When you purchase with web links on our write-ups, Future and its submission companions might gain a compensation.


NASA’s Chandra X-ray area telescope has actually developed a three-dimensional map of celebrities near to the sunlight that might aid astronomers look for unusual earths that might hold life.
The map developed by Chandra— which simply commemorated 25 years in orbit however is encountering an unpleasant budget plan crisis– might notify researchers which exoplanets to route future telescopes towards to perform look for habitable problems.
The celebrities mapped by the telescope are organized in concentric rings around the sun, at ranges in between 16.3 light-years and 49 light-years. This is close adequate that telescopes might gather wavelengths of light or “ranges” from earths in the habitable areas of these celebrities. The habitable area or “Goldilocks zone” is an area around a celebrity that is neither as well warm neither as well chilly to enable fluid water to feed on a globe’s surface area.
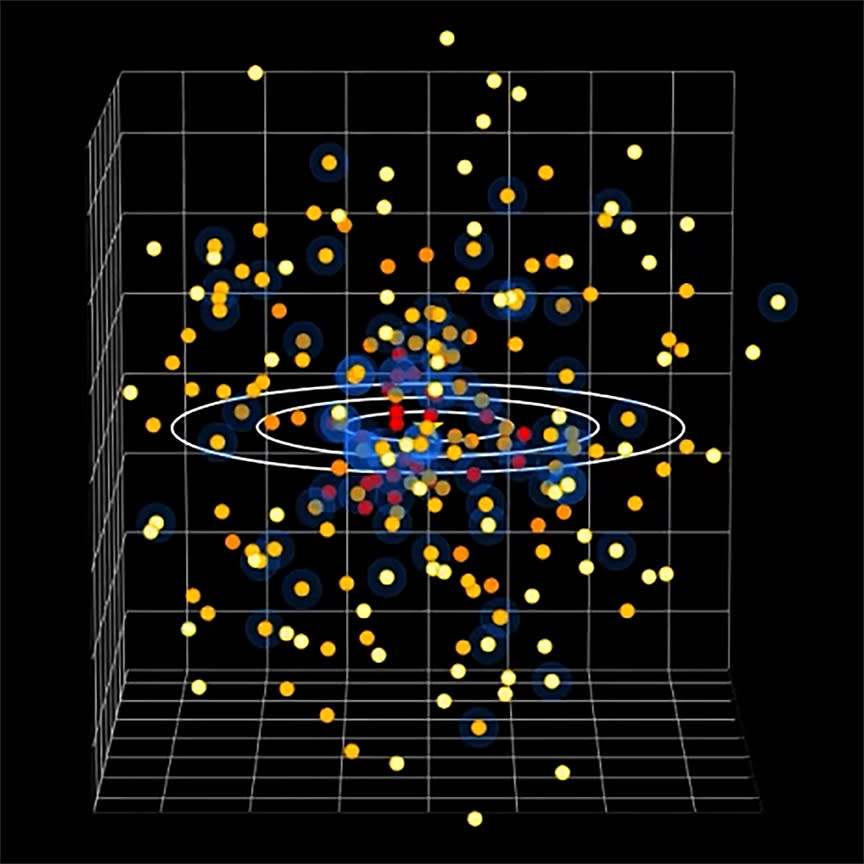

The ranges from these earths developed as starlight beams with their air might possibly expose surface area attributes like continents and oceans, and climatic features like clouds and chemical materials.
Associated: Satisfied 25th wedding anniversary, Chandra! NASA commemorates with 25 spectacular pictures from front runner X-ray observatory
Chandra’s X-ray capacity is essential to picking which earths to explore for feasible habitability. High-energy light like X-rays and ultraviolet radiation can remove a world’s ambience and likewise damage down the complicated particles required as the foundation of living points, wrecking its habitability.
Therefore, if Chandra sees a world under hefty X-ray barrage, researchers can presume it isn’t the very best globe to examine in the look for alien life.
” Without defining X-rays from its host celebrity, we would certainly be missing out on a crucial element on whether a world is absolutely habitable or otherwise,” Breanna Binder of The Golden State State Polytechnic College, the leader of the group behind the brand-new map,said in a statement “We require to take a look at what sort of X-ray doses these earths are obtaining.”
X-rays misbehave information permanently, also in Goldilocks areas
Binder and coworkers constructed their map by originally beginning with a checklist of 57 celebrities close sufficient to our planetary system that future telescopes precede, like the Habitable Globes Observatory, and on dry land, like the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT), might photo earths orbiting in their Goldilocks areas.
Simply remaining in the habitable area isn’t a warranty that a world is welcoming, nonetheless. Venus and Mars are both in the habitable area of the sunlight, on either side of Planet, however the Martian surface area appears to be inappropriate permanently as we understand it, and superheated Venus is straight-out hostile to it.
So, to limit their checklist, the group utilized information from 10 days of Chandra monitorings and 26 observing days of the European Area Company’s (ESA) XMM-Newton space telescope to see just how intense the celebrities remain in X-rays. After that, they figured out just how energised these X-rays are and just how swiftly the celebrities’ X-ray exhaust adjustments.
The researchers reasoned that, the more vibrant and even more energised the X-rays were, the more probable any kind of orbiting exoplanets had actually suffered major damages to their ambiences or shed them totally.
” We have actually recognized celebrities where the habitable area’s X-ray radiation setting resembles and even milder than the one in which Earth advanced,” staff member Sarah Peacock, from the College of Maryland, described. “Such problems might play a crucial function in suffering an abundant ambience like the one discovered in the world.”


A few of the celebrities analyzed by the group are currently understood to be orbited by exoplanets with masses and dimensions comparable to the planetary system titans Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, and Uranus, with a handful of prospects under around half the mass of Planet.
There might likewise be earths in these systems with masses and dimensions extra suitable with Planet’s that are presently obscure.

Earth-sized earths in these systems might have been missed out on by the most trusted approach of exoplanet discovery, thetransit method This method relies on a world going across or “transiting” the face of its celebrity, creating a small dip in the outcome of starlight while doing so.
This relies on a world interposing its celebrity and Planet, suggesting some systems simply aren’t oriented properly to see globes with the transportation approach. The method is much better at detecting substantial earths near to their celebrity, so smaller sized globes that orbit fairly far might be missed out on.
The various other main exoplanet discovery method, the radial speed approach, depends upon detecting the “totter” a world triggers as it orbits its celebrity and gravitationally pulls on it. Once again, this approach prefers substantial earths near to their celebrities, which create an even more considerable wobble.
ASSOCIATED TALES:
— Journey! Explore deep space with these beautiful pictures from NASA’s Chandra X-ray telescope
— The 10 most Earth-like exoplanets
— NASA’s Chandra X-ray telescope records closest very galaxy to Planet (photo)
” We do not recognize the number of earths comparable to Planet will certainly be uncovered in pictures with the future generation of telescopes, however we do recognize that observing time on them will certainly be valuable and incredibly tough to get,” staff member and College of The golden state, Waterfront scientist Edward Schwieterman ended. “These X-ray information are assisting to fine-tune and focus on the checklist of targets and might enable the very first photo of a world comparable to Planet to be gotten quicker.”
The group’s study existed at the 244th meeting of the American Astronomical Society conference in Madison, Wisconsin.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
