Workout has actually long been acknowledged by medical professionals, researchers and public wellness authorities as an important way to maintain health throughout an individual’s life expectancy. It enhances general health and fitness, aids construct solid muscular tissues and bones, minimizes the threat of persistent condition, enhances state of mind and slows down physical decrease.
Workout can likewise dramatically decrease the threat of establishing problems that adversely impact heart health, such as hypertension, high cholesterol and weight problems. However huge quantities of workout throughout life might likewise damage the heart, resulting in the advancement of a problem called athletic heart.
As the sports cardiology director at the College of Colorado Anschutz Medical School, I’m commonly asked just how much and what type of workout is essential to obtain the advantages of workout. Lots of people likewise question the threats of workout, and what takes place if you work out excessive.
The American Heart Association generally recommends 150 mins of moderate-intensity workout, such as vigorous strolling, or 75 mins of vigorous-intensity workout, such as running, weekly. It likewise suggests muscle mass enhancing workouts a minimum of two times weekly.
When individuals surpass these standards, the heart might redesign itself in reaction– that is, it starts to transform its shapes and size. Consequently, heart feature might likewise transform. These modifications in heart framework and feature amongst individuals that take part in high degrees of workout are described as the sports heart, or professional athlete’s heart. Sports heart does not always create troubles, yet in some individuals it can enhance the threat of particular heart concerns.
What is sports heart?
To comprehend exactly how workout impacts the heart, it is necessary to consider what type of workout you’re joining.
Workout is typically separated right into two broad categories: vibrant and fixed.
Dynamic workouts, like running, cross-country snowboarding and football, need the heart to pump a raised quantity of blood, contrasted to the quantity supplied to the body at remainder, in order to maintain the task. For instance, when running, the quantity of blood the heart pumps to the body might enhance by threefold to fivefold contrasted to at remainder.
Fixed workouts, like weight training, acrobatics or rock climbing, need the body to make use of skeletal muscle mass in order to press or draw hefty quantities of weight. While the heart does pump even more blood to skeletal muscular tissues that are functioning throughout these tasks, these sort of workouts rely on a muscular tissue’s capability to relocate the weight. For instance, in order to do swirls with pinheads, the arms need to be solid sufficient to raise the preferred weight.
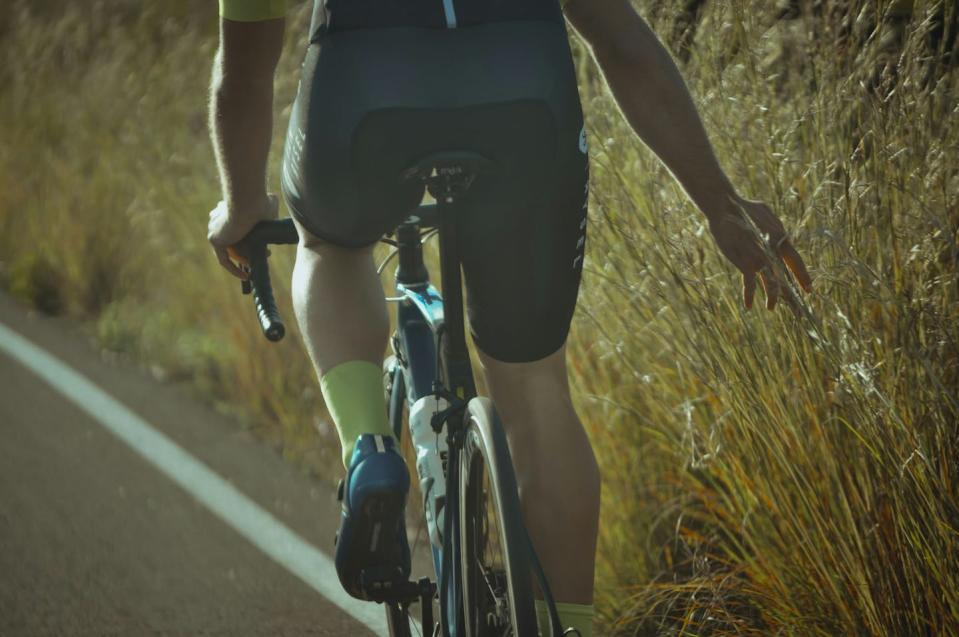


Some workouts, like rowing or biking, are both very vibrant and very fixed since they need the heart to pump huge quantities of blood while concurrently calling for a huge quantity of muscle mass toughness to maintain initiative.
It is very important to compare vibrant and fixed workout since the heart adjusts in different ways according to the sort of workout you take part in with time. Dynamic workout boosts the quantity of blood pumping with the heart and can create the heart to end up being bigger, or expanded, with time. Fixed workout boosts the quantity of stress on the heart and can likewise create it to end up being bigger with time yet with thick wall surfaces.
That creates sports heart?
Workout that surpasses standards, such as working out greater than an hour most days of the week, might bring about advancement of sports heart. Sports heart frequently takes place among endurance athletes, that routinely contend in tasks like marathons or various other long-duration occasions. Lots of workout numerous hours each day and greater than 12 to 15 hours weekly.
Amongst joggers, for instance, the heart renovates itself in reaction to needing to pump a high quantity of blood. Consequently, the chambers of the heart increase the size of to hold and pump even more blood. Amongst weightlifters, the heart renovates itself by enlarging in reaction to the rise in stress used on the heart.
Workout benefits the body, and sports heart arises from a long-lasting dedication to a task that advertises healthiness. However there might be some concerns that occur from a sports heart.
Initially, professional athletes with noticeably bigger hearts might go to threat of establishing atrial fibrillation, which is unusual heart rhythms that commonly happen amongst older grownups or individuals with hypertension or cardiac arrest. Irregular heart rhythms are uneasy since they might bring about a stroke.
There are numerous prospective factors atrial fibrillation takes place in professional athletes. A dilated room– the leading chamber in the heart– might end up being irritated and create mark cells, raising the threat of atrial fibrillation. Stress and environmental factors might likewise interact to enhance the threat of arrhythmia.

Coronary artery calcification, or CAC, is an additional worry amongst elite professional athletes. Coronary artery calcification, which frequently takes place in older grownups or those with threat variables for coronary artery condition, boosts the threat of having a cardiac arrest or stroke. In recent times, physicians have actually been making use of imaging examinations to keep an eye on calcium accumulation in the arteries of their individuals to attempt to identify their threat of cardiac arrest or stroke with time.
It is not completely clear why elite professional athletes create coronary artery calcification. Luckily, it does not show up that professional athletes have actually a raised threat of cardiac arrest, also amongst those with really high degrees of CAC. For instance, a huge research of nearly 22,000 individuals located that also professional athletes that participated in high quantities of workout and had raised degrees of CAC did not have an increased risk of fatality from heart disease over a years of follow-up.
Some professional athletes are suitably worried concerning having calcium accumulation in their heart arteries and might question whether they ought to be taking medicines like pain killers or statins. However threats vary from person to person, so anybody worried concerning CAC ought to talk with their physician
Placing workout in its location
Though elite professional athletes might have a raised threat of establishing sports heart, workout most certainly continues to be among, otherwise the most effective, approaches to keep a healthy and balanced way of life.
For instance, if somebody does not work out regularly, their heart will become stiff and not pump blood along with it as soon as did. Regular workout– specifically vibrant workout like running– keeps a certified heart and avoids tensing. A certified heart will certainly increase a great deal much more as it loaded with blood and, subsequently, drain even more blood with each heart beat. A rigid heart has problem filling with blood and has problem pumping blood with the body.


Normally, regular workout throughout their adult years motivates the heart to remain strong and flexible also in aging. Also if somebody were just to start routinely working out in their 40s to 50s, it is feasible to reverse some of the effects of inactive aging.
For instance, a 2018 research of 53 inactive individuals primarily in their very early 50s located that those that joined a two-year workout training program making use of a mix of running, biking and elliptical exerciser workout had hearts that became more compliant contrasted to the hearts of those that did not workout.
It is never ever far too late to begin working out. Consistently adhering to workout standards can aid advertise physical and psychological wellness and aid your heart remain young throughout your life.
This short article is republished from The Conversation, a not-for-profit, independent wire service bringing you realities and credible evaluation to aid you understand our intricate globe. It was created by: William Cornwell, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
Learn More:
William Cornwell does not benefit, seek advice from, very own shares in or obtain financing from any type of firm or company that would certainly take advantage of this short article, and has actually divulged no pertinent associations past their scholastic consultation.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
