one more intriguing impact, as well. When light passes an item with a solid bending impact, an item we’ll currently call a “gravitational lens,” the light’s course obtains curved around the item’s warp. The course the light takes relies on exactly how close it reaches the gravitational lens.
That implies light from the very same item can take courses curved to various levels and with various sizes. For that reason, that light can come to telescopes like the JWST at varying times. This is exactly how a lensed history item can appear “smeared” like taffy or show up in numerous areas in the very same photo.
That’s what is occurring to supernova Hope in this photo as its light passes the gravitational lens G165.
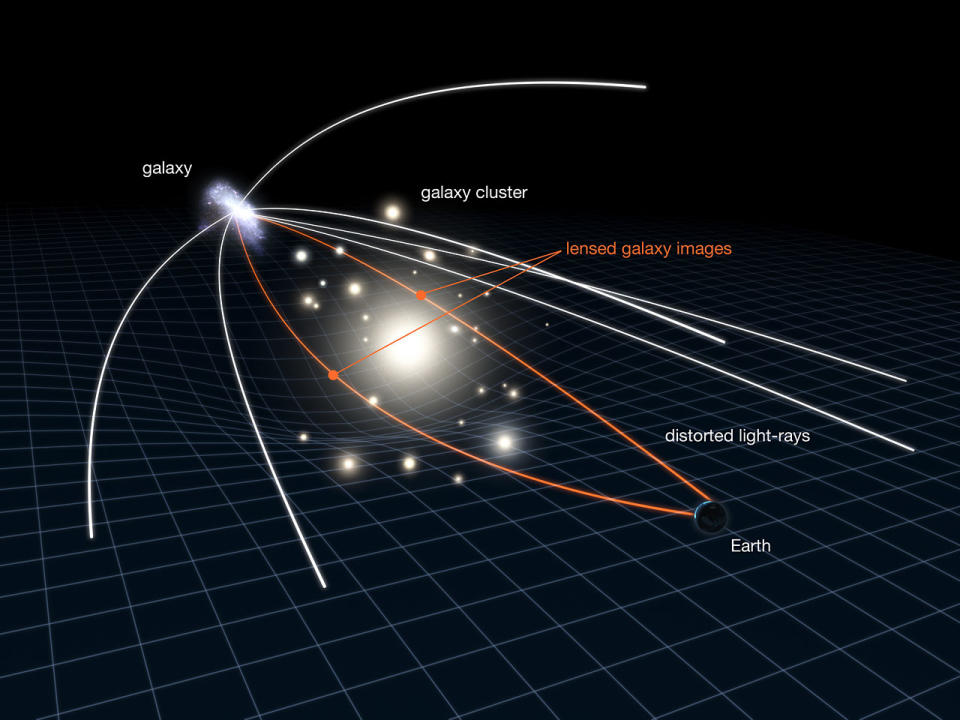

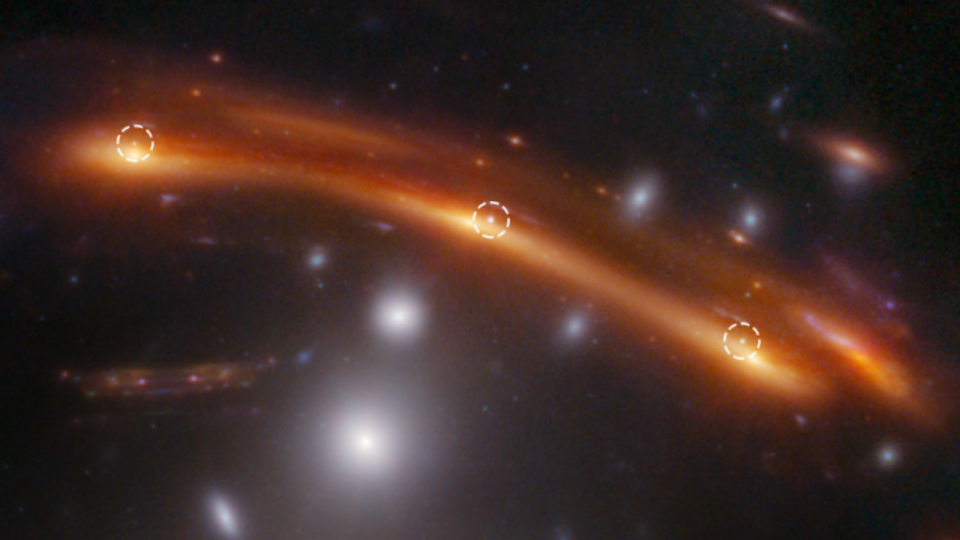
” Gravitational lensing is very important to this experiment. The lens, including a collection of galaxies that is positioned in between the supernova and us, flexes the supernova’s light right into numerous photos,” Frye stated. “This resembles exactly how a trifold vanity mirror offers 3 various pictures of an individual being in front of it.”
The College of Arizona scientist discussed the impact was shown right prior to the eyes of the group in the G165 JWST photo, where the center supernova photo appeared turned about the various other 2 photos.
” To attain 3 photos, the light followed 3 various courses. Considering that each course had a various size, and light taken a trip at the very same rate, the supernova was imaged in this JWST monitoring at 3 various times throughout its surge,” Frye proceeded. “In the trifold mirror example, a dead time taken place in which the right-hand mirror portrayed an individual raising a comb, the left-hand mirror revealed hair being brushed, and the center mirror presented the individual taking down the comb.
” Trifold supernova photos are unique. The moment hold-ups, supernova range, and gravitational lensing homes produce a worth for the Hubble constant.”


The group acted on supernova Hope with the JWST in addition to some Earth-based tools, consisting of the MMT 6.5-meter telescope on Mount Hopkins and the Large Binocular Telescope on Mount Graham, both situated in Arizona.
This led the group to verify that supernova Hope is secured to a history galaxy well behind the lensing collection G165. Light from the planetary surge has actually been taking a trip to Planet for 10.3 billion years, indicating this white dwarf blew its leading simply 3.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
” A various employee made afterward hold-up dimension by evaluating the advancement of its light spread right into its component shades or ‘range’ from the JWST, verifying the Kind Ia nature of supernova Hope,” Frye stated. “Supernova Hope is just one of one of the most far-off Kind Ia supernova observed to day,”
RELEVANT TALES:
— Dark issue found hanging from the planetary internet for first time
— Unique ‘Einstein ring’ recommends that strange dark issue communicates with itself
— Tiny great voids left over from the Big Bang might be prime dark issue suspects
In spite of existing in the very early world, the worth of the Hubble continuous provided by the monitorings of supernova Hope appears to refer dimensions of various other common candle lights in the regional world, hence differing with dimensions of various other items in the very early world.
” Our group’s outcomes are impactful,” Frye ended. “The Hubble continuous worth matches various other dimensions in the regional world and is rather in stress with worths gotten when deep space was young. JWST monitorings in Cycle 3 will certainly enhance the unpredictabilities, enabling much more delicate restraints on the Hubble constant.”
The group’s research study remains in the procedure of being peer-reviewed prior to magazine.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
