Enroll In CNN’s Marvel Concept scientific research e-newsletter. Explore the universe with news on fascinating discoveries, scientific advancements and more
Some sorts of sea robins, a strange bottom-dwelling sea fish, usage preference bud-covered legs to feeling and collect target along the seafloor, according to brand-new study.
Sea robins are so experienced at rooting out target as they stroll along the sea flooring on their 6 leglike appendages that fish follow them around in the hope of getting some newly exposed target themselves, stated the writers of 2 new studies released Thursday in the journal Current Biology.
David Kingsley, coauthor of both research studies, initially stumbled upon the fish in the summertime of 2016 after providing a workshop at the Marine Biological Lab in Woods Opening, Massachusetts. Kingsley is the Rudy J. and Daphne Donohue Munzer Teacher in the division of developing biology at Stanford College’s College of Medication.
Prior to entrusting to capture a trip, Kingsley quit at a tiny public fish tank, where he snooped sea robins and their fragile fins, which appear like the downy wings of a bird, along with leglike appendages.
” The sea robins on display screen entirely rotated my head around due to the fact that they had the body of a fish, the wings of a bird, and numerous legs like a crab,” Kingsley stated in an e-mail.
” I would certainly never ever seen a fish that appeared like it was constructed from body components from various sorts of pets.”
Kingsley and his associates determined to research sea robins in a laboratory setup, revealing a riches of shocks, consisting of the distinctions in between sea robin types and the genes in charge of their uncommon attributes, such as leglike fins that have actually progressed to make sure that they mostly work as sensory body organs.
The searchings for of the research study group’s brand-new study demonstrate how development brings about intricate adjustments in particular settings, such as the capability of sea robins to be able to “taste” target utilizing their promptly hurrying and extremely delicate appendages.
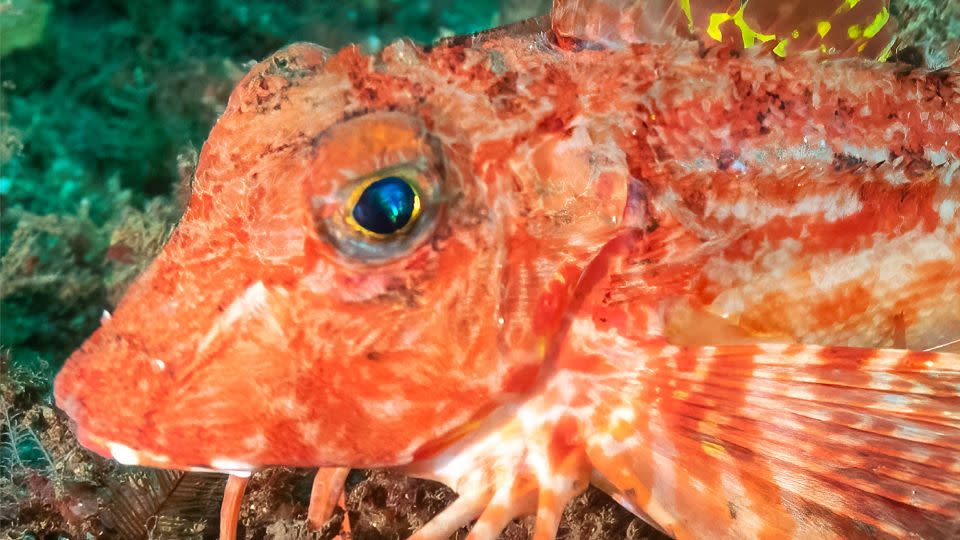


A very uncommon pet
The distinct extremities of the sea robins are really expansions of their pectoral fins, stated research study coauthor Amy Herbert, a postdoctoral scholar in Kingsley’s laboratory at Stanford.
” We picked the term ‘legs’ due to the striking strolling feature of these appendages,” Herbert stated in an e-mail. “Nonetheless, they do not have the exact same framework as human ‘legs’ neither are they in the exact same placement.”
Various other fish types have alterations to their pectoral or pelvic fins that enable them to stroll or perch, however sea robins can relocate their legs independently, that makes them extra experienced at strolling and excavating, Herbert stated.
” Sea robins are an instance of a types with a really uncommon, extremely unique attribute,” lead research study writer Corey Allard stated in a declaration. “We intended to utilize them as a version to ask, ‘Just how do you make a brand-new body organ?'” Allard is a postdoctoral other in the division of molecular and mobile biology at Harvard College, where he operates in the laboratory of research study coauthor Nick Bellono, a Harvard teacher.
The scientists brought some sea robins back to Bellono’s laboratory for research study and to see whether they can reveal hidden target. The group observed the fish rotating in between brief spells of swimming and strolling. They were additionally seen scraping at the sandy surface area covering all-time lows of the storage tanks with no aesthetic signs to allow them understand where target may be hidden.
” To our shock, they were extremely, excellent at it and can also reveal ground up and filteringed system mussel remove, and solitary amino acids,” Bellono stated.
To proceed their study, the research study writers had extra sea robins delivered to the laboratory– just to uncover that they stood for a completely various types with differing attributes.
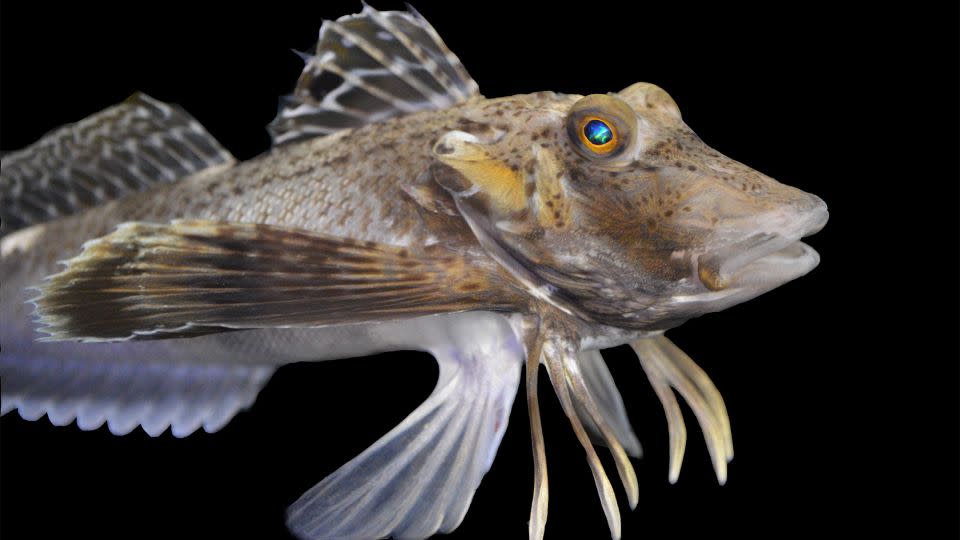


Genetically unique strolling fish
Both example teams of sea robins looked the exact same, however the recently provided fish really did not dig or locate hidden target.
” This moment, the brand-new sea robins really did not locate anything, regardless of easily consuming exploit the surface area,” Bellono stated by e-mail. “We assumed we were perhaps doing glitch, however it ended up that we mistakenly obtained a various types.”
The mix-up allowed some serendipitous explorations for the scientists. The extremely delicate fish they originally examined come from the types called the north sea robin, or Prionotus carolinus. And the fish that did not have sensory capacities and utilized their legs primarily for strolling were candy striped sea robins, or Prionotus evolans.
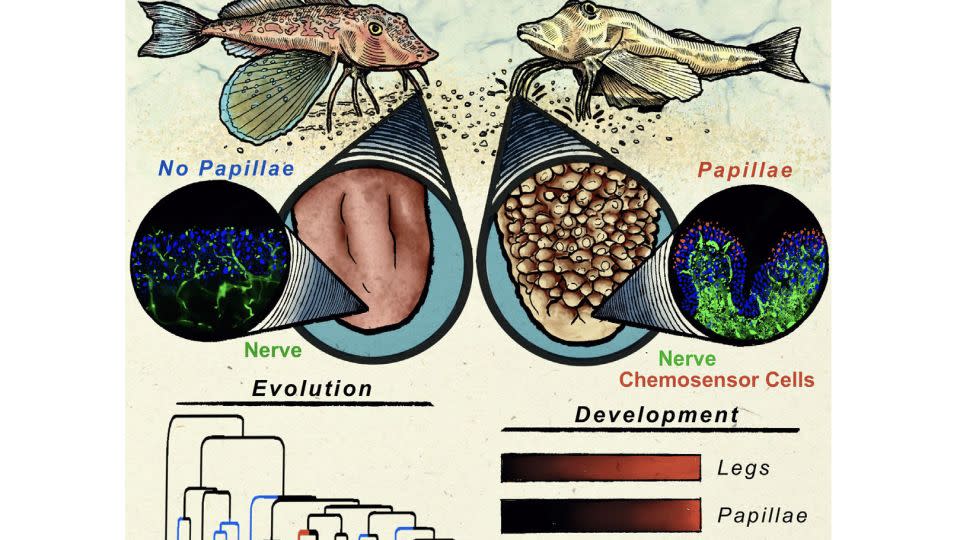
The excavating sea robins had shovel-shaped legs that were covered in outcroppings called papillae, which resemble the palate on our tongues. At the same time, the non-digging sea robins had rod-shaped legs with no papillae.
As the researchers examined the fish on a hereditary degree and contrasted exactly how their legs have actually established in time, they recognized that types that dig are just discovered in a couple of places, such as the sandy superficial waters of New England and the top eastern Atlantic coast, which recommends the fish just lately progressed this attribute.
” We assume that the excavating and non-digging types are divided by around 10 (million) to 20 million years, which indicates that papillae would certainly have needed to arise at some time afterwards,” Allard stated.
While all the sea robin types have leglike appendages, just some have the macroscopic sensory body organs that enable them to taste the atmosphere, Kingsley stated.
The research study writers’ study disclosed that excavating sea robins depend upon a governing genetics called tbx3a not just to establish their specialized fin adjustments however additionally to develop the papillae that trigger them to dig. Tbx3 additionally contributes in arm or leg advancement in human beings, computer mice, poultries and various other fish types, according to the research study writers.
” This is a fish that expanded legs utilizing the exact same genetics that add to the advancement of our arm or legs and afterwards repurposed these legs to locate target utilizing the exact same genetics our tongues make use of to taste food– quite wild,” Bellono stated.
However why did just several of the sea robins establish this sensory capability? The scientists have a number of theories.

” One is that utilizing the legs to reveal hidden target” enables them a brand-new method to choose food than they can previously, Herbert stated. “An additional is that strolling as opposed to swimming in some settings might be extra power reliable for sea robins.”
Sea robins stick out to name a few strolling fishes due to the fact that their pectoral fins, additionally called strolling fin rays, are extremely jointed and their skeletal and muscle makeup display one-of-a-kind alterations that make it possible for sea robins to stroll, stated Jason Ramsay, assistant teacher in the division of biology at Rhode Island University. However the fish additionally have adjustments in their nerve system that relate to their legs, recommending their sensory feature, Ramsay stated. He was not associated with the brand-new research studies.
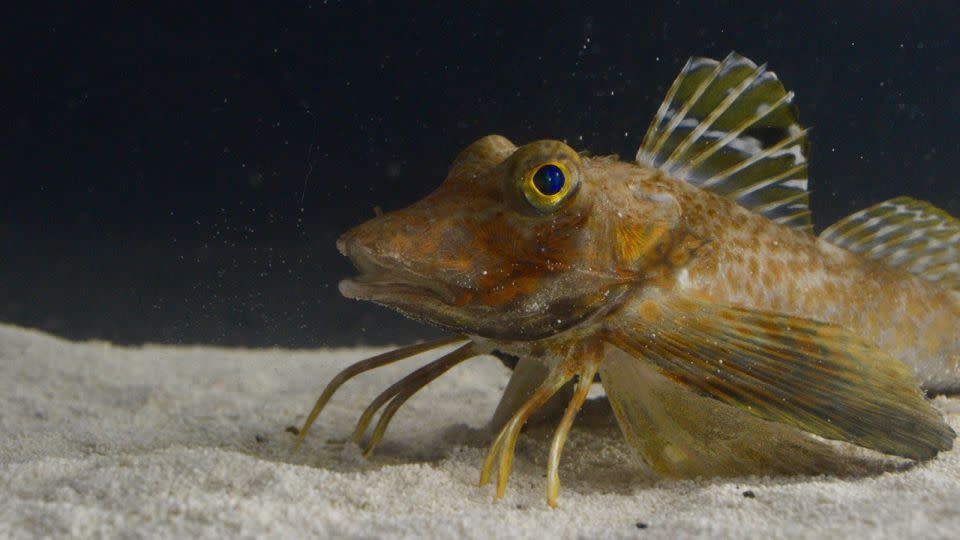


” A frequently asked concern is, did these strolling rays progress because of careful (adjustment) stress that sustain a strolling feature, sensory feature, or some mix of both,” Ramsay stated by e-mail. “These brand-new research studies offer even more proof recommending it was most-likely the latter-most circumstance.”
Allard is beginning his very own laboratory at Harvard, while Herbert is starting a laboratory at the College of Chicago. Both scientists stated they are eager to reveal the specific systems behind the development of the sea robins’ sensory appendages.
For even more CNN information and e-newsletters develop an account at CNN.com
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
