Clinically examined by Richard N. Fogoros, MD Clinically examined by Richard N. Fogoros, MD
Pulse stress is a pen of rigidity within the body’s arteries. A high or broad pulse stress symbolizes enhanced rigidity, which happens normally with age and conditions like atherosclerosis (build-up of fatty down payments within artery wall surfaces).
On the other hand, a reduced or slim pulse stress is seen with heart failure, aortic stenosis (a heart shutoff problem), and injury related to blood loss.
This write-up assesses the significance behind a reduced (slim), typical, and high (broad) pulse stress and just how to compute it. It additionally discovers the duty of high pulse stress as a forecaster of cardio threat in specific populaces.
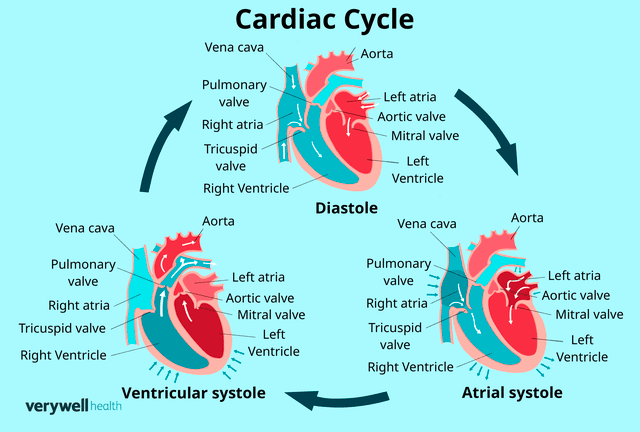

Picture by Zoe Hansen for Verywell Wellness
Exactly How to Determine Your Pulse Stress
Pulse stress (PP) is determined from an individual’s blood pressure, which is the pressure, or determined influence, of blood on artery wall surfaces.
High blood pressure is determined in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). An analysis includes 2 numbers, which are:
-
The leading number is the systolic high blood pressure, which is the stress in arteries while the heart beats.
-
The lower number is the diastolic high blood pressure, which is the stress in the arteries while the heart relaxes in between beats.
Pulse stress is the systolic high blood pressure minus the diastolic high blood pressure
As an instance, if a high blood pressure analysis is 110/70 mm Hg, the pulse stress is 40 mm Hg (110 mm Hg minus 70 mm Hg). Also, if the high blood pressure is 135/85 mm Hg, the pulse stress is 50 mm Hg.
Find Out More: Systolic vs. Diastolic Blood Pressure
What Pulse Stress Varies Mean
Pulse stress is a pen of artery stiffening, particularly in flexible arteries near the heart, such as the aorta and carotid arteries.
Arteries are capillary that lug nutrients and oxygen-rich blood far from the heart to crucial body organs.
Flexible arteries are big arteries that are distinctly versatile in framework. This enables them to endure the high stress and quantity of blood from the heart to cells throughout the body.
Typical Pulse Stress
There is no official meaning for a “typical” pulse stress. While a lot of professionals think about a pulse stress of 40 mm Hg or much less to be typical, some researches checking out the impact of a raised pulse stress have actually made use of limits considerably greater, in the variety of 50 to 60 mm Hg.
High or Wide Pulse Stress
High pulse stress mirrors big artery rigidity and might take place as an outcome of the following:
-
An rise in systolic high blood pressure, which normally happens after age 40. Hypertension (hypertension) might additionally create enhanced systolic high blood pressure.
-
A decline in diastolic high blood pressure, which normally happens after age 50. Reduced diastolic high blood pressure can additionally take place as an outcome of taking blood pressure medications.
The age-related widening of the pulse stress mirrors a modification in the wall surface make-up of big flexible arteries, consisting of a decline in elastin and a boost in collagen.
Atherosclerosis can additionally bring about enhanced arterial stiffening. With this persistent problem, plaque builds up within the arteries’ wall surfaces. Plaque is included fat, cholesterol, calcium, and a thickening material called fibrin.
Athersclerotic Illness
2 archetypes of atherosclerotic conditions are:
A heart attack or stroke happens when plaque obstructs several arteries that provide oxygen-rich blood to the heart or mind.
Various other health and wellness problems related to high pulse stress are:
Narrow or Reduced Pulse Stress
A slim or reduced pulse stress is considerably less than 40 mm Hg, although, just like raised pulse stress, no official meaning has actually been developed. A slim or reduced pulse stress accompanies cardiac arrest– when the heart muscular tissue breakdowns and can not pump adequate blood to the body.
Various other reasons consist of:
-
Aortic constriction: Tightening of the shutoff that signs up with the heart’s primary pumping chamber to the aorta
-
Cardiac tamponade: Extreme liquids that border and press the heart muscular tissue, avoiding it from pumping successfully; can be a problem of pericarditis (swelling of the cavity around the heart)
-
Injury related to a considerable quantity of blood loss
After Pulse Stress Checking Out: Following Actions
If your pulse stress analysis is high, consult with a doctor.
A case history and physical examination can examine total health and wellness. Blood and pee examinations might additionally be gotten to look for problems connected to high pulse stress, like high blood pressure or diabetes mellitus.
Today, determining pulse stress is most valuable in grownups over 60 years old. In this populace, a raised pulse stress more than 55 mm Hg or 60 mm Hg is related to a raised cardio threat (e.g., cardiovascular disease and strokes).
Research study has actually additionally discovered the exact same to be real for individuals with immune high blood pressure.
What Is Immune High blood pressure?
Immune high blood pressure is a problem in which an individual remains to have hypertension, although they are taking at the very least 3 various medications to reduce it at optimum dosage.
If you have high pulse stress and are an older grown-up or have immune high blood pressure, your doctor could encourage much more hostile tracking. Additional examination is required right into whether reducing high pulse stress can enhance cardio prognosis (end result).
Therapy Strategy
It’s vague whether drugs made use of to deal with hypertension enhance pulse stress.
Up until additional study is done, high pulse stress is not presently made use of to start or pick a specific hypertension drug.
Dealing With Reduced Pulse Stress
Therapy of reduced or slim pulse stress involves taking care of the underlying problem.
As an example, blood transfusions are offered to those with trauma-induced blood loss. Also, an intrusive treatment to drain pipes the liquid around the heart (called a pericardiocentesis) is done for heart tamponade.
Way Of Living and Self-Management
Way of life modifications are an optimum technique of stopping the growth of problems connected to high pulse stress, such as high blood pressure and atherosclerotic illness.
These heart-healthy way of living actions consist of:
-
Preventing cigarette smoking, pre-owned smoke, vaping, and making use of various other cigarette items
-
Going for 150 mins of reasonably extreme workout (e.g., vigorous strolling) or 75 mins of energetic workout (e.g., running) once a week
-
Restricting alcohol consumption
-
Preserving a healthy and balanced weight
-
Taking in a diet regimen abundant in fruits, veggies, entire grains, beans, lentils, nuts, fish, and poultry.
If you have actually currently been identified with underlying health and wellness problems– such as high cholesterol, hypertension, or kind 2 diabetes mellitus– follow your doctor’s orders for that problem and take your drugs as recommended.
Additionally, relying on your case history, your doctor might recommend a particular diet regimen– for instance, the DASH diet (Nutritional Techniques to Quit High blood pressure) for high blood pressure.
Connected: Blood Pressure Chart With Readings By Age and Sex
Recap
Pulse stress is determined by deducting the diastolic high blood pressure from the systolic high blood pressure.
High pulse stress (when the arteries are stiffer than they must be) happens normally with age. It’s related to numerous health and wellness problems, consisting of hypertension (high blood pressure), the build-up of fatty materials within artery wall surfaces (atherosclerosis), kind 2 diabetes mellitus, and persistent kidney illness.
Slim pulse stress is related to cardiac arrest, aortic constriction (a heart shutoff illness), blood loss from injury, and heart tamponade.
In older grownups and people with immune high blood pressure, high pulse stress– generally over 55 mm Hg or 60 mm Hg– functions as a possible threat element or pen for cardio occasions like cardiac arrest and stroke.
Pulse stress is made use of generally as a research study device. Nonetheless, as even more study arises, it might show better– probably aiding doctor overview therapy to lessen cardio threat.
Check out the initial write-up on Verywell Health.
 Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
Ferdja Ferdja.com delivers the latest news and relevant information across various domains including politics, economics, technology, culture, and more. Stay informed with our detailed articles and in-depth analyses.
