When you purchase with web links on our posts, Future and its submission companions might make a compensation.


Astronomers have actually found a brand-new attribute in the circulation of worlds past the planetary system, and this searching for can assist us comprehend the characteristics that figure out the development of exoplanets near their celebrities.
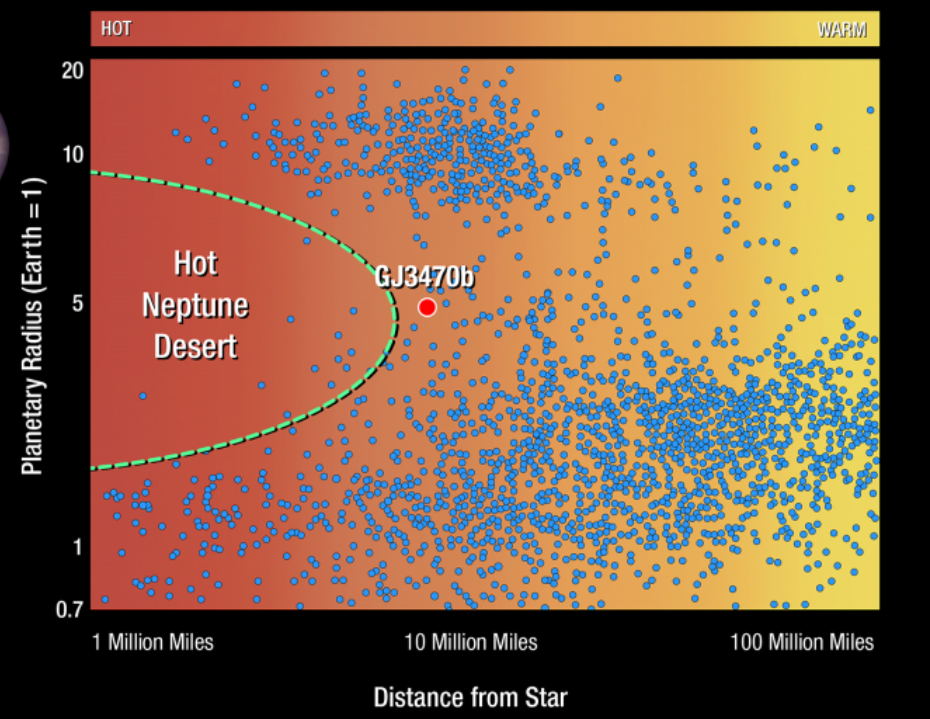
The exploration– made by a group of researchers from the College of Geneva, the National Centers of Proficiency in Study ( NCCR) Planets team, and the Centro de Astrobiología (TAXICAB)– has actually been labelled the “Neptunian ridge.” The Neptunian ridge is a function in the circulation of Neptune-sized exoplanets that rests in between the called the “Neptunian desert,” where there’s a lack of Neptunian worlds near their celebrity, additionally referred to as “hot-Neptunes,” and the “Neptunian savanna,” where there’s a wealth of these globes existing better of their celebrity.
The Neptunian desert has actually long been a perplexing attribute to astronomers and global researchers, indicating unusual traits in the advancement of global systems.
” We located an overdensity of worlds in this area, showing a sharp change in between the barren Neptunian desert and the much more booming Neptunian savanna,” Vincent Bourrier, Aide Teacher at the Astronomy Division of the UNIGE Professors of Scientific research and co-author of the research study, said in a statement.
This freshly recognized ridge notes a crucial area where worlds have actually taken care of to move internal while withstanding extreme radiation near their celebrities.
Connected: Why exist so couple of ‘warm Neptune’ exoplanets?
The desert, the ridge and the savanna
To comprehend where the idea of the Neptunian desert originates from, it deserves taking into consideration exactly how researchers in some casescategorize planets beyond the solar system Because the exploration of the initial extrasolar earth in the mid-1990s, researchers have actually discovered over 6,000 worlds past the planetary system, with thousands much more waiting for verification.
Exoplanets can be of a substantial variety of dimensions and masses, and can exist at various ranges from their celebrities. They’re typically contrasted to globes within the planetary system so researchers can comprehend several of their attributes. So, “super-Jupiters” are worlds much more large than Jupiter, super-Earths are much more large than Planet, and sub-Neptunes are worlds smaller sized than Neptune.
The prefix “warm” explains an earth close sufficient to its celebrity to finish an orbit in plain days or perhaps hours.
Describing an earth as “Neptune” in this regard does not show it is an ice titan, nonetheless, like our very own Neptune. Furthermore, super-Earths do not always need to be earthbound worlds– they can be tiny gas worlds. “Super-Jupiters” and “hot-Jupiters” are more probable to be gas giants like Jupiter, however, due to their huge dimension.


When researchers started to outline exoplanets based upon points like their sizes and the moment they require to orbit their celebrities, numerous interested and interesting patterns of global circulation arised. One was the absence of Neptune-size globes orbiting near their celebrities: hot-Neptunes.
Researchers think this lack exists since near celebrities, severe radiation remove the ambiences of worlds, therefore “diminishing” them. This procedure is called photoevaporation.
In Addition, past the barren metaphorical landscape of the Neptunian desert exists an area where Neptune-size globes are located in wealth. That’s the Neptunian savanna. Below, at better ranges from their celebrities, the globes can hold on to their ambiences and keep their dimension. Neptunian worlds hiding in the Neptunian savanna are thought to move from their farther areas far from their celebrities to the Neptunian desert, where they obtain closer to those celebrities and are promptly burglarized of their ambiences.
To comprehend exactly how the Neptunian desert and savanna progressed, Bourrier and associates utilized information fromNASA’s Kepler space telescope Specifying accurate areas of the “Neptunian landscape,” they located a distinctive area in between the desert and the savanna, standing for an orbital duration of 3.2 to 5.7 Planet days. They called this the “Neptunian ridge,” locating that it exposes several of the complex procedures of Neptunian earth movement.

” The Neptunian ridge stands high over the desert and savanna,” Bourrier stated. “It supplies us with an essential to comprehending the physical devices forming the desert.”
The truth that this ridge exists recommends that some Neptune-size worlds are given this area by a sort of motion called “high-eccentricity movement.” This occurs later on in an earth’s life, and it permits a globe to make it through the disintegration of its environment through radiation blowing up from its celebrity.
These movement procedures and the photoevaporation of ambiences are most likely what form the Neptunian desert, ridge and savanna observed in the Neptunian landscape.
Associated Stories:
— NASA area telescope discovers Earth-size exoplanet that’s ‘not a poor location’ to quest for life
— Severe ‘warm Jupiter’ exoplanet has an odor like rotten eggs and has raving glass tornados
— Iron winds and liquified steel rainfalls wreck a terrible warm Jupiter exoplanet
The group will certainly currently transform to the Very Large Telescope (VLT) and its Coffee (Echelle Spectrograph for Rocky Exoplanets and Secure Spectroscopic Monitorings) tool to read more regarding the Neptunian desert, savanna, and ridge.
This ought to enable the scientists to evaluate the positioning of an example of unusual hot-Neptunes. Recognizing the positioning of an earth is essential since it is a consider comprehending any type of exoplanet movement procedure, implying it’s a vital item of missing out on details regarding the advancement of close-in worlds and why they do not have a tendency to be Neptune-size.
” The Neptunian ridge is simply the start,” research study initially writer Amadeo Castro-González, a Ph.D. pupil at the Facility for Astrobiology in Madrid, stated in the declaration. “With upcoming arise from this empirical program, we’ll have the ability to evaluate our theories regarding the beginnings and advancement of these fascinating globes, supplying a much more detailed sight of the close-in Neptunian landscape.”
The group’s research study was released on Tuesday (Sept. 17) in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
