When you acquire via web links on our short articles, Future and its submission companions might make a payment.


Cities all over the world are expanding up greater than they are spreading out exterior, researchers examining years of satellite information lately revealed– measuring an extensive, worldwide change in growth of cities, where chains of high-rise buildings have additionally become their single biggest contributor to increasing heat.
” Cities almost everywhere have actually expanded,” research study lead writer Steve Frolking of the College of New Hampshire informed Space.com. “I do not believe it’s specifically a shocking outcome– everyone’s private experience with a specific city is that there are possibly a lot more high structures currently than there were two decades back.”
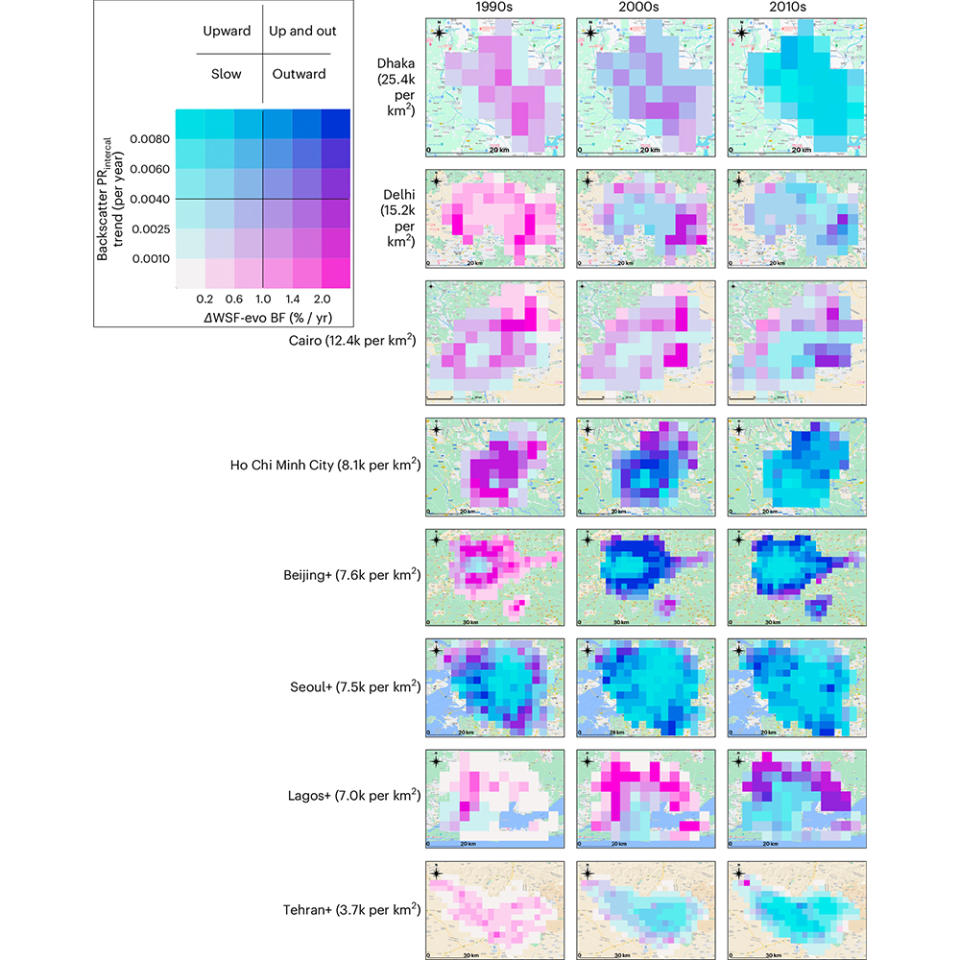
For the very first time, Frolking and his associates have actually placed numbers to that feeling of change. Making use of information from numerous Earth observing satellites, the scientists researched the development of greater than 1,550 cities worldwide from 1990 to 2020– a duration throughout which city populaces about increased from regarding 2 billion to 4 billion. The group made use of details gathered by NASA’s Landsat, for example, which tape-recorded just how much land structures all over the world inhabited. On the other hand, information from a collection of sensing units flown on European Remote Sensing (EMERGENCY ROOMS) satellites cataloged the structures’ higher development.
Incorporating both sort of information, the scientists discovered fast-developing nations like China, southeast Asia, components of Africa and the Center East expanded up significantly, while industrialized nations like The United States and Canada, Europe, Japan, Taiwan and South Korea included taller structures at a slower price, the scientists composed in a paper released previously this month in Nature Cities.
Associated: Earth’s Cities at Night: Photos From Space
While each nation’s economic situation, land costs and policies around constructing elevations all appeared to affect the rate at which its cities expanded, the evaluation additionally reveals that city development is not restricted any longer to simply a handful of cities fresh York, Tokyo and Shanghai. Historically, that has actually held true.
” We see this change mainly in big cities with greater than a million individuals,” Frolking claimed. “Normally– although not constantly– the change occurs initially in the facility of the city and after that spreads out exterior.”
Such town hall, which have a tendency to be called “midtowns,” are favored domestic areas since they provide much shorter job commutes, home entertainment centers and various other features, in addition to less complicated accessibility to public transport. By 2050, 68% of the globe’s populace is anticipated to relocate to a midtown location, with much of that rise happening in India, China and Nigeria, a 2018 report by the United Nations discovered.
Yet, city development additionally brings with it air, sound and light contamination. Skyscraper frameworks can aggravate strong gusts in surrounding streets, and largely inhabited cities are understood to be warm islands– big human-made frameworks like structures and roadways soak up and launch solar warm more than rural, greenery-rich areas do.

Associated Stories:
— Worrying satellite monitorings reveal significant cities on United States East Shore are sinking
— These 2 United States cities are one of the most prone to solar tornados, researchers state
— Human-caused worldwide warming at all-time high, brand-new record wraps up
Previous study has actually discovered such frameworks, which heat up throughout the day and launch warm gradually after sundown, air vent that warm not simply right into the air however additionally right into the ground. Alessandro Rotta Loria, an assistant teacher of civil and ecological design at Northwestern College that led that study, called underground climate change a “silent hazard” that deteriorates the structures of structures and impacts their functional efficiency and sturdiness.
” It has effects for greenhouse gas discharges, from both frameworks themselves and transport facilities around that so as to get individuals to live there or function there,” claimed Frolking.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
